Updated April 18, 2023
What is EIGRP?
EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol) is a distance-vector protocol developed by Cisco that operates on DUAL (Diffusing Update Algorithm). It transfers information or data from one router to neighboring routers in the same range. Even though it is a complex protocol, it is simple to set up and run in both small and big networks. EIGRP was created to address the drawbacks of traditional distance vector routing protocols such as IGRP and RIP, which were difficult to scale to meet the network’s needs. Because it combines the features of the link-state routing and distance vector routing protocols, EIGRP is termed a hybrid. EIGRP receives updates from its neighbors the same as the distance vector routing protocol does. EIGRP, on the other hand, maintains a network topology of advertised routes and uses the Diffusing Update Algorithm (DUAL) to choose loop-free routes like link-state protocol. The time it takes for all routers in a network to accept a network update is known as the convergence time. If convergence time is short, the router can quickly adapt to changes in the network topology.
Because the EIGRP doesn’t transfer full periodic routing updates, it has a quick convergence time. EIGRP, on the other hand, is unaware of all network connections and must rely on the advertisement of its neighbors.
What is OSPF?
Like EIGRP, OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a routing protocol, however, it is an open IETF standard that can be utilized as well as deployed in a wide range of networks. The OSPF protocol was created with the goal of creating a link-state protocol that could provide higher scalability and efficiency than RIP. OSPF is a classless routing system that also aids discontinuous networks with variable-length subnet masking (VLSM). OSPF uses multicast addresses such as 224.0.0.5 and 224.0.0.6 to send Hello and updates. There’s also authentication, which is in two types: plain text and message-digest algorithm 5.
The OSPF, as previously stated, uses the Dijkstra algorithm to generate routes by building the shortest path tree (SPT). Each router displays itself as well as links to its neighbors in an understandable manner in link-state ads, allowing OSPF to layout the topology based on the data from the shortest-path tree.
Head to Head Comparison between EIGRP vs OSPF (Infographics)
Below are the top 10 differences between EIGRP vs OSPF:
Key Differences Between EIGRP and OSPF
i. EIGRP is a comprehensive distance vector routing system that uses triggered and incremental updates. The triggered updates, in this case, indicate that the router will not deliver updates unless and until something changes. Furthermore, because of the incremental updates, the router will only relay the information that has changed, rather than all of the network’s information. OSPF, on the other hand, is a link-state routing protocol that resembles a map and stores all of the information about all of the routes in a given area. Every time something changes in the area, all routers in that area must recalculate their databases and routes. This makes OSPF more CPU demanding than EIGRP, and because it requires storing route information in its database, it also requires more RAM.
ii. In comparison to OSPF, EIGRP is a superior alternative for backward compatibility with old routers.
iii. The OSPF requires rigorous area planning, whereas the EIGRP does not; in fact, it is ideal for multivendor environments.
iv. When it comes to convergence time, the EIGRP is faster since it employs the DUAL algorithm, which selects the best and alternate best paths. If the best path fails, it will automatically switch to the other best way. Whereas, OSPF takes a different technique, which results in a longer convergence time.
v. OSPF has higher scalability than EIGRP since EIGRP is difficult and vendor-specific, making it impossible to transfer from one vendor to another. OSPF, on the other hand, is an open standard and simple protocol that allows the network to scale efficiently.
vi. EIGRP is the only protocol that allows for uneven path load balancing, whereas OSPF lacks this capability.
vii. As OSPF is widely utilized in traditional systems, it provides better support for service providers and data centers. It also improves the sharing of routing information.
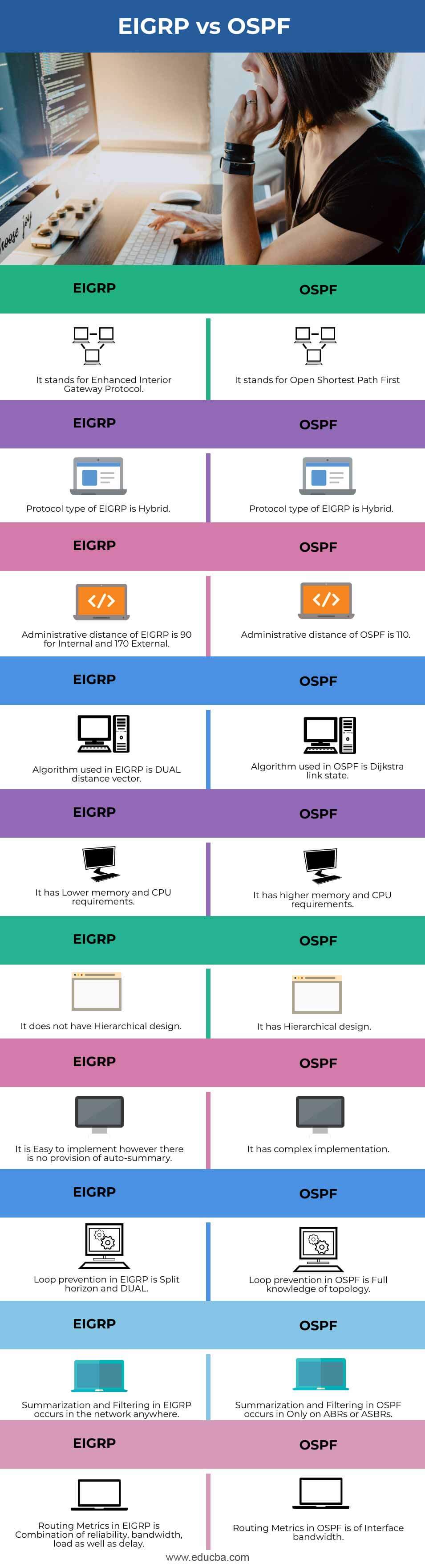
Difference Table of EIGRP and OSPF
| Sr. No. | EIGRP | OSPF |
| 1. | It stands for Enhanced Interior Gateway Protocol. | It stands for Open Shortest Path First |
| 2. | Protocol type of EIGRP is Hybrid | The protocol type of OSPF is Link State. |
| 3. | The administrative distance of EIGRP is 90 for Internal and 170 for External. | The administrative distance of OSPF is 110. |
| 4. | The algorithm used in EIGRP is a DUAL distance vector. | The algorithm used in OSPF is Dijkstra link state. |
| 5. | It has Lower memory and CPU requirements. | It has higher memory and CPU requirements. |
| 6. | It does not have a Hierarchical design | It has a Hierarchical design |
| 7. | It is Easy to implement however there is no provision of auto-summary | It has a complex implementation |
| 8. | Loop prevention in EIGRP is Split horizon and DUAL | Loop prevention in OSPF is Full knowledge of topology |
| 9. | Summarization and Filtering in EIGRP occurs in the network anywhere | Summarization and Filtering in OSPF occurs Only on ABRs or ASBRs |
| 10. | Routing Metrics in EIGRP is a combination of reliability, bandwidth, load as well as delay. | Routing Metrics in OSPF is of the Interface bandwidth |
Conclusion
When comparing EIGRP with OSPF, we can see that EIGRP is more sophisticated, whereas OSPF is easier because it only uses cost as a metric. The primary distinction between both protocols is because EIGRP only exchanges entire routing information once, when neighboring routes are formed, and then it merely tracks modifications.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to EIGRP vs OSPF. Here we discuss EIGRP vs OSPF key differences with infographics and comparison table, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –