Updated July 26, 2023
Overview of Equity Examples
Equity, also called net worth, determines what an entity owns.
In other words, equity can be defined as the degree of ownership an entity has in various assets (properties, machines, etc) after deducting all the associated liabilities (debts or loans).
Equity can be of various types:-
- Household Equity: For individuals, equity is determined by ownership of a house and car.
- Shareholders’ Equity: For businesses, the amount of money (capital) the business owners invest to buy various assets. It is also referred to as owners’ equity
Calculation of Equity
Equity tells us the financial health of the entity. That means whether an individual is financially stable and whether a company (or a business) can return the invested capital (ROE)
Examples of Equity (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Equity in a better manner.
Equity Examples #1 – Household Equity
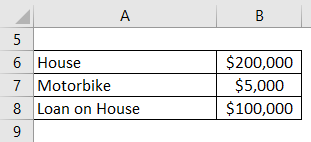
Mr. Robert Downey is a small farmer; he owns a house in the village with a home loan on it, a tractor for his farming business, and a motorbike (which he uses for both household and business purposes)
The current market value of his house is $200,000, and the amount of money he owes on a home loan is $100,000. The current value of the bike is $5000. The usage of a motorbike is 60% for business and the remaining for household purposes.
The tractor cannot be considered a household asset. Hence it will not be included in the calculation.
Solution:
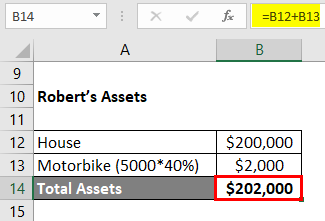
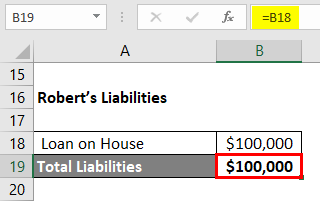
Robert’s Equity
Equity = Assets – Liabilities
- Equity = $202,000 – $100,000
- Equity = $102,000
Equity Examples #2 – Owners’ Equity
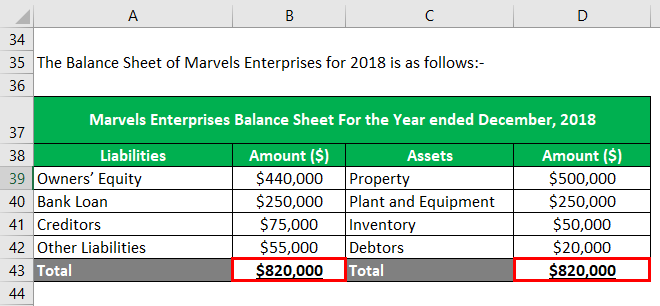
Mr. Robert Downey is a small entrepreneur in the business of iron crafting. To calculate the owner’s equity and create a balance sheet, he arranged the following data related to his proprietorship firm, Marvels Enterprises:-
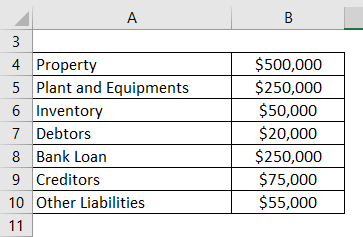
Owns property worth $500,000, plant and equipment of $250,000, inventory = $50,000, debtors = $20,000.
Owes bank loan = $150,000, creditors = $55,000, other liabilities = $45,000.
Solution:
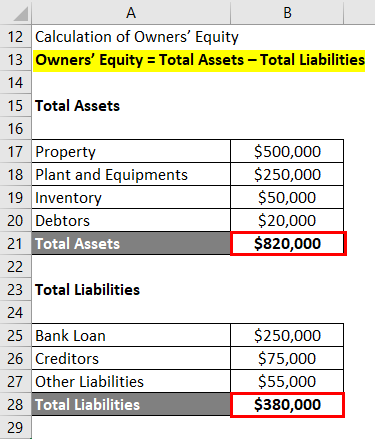
Owners’ Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
Owners’ Equity is Calculated as:
Owners’ Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
- Owners’ Equity = $820,000 – $380,000
- Owners’ Equity = $440,000
Equity Examples #3 – Shareholders’ Equity
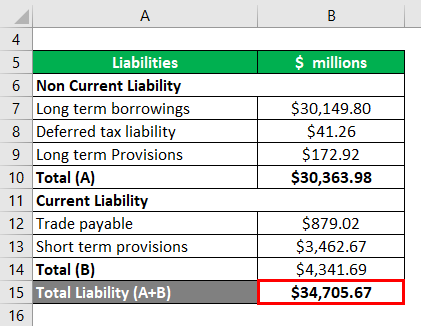
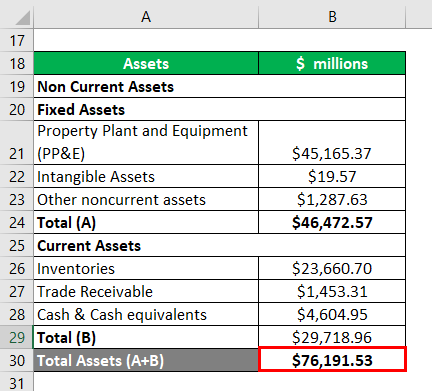
Stark Inc is a well-established company tasked with the risk manager Mr. Robert Downey to Calculate the company’s shareholder’s equity. Mr. Downey has collected the following information from the annual reports of the company for the year 2018:-
Calculation of Shareholders’ Equity
Shareholders’ Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
- Shareholders’ Equity =$ 76,191.53 – $34,705.67
- Shareholders’ Equity = $41,485.86
Equity Examples #4 – Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE: The ratio of ROE is a very important profitability metric that determines the investors about the income-generating capacity of the company from the money invested by the existing shareholders.
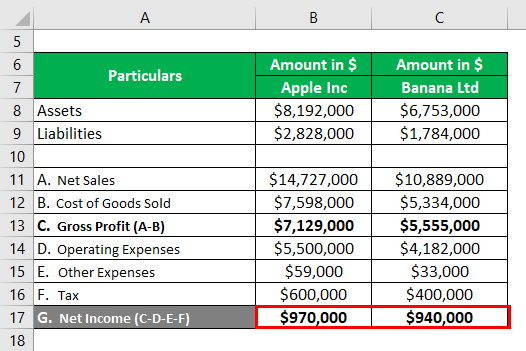
Mr. Robert Downey wants to invest $2 million in equity stocks. Aftermarket research, he picks two stocks: 1. Apple Inc and 2. Banana Ltd. Both are identical companies. He collects the following data to conduct a comparative analysis to select the more profitable stock out of the two. He decides to calculate ROE on both stocks and invest in the stock with higher ROE.
Solution:
Apple Inc:
Calculation of Shareholders’ Equity
Shareholders’ Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
- Shareholders’ Equity= $8,192,000 – $2,82,8000
- Shareholders’ Equity= $5,36,4000
Calculation of Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE = Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity
- ROE = ($9,70,000/ $5,36,4000) * 100
- ROE = 18.08%
Banana Ltd:
Calculation of Shareholders’ Equity
Shareholders’ Equity = Total Assets – Total Liabilities
- Shareholders’ Equity = $6753000 – $1784000
- Shareholders’ Equity = $4,96,9000
Calculation of Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE = Net Income / Shareholders’ Equity
- ROE = (9,40,000/ 4,96,9000) * 100
- ROE = 18.92%
Net Income: Apple Inc > Banana Ltd
($97000) > ($94000)
ROE: Banana Ltd > Apple Inc
(19%) > (18%)
Advice: However the Net income of Apple Inc is higher, but ROE says that Banana Ltd is generating a larger amount of income with the Equity Capital invested in the business. Banana Ltd efficiently uses its invested equity funds to generate higher profits.
Hence Mr. Downey should invest his funds in Banana Ltd based on higher ROE.
Conclusion – Equity Examples
Equity is a measure of the financial health of an entity because it informs the entity about the assets it owns that will generate future cash inflows and the liabilities it has to pay i.e. future cash outflows.
Equity is the difference between assets and liabilities. A negative figure suggests poor financial health; a positive value says survival is possible. Still, a high positive value suggests that assets efficiently generate regular incomes and can pay off their liabilities.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Equity Examples. Here we discuss the top 4 Examples of Equity, a detailed explanation, and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –