Introduction to Enumset in Java
Enum set are the implementation of a set interface, and it extends Abstract class in java for enumeration type. The are Set collection provides the functionality to work with enums in java. Enum sets are not synchronized; hence they provide faster accessing of elements. Enum sets do not allow adding null elements; if we try to add a null value, it will throw a null pointer exception.
Syntax:
public abstract class EnumSet<E extends Enum<E>> || This is the class decralation of enum set.
EnumSet<E extends Enum<E>> enum1, enum2, enum3, enum4; || Declare different enum.As enum sets are not synchronized, they are much master, but we can synchronise them by using collections class synchronized method() below find the syntax for synchronized.
Collections.synchronizedSet(java.util.Set<T>)
Set<Enum_Type> s = Collections.synchronizedSet(EnumSet.noneOf(EnumClass.class));Methods of Enumset in Java
- static <E extends Enum<E>> allOf(Class<E> elementType): This method is used to create the enum with all elements mentioned.
- EnumSet<E> clone(): This method is used to create the copy of the set. Return type is EnumSet<E>.
- static <E extends Enum<E>> complementOf(EnumSet<E> s): This method is used to create the enum set specified in the method , this enum will contain all the elements which are not contained in set.
- static <E extends Enum<E>> copyOf(Collection<E> c): This will create a copy of enum set which is specified in the method. But it takes the collection parameter.
- static <E extends Enum<E>> copyOf(EnumSet<E> s): This will create a enum, specified as enum set. This will return an EnumSet<E>.
- static <E extends Enum<E>> noneOf(Class<E> elementType): This will also create an enum which specified in the method. Return an EnumSet<E>.
- static <E extends Enum<E>> of(E e): Also create an enum with initially elements. Return type is EnumSet<E>.
- static <E extends Enum<E>> of(E first, E… rest): Creates enum containing elements and it returns EnumSet<E>
- static <E extends Enum<E>> of(E e1, E e2): This method will create an enum with mentioned elements. Return type is EnumSet<E>
- static <E extends Enum<E>> of(E e1, E e2, E e3): This method will create an enum. Method return type is EnumSet<E> .
- static <E extends Enum<E>> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4): This methods will also create the enum with specified elements. Return type is EnumSet<E>
- static <E extends Enum<E>> of(E e1, E e2, E e3, E e4, E e5): This method is also create the enum with specifies elements passed as enum. Return type is EnumSet<E>
- static <E extends Enum<E>> range(E from, E to): In this method we can specified the range. Then it will create a new enum. Return type is EnumSet<E> .
Note:
- Enum set implements various class and interface. Enum set class declaration :
- public abstract class EnumSet<E extends Enum<E>> extends AbstractSet<E> implements Cloneable, Serializable
Interfaces which are implemented by enum set:
- Cloneable
- Set<E>
- Serializable
- Collection<E>
- Iterable<E>
Classes that are extending by enum set are the following:
- AbstractSet<E>
Examples of Enumset in Java
Following are the example of enumset are given below:
Example #1
In the below example, w are adding elements to the enum set.
Code:
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumsetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creating reference
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum1;
// here we are adding elements to the enum1 which we create above.
enum1 = EnumSet.of(EnumDemo.JAVA, EnumDemo.JAVASCRIPT,
EnumDemo.C, EnumDemo.PHP, EnumDemo.GO, EnumDemo.PYTHON, EnumDemo.TYPESCRIPT);
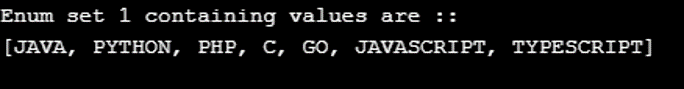
System.out.println("Enum set 1 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum1);
}
}
enum EnumDemo
{
JAVA, PYTHON, PHP, C, GO, JAVASCRIPT, TYPESCRIPT
};Output:
Example #2
In this example, we are creating enum2 by using the value sf enum1 only. Below find an example.
Code:
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumsetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creating reference
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum1;
// here we are adding elements to the enum1 which we create above.
enum1 = EnumSet.of(EnumDemo.JAVA, EnumDemo.JAVASCRIPT,
EnumDemo.C, EnumDemo.PHP, EnumDemo.GO, EnumDemo.PYTHON, EnumDemo.TYPESCRIPT);
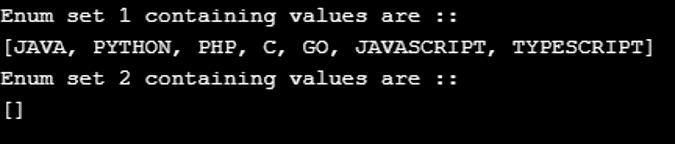
System.out.println("Enum set 1 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum1);
// adding value to another enum set using addAll method
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum2 = EnumSet.allOf(EnumDemo.class);
System.out.println("Enum set 2 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum2);
}
}
enum EnumDemo
{
JAVA, PYTHON, PHP, C, GO, JAVASCRIPT, TYPESCRIPT
};Output:
Example #3
In this example, we are finding complements f enum1 to enum2.
Code:
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumsetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creating reference
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum1;
// here we are adding elements to the enum1 which we create above.
enum1 = EnumSet.of(EnumDemo.JAVA, EnumDemo.JAVASCRIPT,
EnumDemo.C, EnumDemo.PHP, EnumDemo.GO, EnumDemo.PYTHON, EnumDemo.TYPESCRIPT);
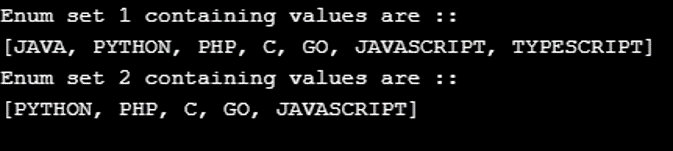
System.out.println("Enum set 1 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum1);
// finind completents of enum1 to enum2
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum2 = EnumSet.complementOf(enum1);
System.out.println("Enum set 2 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum2);
}
}
enum EnumDemo
{
JAVA, PYTHON, PHP, C, GO, JAVASCRIPT, TYPESCRIPT
};Output:
Example #4
Specifying range to elements to be copied.
Code:
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumsetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creating reference
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum1;
// here we are adding elements to the enum1 which we create above.
enum1 = EnumSet.of(EnumDemo.JAVA, EnumDemo.JAVASCRIPT,
EnumDemo.C, EnumDemo.PHP, EnumDemo.GO, EnumDemo.PYTHON, EnumDemo.TYPESCRIPT);
System.out.println("Enum set 1 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum1);
// here we are specifing the range to another enum using enum1
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum2 = EnumSet.range(EnumDemo.PYTHON, EnumDemo.JAVASCRIPT);
System.out.println("Enum set 2 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum2);
}
}
enum EnumDemo
{
JAVA, PYTHON, PHP, C, GO, JAVASCRIPT, TYPESCRIPT
};Output:
Example #5
Making copy from existing enum.
Code:
import java.util.EnumSet;
public class EnumsetDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// creating reference
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum1;
// here we are adding elements to the enum1 which we create above.
enum1 = EnumSet.of(EnumDemo.JAVA, EnumDemo.JAVASCRIPT,
EnumDemo.C, EnumDemo.PHP, EnumDemo.GO, EnumDemo.PYTHON, EnumDemo.TYPESCRIPT);
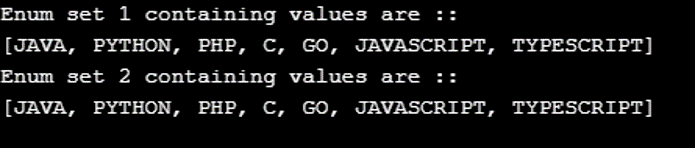
System.out.println("Enum set 1 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum1);
// here we are copying elements of enum1 to enum2.
EnumSet<EnumDemo> enum2 = EnumSet.copyOf(enum1);
System.out.println("Enum set 2 containing values are :: ");
System.out.println( enum2);
}
}
enum EnumDemo
{
JAVA, PYTHON, PHP, C, GO, JAVASCRIPT, TYPESCRIPT
};Output:
Conclusion
Java EnumSet is the implementation of the SET interface in java. They are a special type of java collection framework that provides support for enum types in java. We can also make them synchronized as these are not synchronized.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Enumset in Java. Here we discuss the introduction and methods of enumset in java along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –