Updated March 20, 2023
Introduction to Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
The following article provides an outline for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Have you ever thought how computers talk to each other or how your mobile or laptop talk to the Internet or communicate within any network? How do they immediately connect to the Internet or any network on just a click by you and you start watching videos, playing games, immediately?
Given below is the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol logic behind it.
Let’s see its acronym meaning:
- Dynamic: Anytime/on runtime automatically.
- Host: A computer (PC) or devices connected to a network.
- Configuration: To setup with some settings.
- Protocol: A set of rules for data transfer between electronic devices.
DHCP:
- Is a set of network rules used on IP networks.
- Consisting of a server called DHCP server.
- It assigns an IP address automatically to each & every device on the network so that all the devices can communicate with each other properly.
Let’s consider a company with a boss & some senior employees of a company with whom many salespersons want to communicate for pitching their products or services. For this, they need to request Mary (secretary), the intermediary who is going to schedule the meetings. Thus, Mary is like a mini DHCP server that gives an appointment (IP Address) to a salesperson (host). This task can be done manually by Mary if there are 20 salesperson requests daily but what if there are 200 or 2000 salespersons who request to meet the boss? How is she going to schedule the meetings manually? She would be tired, will forget everything, and start making mistakes.
For this, there can be an automated server & software which automatically assigns appointments to the requestors. This server will be called DHCP. The server will assign IP addresses (date & time of meeting) to each host (salesperson) to communicate with the other hosts (boss or other senior employees). Similarly, If a PC or host wants to communicate in any network, a DHCP server is who helps that PC by assigning IP addresses dynamically to that PC so that it can talk to the other computers on that network.
Components of DHCP
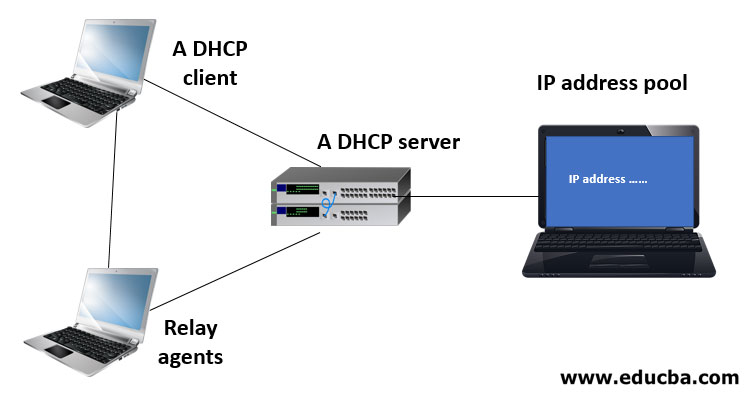
Given below shows the components of DHCP and how it works.
1. A DHCP Client
It is the device that receives information from a DHCP server. It can be a computer, mobile device, or anything else that requires connectivity to the network. By default, most devices are already configured to receive DHCP information.
2. A DHCP Server
It is a networked device running the DHCP service holding the IP addresses (in its IP address pool) and related configuration information. It is mostly a server or a router but could be anything that acts as a host.
3. Relay Agents
These are devices or routers that take client messages broadcasted by the clients on a network to join that network and forward those messages to a configured DHCP server which then sends responses back to these relay agents that passes them along to the client. These are used to centralize DHCP servers.
4. IP Address Pool
It is the bucket of IP addresses possessed by the DHCP server. It is the range of addresses that can be allotted to the requesting devices i.e. DHCP clients.
IP addresses are allotted in a serial-wise order from lowest to highest.
- Lease time: The time duration for which a client device holds its IP address information provided to it by the DHCP server. When the lease time expires, the client must renew it.
How Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Works?
DHCP works on a client-server model. A router or switch can also be used as a DHCP server. Client devices like a laptop or mobile phone request the DHCP service from the server to get an IP assigned from the IP address pool so that it can communicate with other devices on that network.
There are 5 messages broadcasted by the DHCP server & clients in the process:
- DISCOVER: A new client on entering the network sends this message to the server.
- OFFER: The client can accept any offer as there can be multiple servers so multiple offers.
- REQUEST: Client or host sends this request message.
- PACK: Assign an available IP address to the client with other details packed.
- RELEASE: When the client device wants to leave the network or join another network.
Benefits of DHCP Servers
Some of the benefits are given below:
1. Easy management & configuration of multiple devices in a network.
2. Accuracy of IP settings.
- When IPs like “xxx.xxx.xxx.x” are used then they are much prone to mistakes.
- Such types are very difficult to find out and remove. For this DHCP can help.
3. Alleviated confliction of IP address.
DHCP solves the problem of confliction of IP addresses by making sure that every device has a unique IP.
1. No manual work (Automation of the whole process): With the use of DHCP the need to assign, track and manage IP addresses manually is eradicated. In the past, the network managers had to track each device and its IP address manually which was completely inefficient. With the inception of DHCP, all these tasks have been automated & centralized and have been a boon for network admins.
2. Modification of IP address: Editing of IP addresses is very easy due to DHCP. A DHCP server automatically broadcasts the changes to all the connected devices.
Conclusion
We found out that the primary reason DHCP is needed is to simplify the management of IP addresses on networks. There cannot be two hosts having the same IP address, and configuring them manually will lead to errors. Even on small networks assigning IP addresses manually can be confusing, mostly with mobile devices that require IP addresses on a temporary basis. Also, most users are not technically sound enough to locate the IP address information on a computer and assign it. Automating this process makes life easier for users and the network administrator.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. Here we discuss the introduction, components of DHCP, working, and benefits respectively. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–