Health Effects of Sugar on the Body – Overview
If you are health conscious or have a sweet tooth, you might have definitely wondered what are the effects of sugar on the body.
But the answer is not very simple. Sugar comes in various forms, including natural sugars found in fruits and added sugars incorporated into processed foods and beverages. While natural sugars provide essential nutrients and energy, added sugars contribute empty calories and can lead to health issues and disease.
According to an American Heart Association study, Americans intake 17 teaspoons of added sugar per day on average, which is more than two to three times the recommended amount. This excessive intake is linked to various health issues, including obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and dental problems requiring regular dental care. On the other hand, a few medical faculty members extensively explored the impact of free sugar on human health, stating that by making informed choices about carbohydrate intake, we can support optimal health.
With evidence supporting both sides, join us in uncovering the truth: “is sugar bad for health?.”
Understanding the Role of Sugar in the Body
Let us understand how sugar contributes to our body’s energy metabolism through the steps below.
Step #1: Carbohydrate Digestion
During digestion, the body breaks down carbohydrates into simple natural sugars, primarily glucose, fructose, and galactose. This process begins in the mouth with enzyme action and continues in the small intestine.
Step #2: Glucose Absorption
The intestinal walls absorb glucose into the bloodstream, making it readily available for energy production and utilization by various cells and tissues.
Step #3: Glycogen Storage
Any extra glucose not needed immediately for energy is turned into glycogen and stored in the liver and muscles. This glycogen is a readily available energy reserve that maintains blood sugar levels during fasting or increased energy demand.
Effects of Sugar on the Body – The Positive Aspects
Before we evaluate whether consuming too much sugar can have negative health effects, let’s look at some of the positive impacts of sugar intake.
1. Energy Production
Glucose serves as the immediate energy source for cells, fueling essential physiological functions such as muscle contraction, brain activity, and cellular metabolism.
2. Brain Function
Glucose is essential for brain function, as the brain relies heavily on this sugar for energy. Adequate glucose supply ensures proper cognitive function, concentration, and overall mental well-being.
3. Blood Sugar Balance
Glucose from sugar, also known as blood sugar, helps keep our body’s blood sugar levels at an optimal range, which is crucial for good health. Therefore, the body can carefully control blood glucose levels to avoid hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
4. Insulin Regulation
Insulin, produced by the pancreas, is vital for controlling blood sugar levels. It helps cells absorb glucose more easily and encourages storing it as glycogen in the liver and muscles. However, the pancreas releases insulin only when glucose (sugar) enters your bloodstream. This emphasizes the positive effects of sugar on the body.
Effects of Sugar on the Body – Hidden Dangers of Added Sugars
Many processed and packaged foods have hidden added sugars that people might not realize. There are hidden sugar health risks contributing to various health problems. Let us get to the depth of eating sugar, good or bad:
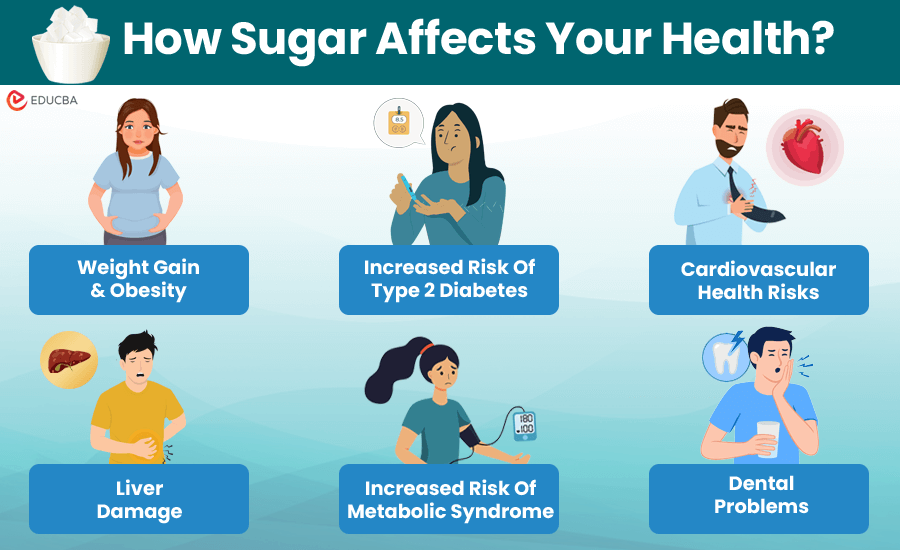
#1. Weight Gain and Obesity
Consuming too much sugar can lead to gaining unwanted body fat, particularly around organs, increasing the risk of metabolic issues. Moreover, excess sugars in foods offer no calories and lack essential nutrients, which can hamper your weight loss plan.
#2. Dental Problems
Sugary foods and beverages contribute to tooth decay and cavities. According to Geraldton dental experts, bacteria in the mouth consume the sugar, creating acids that wear away tooth enamel and encourage cavities. It can eventually result in dental issues and problems with oral health.
#3. Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Regularly consuming excessive amounts of added sugars can result in insulin resistance, a crucial element in the onset of type 2 diabetes. These sugars prompt rapid increases in blood sugar levels, which strain the pancreas and gradually interfere with insulin effectiveness.
#4. Cardiovascular Health Risks
Consuming excess sugar can lead to heart problems like heart disease, high blood pressure, and raised triglyceride levels. Added sugars contribute to inflammation, arterial stiffness, and other factors that increase the risk of heart issues.
#5. Liver Damage
The liver is responsible for metabolizing fructose, a common type of added sugar, but its excessive consumption can overload it, causing NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease). This can lead to liver scarring, reduced function, and inflammation.
#6. Increased Risk of Metabolic Syndrome
Consuming excessive added sugar can result in metabolic syndrome, which means a cluster of health problems such as hypertension, elevated blood sugar, irregular cholesterol levels, and excess abdominal fat.
Tips On How To Reduce Sugar Intake
Here are a few tips to reduce your sugar intake by making minor adjustments to your diet and choosing healthier options.
- Opt for sugar-free choices.
- Inspect food labels to spot any hidden sugars in packaged foods and drinks.
- Choose whole fruits instead of processed snacks or desserts.
- Cut down on packaged foods and opt for fresh, whole foods.
- Swap sugary drinks like soda for water, herbal teas, or water infused with fruits and herbs for flavor.
- Instead of refined sugars, experiment with natural sweeteners like stevia, monk fruit, or erythritol.
- Pay attention to condiments and sauces, as they might contain hidden sugars. Choose homemade versions or sugar-free options instead.
- Use brown sugar over white sugar due to its slightly higher mineral content.
By following these suggestions and being mindful of your choices, you can slowly reduce sugar consumption and experience the advantages of a better diet.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the effects of sugar on the body is crucial to making informed dietary choices. To reduce the unfavorable effects of sugar on the body, be mindful of your sugar intake, read labels, and opt for whole foods over processed options. By doing this, you can greatly decrease your chances of obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and dental issues. It’s also important to note that using natural sweeteners, preparing meals at home, and being mindful of flavorings can further improve your health.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article explaining the numerous positive and negative effects of sugar on the body was helpful to you. To learn more, refer to the articles below.
