Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to Edge Computing Architecture
Edge Computing Architecture is a new model for providing storage and substantial computing properties near to the devices. This bringing of storage and computing nearer to the devices improves response time and lessens the bandwidth. Edge computing involves all types of computations which occur at the edge of a network outside the cloud. Edge time works on real-time data generated by sensors and real-time applications. The enormous emergence of IoT devices has pushed the bandwidth demands to the extreme levels, resulting in delay. Edge computing moves services closer to the edge and enhances service delivery.
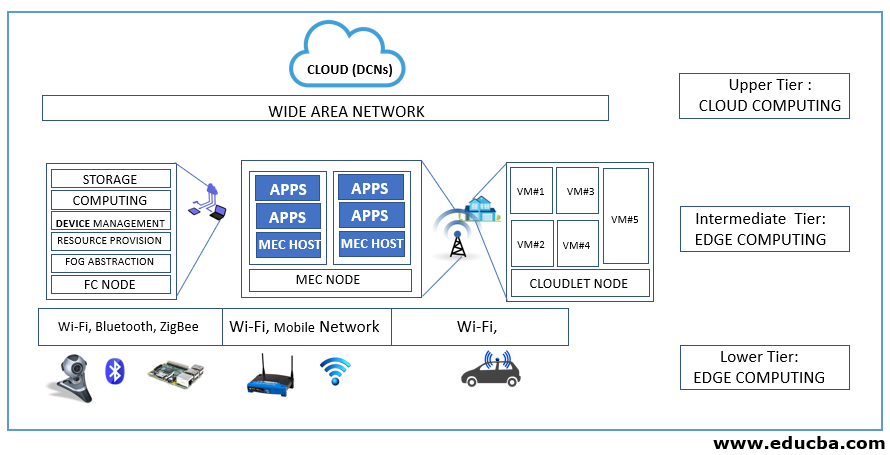
Edge Computing Architecture
An Edge Computing Architecture comprises of the following components
Data source/devices
The data sources in an edge computing environment can be applications capturing data, sensors, appliances, or any data capturing device. Data generated by these devices is different depending upon the source. Data sources vary from one another depending upon their functionalities and locations. The various edge devices capture data and communicate via IoT protocols, sending data to the edge gateways. The protocols used for the data transfer can be Ethernet, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, NFC, ZigBee, etc. In short every data generating device will be considered as an edge device.
Edge gateway
An edge gateway acts as a node between edge devices and a core network. A core network comprises devices powerful enough to pre-process data. Edge gateways are employed to provide interfaces to wired and radio-based transmissions.
The various standards used are:
- Z-Wave: Z-Wave is used for 30 meters point-to-point communication and is specified for applications that involve small transmissions like household appliance control applications. Z-Wave functions in ISM bands (around 900 MHz) and allows a transmission rate of 40 kbps. Z-wave is considered to be the best possible option available for household appliances communication.
- LTE-A (Long Term Evolution—Advanced): This communication protocol comprises of a set of various protocols meant for communication that fall under Machine-Type signals and IoT based architectures. In terms of service cost and scalability, it outperforms other cellular solutions.
- EPC-global: Electronic Product Code is used in the supply chain management to identify items, as a unique identification number stored on an RFID tag. The architecture uses RFID technologies along with easy to use RFID tags as well as readers for information sharing.This architecture is recognized as a promising technique for the future of the IoT because of the features of openness, scalability, etc
- Bluetooth Low Energy: Bluetooth Low-Energy (BLE) or Bluetooth Smart makes use of radio signals with short-range and a minimum power requirement. It operates at a range that is nearly about ten times more than classic Bluetooth technology. Its latency factor compared to classic Bluetooth technology is 15 times less. The transmission power between 0.01 mW to 10 mW is feasible for its operation.
Protocols used
The Various Protocols used in this Layer
CoAP
CoAP is an application layer protocol for edge devices and applications, created by IETF Constrained RESTful Environments (CoRE) working group. The CoAP proposes a transfer protocol based on Representational State Transfer (REST) on top of HTTP functionalities. REST is a cacheable connection protocol that relies on the stateless client-server architecture. It represents a proper way to exchange data between clients and servers on top of HTTP. It is used in mobile-based social network applications and it makes complexity less by using HTTP methods(get, post, put, and delete).
MQTT
MQTT is used to make a connection between embedded devices, networks with services as well as middleware. The connection operation is based on a routing mechanism and makes MQTT as the best possible connection protocol for both IoT and M2M. MQTT is built on top of the TCP protocol and is suitable for devices with low resource availability, unreliable or low bandwidth links. MQTT simply consists of three components, subscriber, publisher, and a broker.
AMQP
AMQP focuses on message-oriented environments and is an open standard application layer protocol. It provides reliable Communication through message delivery guarantee primitives which include at-most-once, at-least-once and exactly-once delivery. TCP is used as a reliable protocol for message exchange.
Edge
an edge-computing architecture simply means the edge of the network. The devices present at the edge of the network vary based upon the functionalities. A mobile phone can be employed at the edge. A router can be employed at the edge of the network etc. Edge comprises of those devices which can perform temporary data processing and temporary storage before sending the actual data to the cloud for further storage and processing. The communication between an edge device and an edge is facilitated by an edge gateway. Edge provides data computing capabilities nearer to the source of data. Edge is a demarcation between the core network and the rest of the network in an edge computing environment. It just acts as an interface to connect the edge architecture with either fog domain or cloud environment. The devices which are employed at the edge should be capable of providing storage and computing services. The edge of a network can be at a distance from the actual edge device. In most of the cases, depending upon the response time and bandwidth available, the edge can be just a hop distance from the main edge device, collecting the data.
Conclusion
It is designed to enable real-time applications to work efficiently and to provide responses within a specified time. The architecture focuses on reducing bandwidth usage and minimizing latency. The architecture can include cloud-based features, as happens in most of the cases, and in some of the cases, cloud properties aren’t included in the edge architecture model.
The architecture has a proper interface to connect with the cloud datacenters, for permanent data storage and other cloud-based services. The edge architecture is flexible, adding devices from different heterogeneous environments and providing services nearer to the devices.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Edge Computing Architecture. Here we discuss the introduction to Edge Computing Architecture, various protocols used in this layer. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –