Difference Between ELK Stack vs Splunk
Most of Business transactions today take place in Online Digital mode. Any glitch in such online applications will force the customers to shift their loyalty to the competitor, and the business will effectively lose revenue. It’s paramount that the application should be available to the users 24 x7 at the expected performance level. At the same, it should be compliant with the regulatory conditions and security.
The organization suffers a huge loss if there is an issue in performance, even momentarily, or in regulatory compliance or insecurity. Monitoring the performance of the modern application has become a tough task due to its complex landscape dealing with microservices, Kubernetes, containers, and the cloud. It’s impossible to monitor the applications manually with the internal team. IT team needs a tool that will pull data or log from applications/surrounding infrastructure and analyze the data for monitoring and resolving issues.
The log management tool should be capable of handling huge amounts of data from the monitored application and hardware environment and monitoring the performance of applications. ELK stack and Splunk are the leading tools in this category, and let’s analyze their features in detail in this article.
Head to Head Comparisons Between ELK Stack vs Splunk (Infographics)
Below are the top comparisons between ELK Stack and Splunk:
Different Tools
Below are the different tools for ELK Stack vs Splunk
Elk Stack
Elk denotes three products of a company by the name Elastic. The three open-sourced products are
Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana. With the addition of the fourth product, Beats, one year ago, this tool is renamed Elastic Stack. A brief about all these 4 products
- Elasticsearch: The most important player in Elk stack is Elasticsearch, and due to its critical functionalities, the stack itself is named after it. Logically partitioned data is stored as Index and documents. This tool provides efficient storage and index layer.
- Logstash: This open-sourced tool processes large log data collected from multiple sources. It is known for the aggregation of data and analyzing it. This layer creates a solid data structure using the input data and storing it in the NoSQL database in Elastic search. A strong structure enables easy search.
- Kibana: It is an analysis and visualization arm of Elk Stack. A browser-based open-sourced tool helps analysis of the data stored in the index in the Elasticsearch layer and presents the results in a rich graphical mode. This layer enables users to query large volumes of data.
- Beats: This tool focuses on log collection from various sources. These open-source, lightweight log shippers pose as agents in different servers to pump the data either into Elasticsearch indexes or Logstash for additional processing before storing.
Splunk
Headquartered in San Francisco, Splunk deals with Big-data analytics. This tool, using the data captured, generates informative dashboards, reports, graphs, and other GUI visuals. This GUI facilitates the monitoring of applications and alerts abnormalities to users. IT department and End users make use of the results generated by Splunk.
This tool handles regulatory compliance as well as security aspects. The information presented by this tool helps users to do root cause analysis using AI techniques and resolve the issues at the earliest. It handles all the data types and helps users to build operational intelligence from the data collected.
It has 3 product ranges in its stable viz.,
- Splunk Enterprise: Used in big enterprises
- Splunk Light: Has Limited features, and it is a free
- Splunk Cloud: Offered as Hosted services
Key Differences Between ELK Stack vs Splunk
Let us discuss some of the major key differences between ELK Stack and Splunk:
- Approach: Splunk extracts a pile of data dynamically and enables users to analyze the data in the way they want easily. There is no pre-planning required for the extraction of data and analyzing it. Splunk offers great flexibility to users. Once the design is complete, the extraction and viewing are much simpler.
- Technology: Splunk is one single product with three components a. Data forwarder, b. Indexer, c. Search (Front end). ELK has 3 different open-sourced products Elastic Search, Logstash, and Kibana. Logstash extracts, processes, and stores the data in the NoSQL database in Elastic Search. Kibana provides a solid front end. Both Splunk and ELK use a single agent to gather log data from source servers. They store the extracted data in indexes. Splunk uses propriety indexes, and ELK uses Apache Lucene. Splunk uses a search head for search operations, and ELK uses Kibana.
- GUI- Visualization: Splunk offers the flexibility to add new components to the dashboard on the fly. It provides good control to administrators to authorize permission for users to access data. Hence users can customize their dashboard easily by themselves. Kibana provides visualization effects in the ELK stack and offers impressive charts, graphs, and dashboards. But it does not offer user management functions like Splunk.
- Search Functionalities: Splunk uses Search programming language (SPL) for the search operation. Kibana uses Lucene query syntax. Splunk offers a dynamic search facility where users can query data using any data field. Such a facility is unavailable in ELK; only the pre-designed fields can be used for query purposes.
- Cost: Splunk license is priced as per the volume of log data handled on a daily basis. The license is either perpetual or renewed yearly. ELK licenses are open-sourced, and it is free of cost.
- Training; Availability of trained manpower in ELK is plenty, and Users of Splunk will have to spend a substantial amount on training
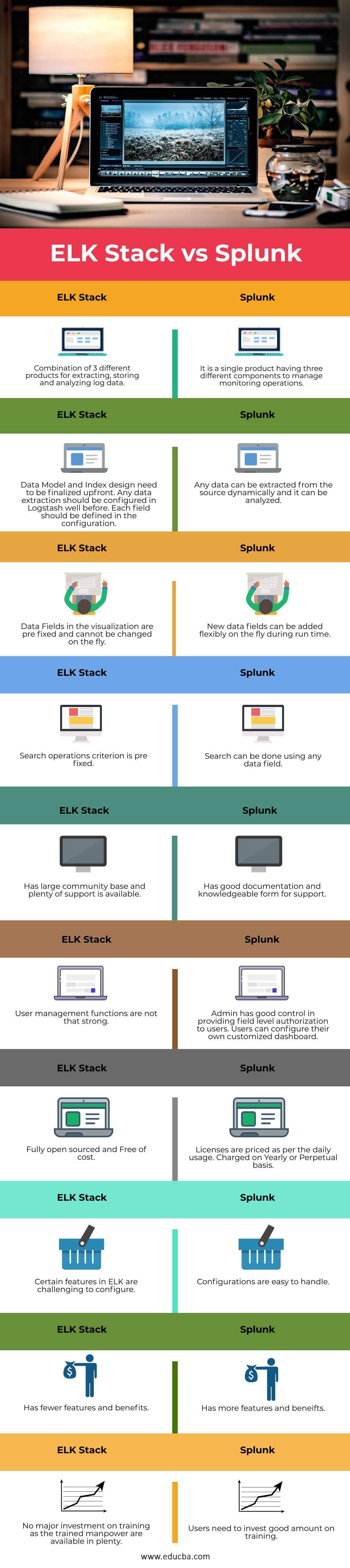
Comparison Table of ELK Stack vs Splunk
Let’s look at the top comparisons between ELK Stack vs Splunk.
| Sr.No |
ELK Stack |
Splunk |
| 1 | Combination of 3 different products for extracting, storing, and analyzing log data | It is a single product having three different components to manage monitoring operations |
| 2 | Data Model and Index design need to be finalized up front. Any data extraction should be configured in Logstash well before. | Any data can be extracted from the source dynamically, and it can be analyzed. |
| 3 | Data Fields in the visualization are prefixed and cannot be changed on the fly. | New data fields can be added flexibly on the fly during run time. |
| 4 | The search operations criterion is prefixed | Search can be done using any data field. |
| 5 | Has a large community base, and plenty of support is available. | Has good documentation and knowledgeable form for support |
| 6 | User management functions are not that strong | Admin has good control in providing field-level authorization to users. Users can configure their own customized dashboard. |
| 7 | Fully open-sourced and Free of cost | Licenses are priced as per daily usage. Charged on a Yearly or Perpetual basis |
| 8 | Certain features in ELK are challenging to configure | Configurations are easy to handle |
| 9 | Has fewer features and benefits | Has more features and benefits. |
| 10 | No major investment in training as the trained manpower is available in plenty. | Users need to invest a good amount in training. |
Conclusion
The platform selection depends on the user’s needs and the ability to manage budgets. Splunk offers a flexible, feature-rich, and user-friendly platform that comes at a heavy cost.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to ELK Stack vs Splunk. Here we discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison tables between ELK v Splunk. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –