Updated July 24, 2023
Elastic Demand Formula (Table of Contents)
What is the Elastic Demand Formula?
The term “Elastic Demand” refers to the strong movement witnessed in a product’s demand due to changes in other economic factors, primarily product price and consumer income. In other words, a slight change in either producer price or consumer income will result in a huge change in the demand for the subject product.
We classify product demand as elastic when the elasticity of demand exceeds one. Based on the driving economic factors, there are two major types of elasticity of demand:
1. Price Elasticity of Demand
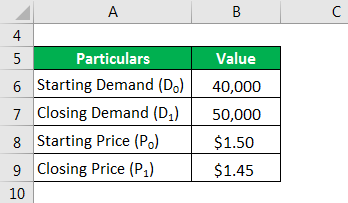
2. Income Elasticity of Demand
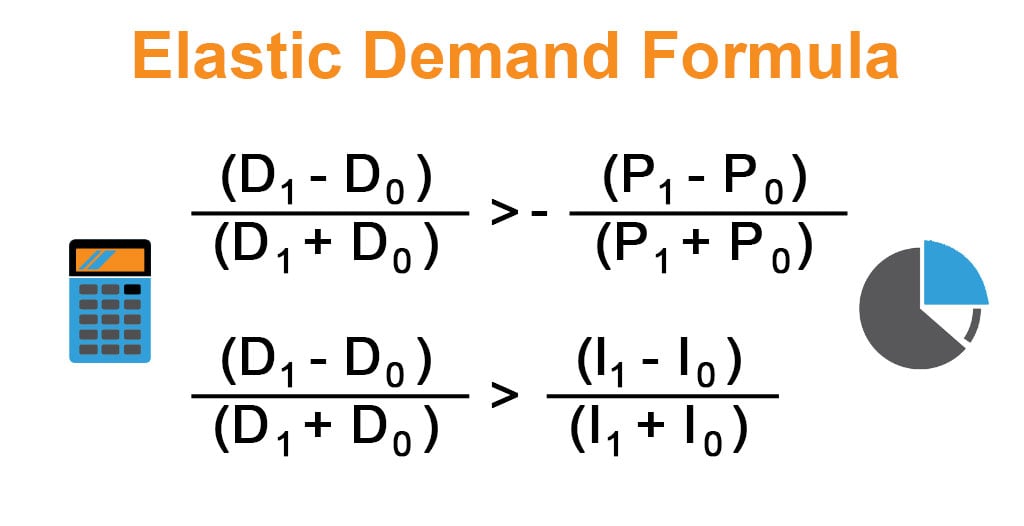
The price elasticity of demand is known as elastic demand when the percentage increase in demand is more significant than the percentage decline in the product price. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Where
- D0: Starting Demand
- D1: Closing Demand
- P0: Starting Price
- P1: Closing Price
If the percentage increase in demand exceeds the percentage increase in consumer income, we classify it as elastic demand, representing the income elasticity of demand. Mathematically, it is represented as,
Where
- D0: Starting Demand
- D1: Closing Demand
- I0: Starting Income
- I1: Closing Income
Example of Elastic Demand Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Elastic Demand in a better manner.
Elastic Demand Formula – Example #1
Let us take the example of a company that manufactures soft drinks to illustrate the price elasticity of demand. Recently the company reduced the price from $1.50 per bottle to $1.45 per bottle, which increased sales from 40,000 bottles to 50,000. Based on the given information, calculate if the demand for soft drinks is elastic or not.
Solution:
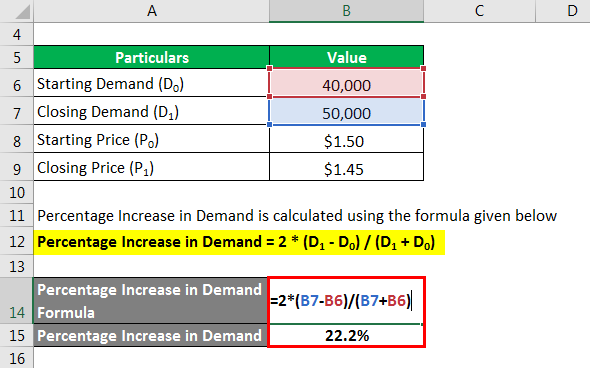
The percentage Increase in Demand is calculated using the formula given below.
Percentage Increase in Demand = 2 * (D1 – D0) / (D1 + D0)
- Percentage Increase in Demand = 2 * (50,000 – 40,000) / (50,000 + 40,000)
- Percentage Increase in Demand = 22.2%
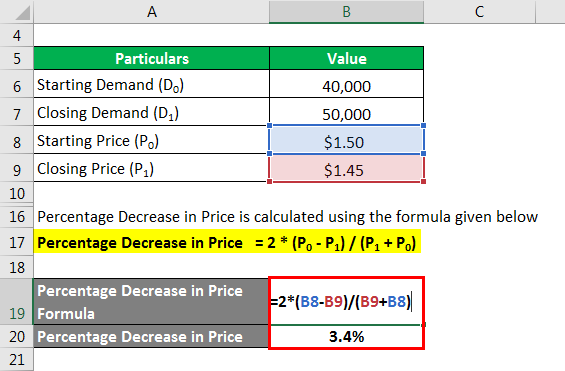
You can calculate the percentage decrease in price using the formula provided below.
Percentage Decrease in Price = 2 * (P0 – P1) / (P1 + P0)
- Percentage Decrease in Price = 2 * ($1.50 – $1.45) / ($1.45 + $1.50)
- Percentage Decrease in Price = 3.4%
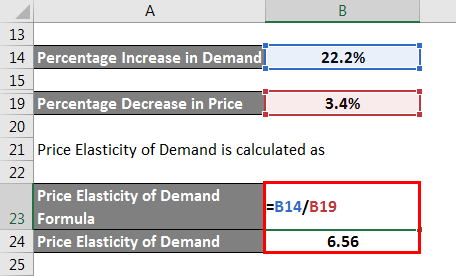
So, it can be seen that the percentage increase in demand is more significant than the percentage decrease in price. Therefore, it is an example of elastic demand.
The price Elasticity of Demand is calculated as
Elastic Demand Formula – Example #2
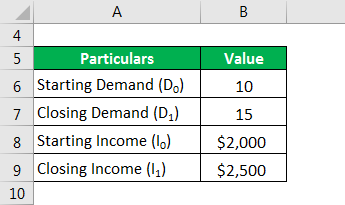
Let us take the example of the demand for ice cream and illustrate how it changes with the change in consumer income. As the per capita income increased from $2,000 to $2,500, the per capita per year consumption of ice cream increased from 10 lbs to 15 lbs. Based on the given information, calculate if the demand for ice cream is elastic or not.
Solution:
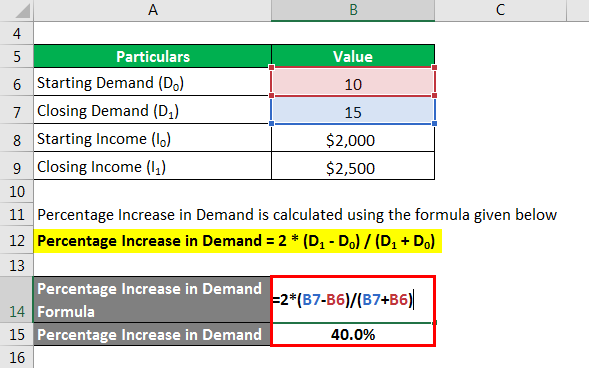
You can calculate the percentage increase in demand using the formula provided below.
Percentage Increase in Demand = 2 * (D1 – D0) / (D1 + D0)
- Percentage Increase in Demand = 2 * (15 – 10) / (15 + 10)
- Percentage Increase in Demand = 40.0%
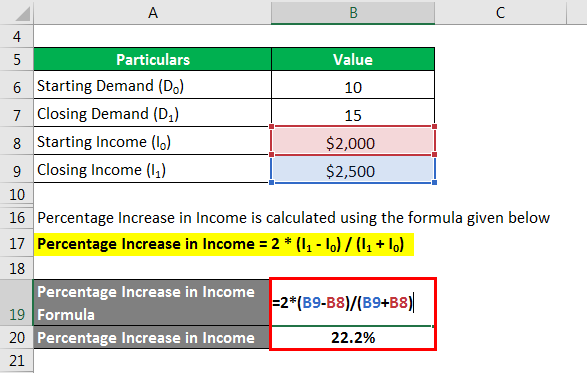
You can calculate the percentage increase in income using the formula provided below.
Percentage Increase in Income = 2 * (I1 – I0) / (I1 + I0)
- Percentage Increase in Income = 2 * ($2,500 – $2,000) / ($2,500 + $2,000)
- Percentage Increase in Income = 22.2%
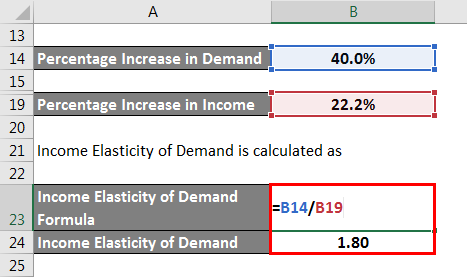
So, it can be seen that the percentage increase in demand is more significant than the percentage increase in income. Therefore, its demand for ice cream is elastic in nature.
Income Elasticity of Demand is calculated as
Explanation
The formula for Elastic Demand can be calculated by using the following steps:
Step 1: Firstly, calculate the increase in demand for the subject product, which is denoted by (D1 – D0), such that D1 > D0.
Step 2: Next, calculate the product’s average demand, denoted by (D1 + D0)/2.
Step 3: Next, calculate the percentage increase in demand by dividing the increase in demand (step 1) by the average demand (step 2) of the product.
Percentage Increase in Demand = 2 * (D1 – D0) / (D1 + D0)
Step 4: Next, calculate the decrease in producer price of the product, which is denoted by (P0 – P1), such that P1 < P0
Step 5: Next, calculate the product’s average price, denoted by (P1 + P0)/2.
Step 6: Next, calculate the percentage decrease in price by dividing the decrease in price (step 4) by the average price (step 5) of the product.
Percentage Decrease in Price = 2 * (P0 – P1) / (P1 + P0)
Step 7: Finally, the formula for elastic demand due to producer price is when the percentage increase in demand (step 3) is greater than the percentage decline in the product price (step 6), as shown below.
2 * (D1 – D0) / (D1 + D0) > 2 * (P0 – P1) / (P1 + P0)
- (D1 – D0) / (D1 + D0) > – (P1 – P0) / (P1 + P0)
Similarly, you can derive the formula for elastic demand caused by changes in consumer income by substituting the percentage increase in consumer income in place of the percentage decrease in producer price.
(D1 – D0) / (D1 + D0) > (I1 – I0) / (I1 + I0)
Relevance and Use of Elastic Demand Formula
It is an interesting topic if you belong to a company’s pricing team or are part of the government’s financial planning wing. Based on elastic demand, the pricing team can change the product price (such as discounts, offers, etc.) to get the desired demand drive. On the other hand, the government can implement policy changes (such as reducing taxes) to boost consumer income, eventually percolating to increasing demand.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Elastic Demand Formula. Here we discuss how to calculate the Elastic Demand along with practical examples. We also provide an Elastic Demand downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –