Introduction to Cruelty Towards Animals
Animal cruelty, a disturbing and pervasive issue, encompasses various forms of abuse and neglect inflicted upon innocent beings. From physical violence to abandonment, its repercussions extend beyond the immediate victims, affecting society as a whole. The undeniable link between animal cruelty and human behavior underscores the urgency of addressing this problem. As we navigate a world intertwined with animal exploitation in industries, a critical examination of the legal framework, coupled with the role of education and advocacy, is essential in fostering a compassionate and ethical coexistence with our fellow inhabitants of the Earth.
Significance of the issue (Cruelty Towards Animals)
The significance of the issue of cruelty towards animals is multifaceted, encompassing ethical, societal, psychological, and environmental dimensions. Understanding and addressing this problem is crucial for several reasons.
- Ethical Considerations: Animals are sentient beings that may experience pain, pleasure, and various emotions. Inflicting harm upon them raises fundamental ethical concerns about humans’ moral responsibility toward the welfare of other living beings. Ethical treatment of animals reflects a society’s values and moral compass, influencing how individuals and communities define compassion and empathy.
- Societal Impact: Broader societal issues often interconnect with animal cruelty. People condoning or ignoring animal cruelty may contribute to desensitizing society to violence, fostering a culture where undervaluing empathy and kindness occurs.
- Psychological Ramifications: Individuals who engage in animal cruelty may exhibit signs of psychological distress or disorders. Exposure to animal cruelty can have detrimental effects on the psychological well-being of witnesses, especially children, potentially normalizing violence and desensitizing them to the suffering of others.
- Environmental Consequences: Specific industries contribute to animal cruelty through practices such as factory farming and animal testing. These actions injure animals and have negative environmental consequences, such as deforestation, pollution, and the depletion of natural resources.
- Global Interconnectedness: Addressing animal cruelty becomes a global responsibility in an interconnected world where information flows seamlessly across borders. Shared values of compassion and respect for all living beings can contribute to a more harmonious global community.
Connection between Animal cruelty and Human behavior
The connection between animal cruelty and human behavior is a complex and well-documented phenomenon, revealing a troubling correlation that extends beyond the immediate act of harming animals. Several key aspects highlight the intricate relationship between animal cruelty and human behavior:
- Early Warning Signs: Numerous studies have established that individuals who engage in acts of cruelty towards animals often display early signs of behavioral problems. Animal abuse can be an indicator of an underlying propensity towards violence, serving as an alarming precursor to potential harm directed at humans.
- The Violence Continuum: The “violence continuum” theory suggests that individuals who commit acts of cruelty towards animals may escalate to committing violence against humans. This progression is not universal, but recognizing the pattern is critical for early intervention and prevention of further harm.
- Psychological Implications: Engaging in animal cruelty can be linked to certain psychological disorders or conditions. Some individuals may use animals as outlets for their frustration, anger, or desire for control. Addressing the mental health of people involved is critical for stopping the cycle of abuse.
- Desensitization to Violence: Individuals exposed to or participating in acts of animal cruelty may become desensitized to violence. This desensitization can extend to a diminished capacity for empathy, potentially making it easier for the person to commit violent acts against both animals and humans.
- Teaching Empathy: Conversely, promoting empathy towards animals can positively affect human behavior. Education and awareness programs emphasizing compassion towards animals contribute to developing empathy in individuals, fostering a more humane society.
- Legal Implications: Recognizing the link between animal cruelty and human behavior has led to changes in legal frameworks. Many jurisdictions have strengthened animal cruelty laws, acknowledging the potential threat posed by those who mistreat animals. This not only protects animals but also serves to prevent escalation to violence against humans.
- Risk Factors and Intervention: Identifying risk factors associated with animal cruelty, such as a history of childhood abuse or neglect, can aid in targeted intervention strategies. Early intervention and counseling for individuals demonstrating concerning behavior towards animals can potentially prevent future violent acts.
- Educational Initiatives: Incorporating education about the connection between animal cruelty and human behavior into school curricula can contribute to shaping attitudes and behavior from a young age. Teaching respect for animals fosters a sense of responsibility and empathy that carries over into interactions with other humans.
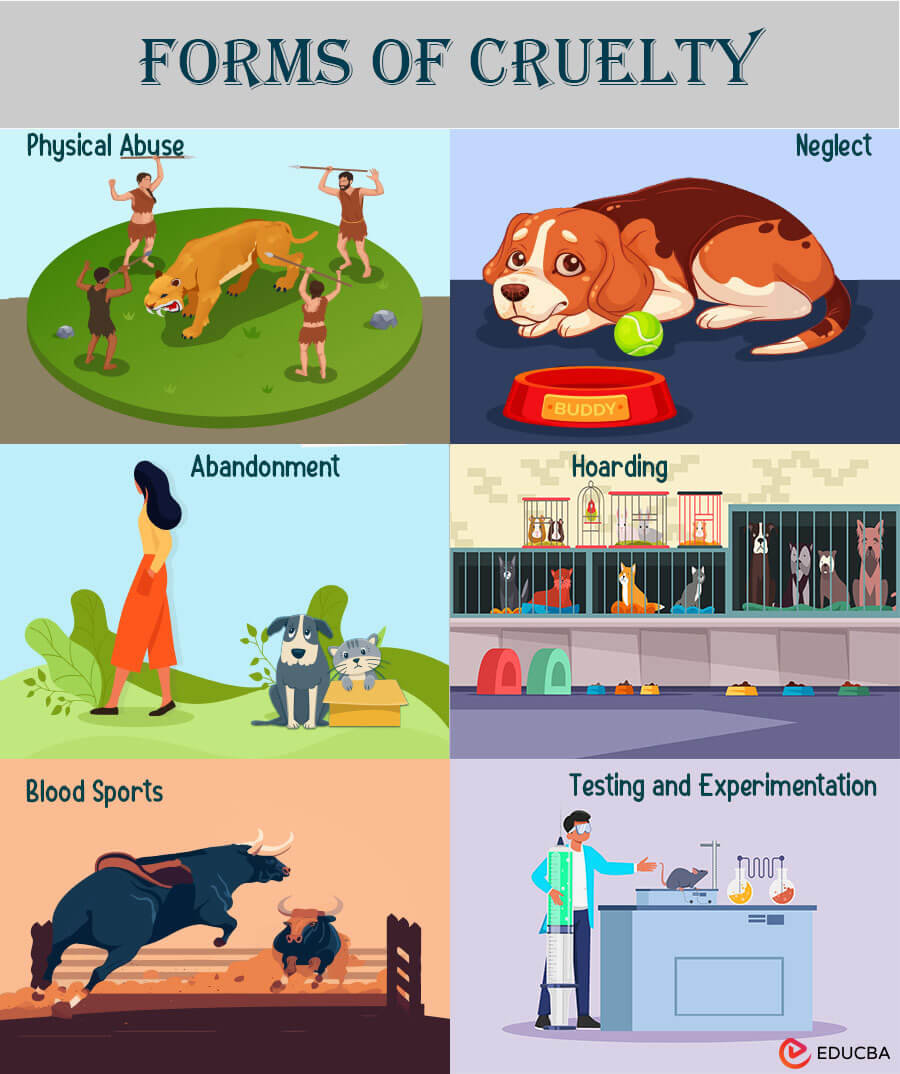
Forms of Cruelty
Forms of cruelty towards animals manifest in various distressing ways, ranging from direct physical harm to neglect and abandonment. Understanding these forms is crucial for identifying and addressing instances of abuse. Here are detailed explanations of each form:
1. Physical Abuse:
- Definition: Physical abuse involves deliberate acts of violence causing harm, pain, or injury to animals.
- Examples: Beating, kicking, hitting, burning, or intentional harm that inflicts physical suffering on animals.
- Impact: Physical abuse not only causes immediate pain and distress but can also lead to long-term physical and psychological trauma. In extreme cases, it may result in permanent injuries or even death.
2. Neglect:
- Definition: Neglect occurs when an individual fails to provide necessary care, food, water, shelter, or medical attention to animals under their care.
- Examples: Withholding food, water, or shelter, lack of veterinary care, and failure to address health issues or injuries.
- Impact: Neglect can lead to malnutrition, dehydration, disease, and suffering. Prolonged neglect may result in severe health complications, weakened immunity, and reduced quality of life for the animals.
3. Abandonment:
- Definition: Abandonment involves leaving animals without providing proper care, often leaving them to fend for themselves.
- Examples: Dumping animals in unfamiliar environments, neglecting former pets, or releasing animals into the wild without regard for their well-being.
- Impact: Abandoned animals face numerous risks, including exposure to harsh weather, hunger, predation, and the spread of diseases. Abandonment can also contribute to overpopulation and strain on local ecosystems.
4. Hoarding:
- Definition: Animal hoarding occurs when individuals accumulate an excessive number of animals, often beyond their capacity to provide proper care.
- Examples: Keeping a large number of animals in cramped conditions without adequate food, water, or veterinary care.
- Impact: Hoarded animals suffer from overcrowding, unsanitary conditions, and a lack of socialization. Health problems, such as disease transmission and malnutrition, are common among animals in hoarding situations.
5. Blood Sports:
- Definition: Blood sports involve using animals for entertainment or competition, often resulting in harm, injury, or death.
- Examples: Cockfighting, dogfighting, bullfighting, and other activities pit animals against each other for the amusement of spectators.
- Impact: Animals subjected to blood sports endure physical trauma and stress and often face death in brutal ways. These activities perpetuate cruelty for the sake of human entertainment, and people widely condemn them for their inhumane nature.
6. Testing and Experimentation:
- Definition: Testing and experimentation involve using animals for scientific or cosmetic purposes, often subjecting them to harmful procedures without adequate care.
- Examples: Animal testing for cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and scientific research that involves invasive procedures or exposure to toxic substances.
- Impact: Animals in testing facilities endure pain, stress, and suffering. Advocates for alternatives argue for the development and adoption of cruelty-free testing methods to eliminate the harm inflicted on animals.
The Role of Industry and Entertainment
In the intricate tapestry of animal cruelty, the industrial and entertainment sectors play significant roles in perpetuating harm to our fellow beings. From factory farming’s grim realities to the exploitation embedded in various forms of entertainment, these industries often prioritize profits over the well-being of animals.
Factory Farming
- Inhumane Conditions: Factory farming, driven by the demand for mass production of animal products, subjects billions of animals to deplorable living conditions. Crowded spaces, unsanitary environments, and routine practices such as debeaking and tail docking highlight the harsh reality faced by animals in these facilities.
- Environmental Consequences: Beyond the immediate suffering of the animals, factory farming contributes significantly to environmental degradation. The overuse of resources, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions associated with large-scale animal agriculture amplify the ecological toll on our planet.
Entertainment Industry
- Circus Exploitation: Traditional circuses, though diminishing, continue to exploit animals for entertainment. The use of wild animals in performances often involves harsh training methods, confining spaces, and a stark departure from their natural habitats. This practice raises ethical concerns regarding the welfare of the animals involved.
- Impact of Animal Tourism: The entertainment industry encompasses various forms of animal tourism, keeping creatures in captivity for public display. From marine parks to exotic animal exhibits, these attractions can subject animals to stress, deprivation, and a compromised quality of life.
Causes of Animal Cruelty
The causes of animal cruelty are multifaceted, often stemming from a complex interplay of societal, cultural, economic, and individual factors. Understanding these root causes is crucial in formulating effective strategies to prevent and combat cruelty towards animals.
- Lack of Awareness and Education: Ignorance about the needs and feelings of animals can contribute to unintentional cruelty. Lack of education about proper care, empathy, and the consequences of harmful actions may result in neglect or mistreatment.
- Societal Norms and Cultural Practices: Some forms of cruelty towards animals are deeply ingrained in cultural practices or societal norms. Activities like animal fighting, traditional rituals, or the use of animals in entertainment can perpetuate cruelty due to a perceived cultural acceptance.
- Economic Factors and Exploitation: Economic considerations often play a significant role in animal cruelty. Industries such as factory farming prioritize profit margins, subjecting animals to harsh conditions, overcrowded spaces, and inhumane practices to maximize production.
- Psychological Factors in Individuals: Individuals with certain psychological traits, such as a lack of empathy or a propensity for violence, may be more prone to committing acts of cruelty towards animals. Cruelty can also be an early indicator of deeper psychological issues.
- Environmental and Community Factors: The environment in which individuals grow up can influence their attitudes about animals. Communities with a prevalence of animal cruelty or a lack of animal welfare resources may foster an environment where such behavior is normalized.
- Lack of Animal Welfare Legislation: In some regions, the absence of comprehensive and enforceable laws perpetuates cruelty. Weak legal frameworks fail to deter offenders and create a culture of impunity.
- Desensitization and Normalization: Exposure to violence, whether in real life or through media, can desensitize individuals to the suffering of animals. When cruelty becomes normalized, individuals may be more likely to engage in abusive behavior without fully grasping its implications.
- Social and Economic Inequality: Communities facing social and economic challenges may prioritize immediate survival over animal welfare. Struggling individuals may exploit animals for economic gain or lack the resources to provide proper care.
Wildlife Exploitation
Wildlife exploitation refers to the utilization of wild animals for various purposes that often prioritize human interests over the well-being of the animals and the conservation of their natural habitats. Several aspects of wildlife exploitation highlight the ethical and environmental concerns associated with this form of cruelty:
- Poaching and Illegal Wildlife Trade: Poaching refers to the illegal hunting or killing of wild animals for their body parts, skins, or other commodities. This practice significantly threatens many species, driving some to extinction. The illegal trade of wildlife is a profitable industry that contributes to the extinction of many endangered species and disrupts ecosystems.
- Trophy Hunting: Trophy hunting involves killing wild animals for sport, with hunters often targeting species prized for their size, rarity, or unique characteristics. While proponents argue that regulated trophy hunting can contribute to conservation efforts and local economies, critics highlight the ethical concerns of killing animals for pleasure and the potential impact on populations, particularly for species already at risk.
- Captive Breeding and Entertainment: The captive breeding of wild animals for entertainment purposes, such as circuses, theme parks, and roadside zoos, raises ethical questions about the confinement, treatment, and exploitation of animals for human enjoyment. Animals in captivity may suffer from stress, inadequate living conditions, and behavioral abnormalities, highlighting the need for responsible and ethical treatment.
- Use of Animals in Traditional Medicine: Certain wildlife species are exploited for their body parts or organs, believed to have medicinal properties in some traditional cultures. This practice threatens various species, particularly those with small populations, as it contributes to habitat destruction and population decline.
- Deforestation and Habitat Destruction: The expansion of human activities, including logging, agriculture, and urban development, often leads to deforestation and habitat destruction. This displaces wildlife and disrupts ecosystems, affecting the balance of predator-prey relationships and leading to population declines in various species.
- Exotic Pet Trade: The exotic pet trade involves capturing and trading wild animals for the pet industry. While some animals may breed in captivity, humans often take many from their natural habitats. This practice often results in stress, injury, and death for the animals and contributes to the depletion of wild populations.
- Environmental Pollution: Human activities, such as industrial pollution and waste disposal, can negatively impact wildlife and their habitats. Pollution can contaminate water sources, soil, and air, affecting the health and survival of wildlife species. This exploitation highlights the interconnectedness of environmental issues with the well-being of wild animals.
Measure to Stop Animal Cruelty
Addressing and preventing animal cruelty requires a multifaceted approach involving legislation, education, public awareness, and responsible pet ownership. Here are vital measures to stop animal cruelty:
- Stringent Legislation: Enforce and strengthen laws against animal cruelty, ensuring that they cover a wide range of offenses and include severe penalties for offenders. Regularly update legislation to address emerging issues and align with evolving societal values regarding animal welfare.
- Law Enforcement and Prosecution: Specialized units within law enforcement agencies should be established to investigate and prosecute animal cruelty cases. Ensure training for investigators to recognize signs of abuse and neglect and ensure that legal proceedings result in meaningful consequences for perpetrators.
- Animal Welfare Standards in Industries: Implement and enforce strict animal welfare standards in factory farming, animal testing, and entertainment industries. Companies must conduct regular inspections and audits to ensure compliance and be held accountable for violations.
- Education and Awareness Programs: Incorporate lessons about ethical ownership of pets, animal welfare, and the consequences of cruelty into school curricula. Public awareness campaigns can also be crucial in informing communities about the importance of treating animals respectfully and kindly.
- Support for Animal Shelters and Rescues: Provide financial support and resources to animal shelters and rescue organizations. These organizations are essential in caring for abused and neglected animals, finding suitable homes, and encouraging adoption rather than purchasing animals from evil sources.
- Animal Cruelty Registries: Establish and maintain animal cruelty registries to track individuals convicted of animal abuse. This can help prevent repeat offenses and allow shelters and adoption agencies to screen potential adopters for a history of cruelty.
- Mental Health Intervention: Identify and address the mental health problems of individuals involved in animal cruelty. Implement intervention programs that provide counseling and support to help break the cycle of abuse and prevent the escalation of violence towards both animals and humans.
- International Collaboration: Foster international collaboration to combat transnational issues such as wildlife trafficking and illegal trade in exotic animals. Countries should collaborate to share information, enact consistent legislation, and enforce measures to protect wildlife globally.
- Whistleblower Protection: Implement whistleblower protection programs to encourage individuals to report animal cruelty without fear of retaliation. This can help reveal hidden cases of abuse and ensure that authorities bring perpetrators to justice.
- Humane Education for Professionals: Provide animal behavior, handling, and welfare education for professionals who work with animals, including veterinarians, farmers, and animal control officers. This knowledge can contribute to better treatment practices and early identification of potential issues.
- Technology and Reporting Platforms: Leverage technology to create accessible platforms for reporting suspected animal cruelty cases. Mobile apps and online reporting systems can facilitate prompt responses from law enforcement and animal welfare organizations.
- Community Engagement: Encourage community involvement in animal welfare initiatives. Neighborhood watch programs, volunteer opportunities at shelters, and community events can foster a sense of shared responsibility for the well-being of animals.
Legal Frameworks for Wildlife Conservation
Wildlife laws vary across countries and regions, reflecting the unique ecosystems, species, and conservation challenges they face. Here are common components found in wildlife laws:
- Species Protection: Wildlife laws categorize species based on their conservation status, designating them as endangered, threatened, or of particular concern. Authorities apply different protection measures to each category. This classification helps prioritize conservation efforts for species at higher risk of extinction.
- Habitat Protection: Laws identify and protect critical habitats and ecosystems essential for the survival of wildlife. Designated areas like national parks and wildlife reserves aim to preserve biodiversity and maintain natural balance within ecosystems.
- Hunting and Harvesting Regulations: Regulations within wildlife laws govern legal hunting, fishing, and harvesting activities. They establish quotas, seasons, and licensing requirements to prevent over-exploitation of wildlife populations, ensuring sustainable practices.
- Poaching and Trafficking Prohibitions: Wildlife laws explicitly prohibit poaching (illegal hunting) and trafficking (illegal trade) of wildlife. These laws establish severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment, to deter individuals engaged in these activities.
- Endangered Species Protections: Special provisions are in place within wildlife laws to protect endangered species. These measures often include strict bans on hunting or trading these species and developing recovery plans to boost their populations.
- International Trade Regulations: Wildlife laws incorporate regulations in line with international agreements such as CITES. These agreements control and monitor the international trade of endangered species, preventing their exploitation and ensuring cooperation among countries in conservation efforts.
- Wildlife Management Authorities: Wildlife laws establish dedicated authorities or agencies responsible for implementing and enforcing the regulations. These agencies have the power to investigate wildlife-related crimes, issue permits, and collaborate with law enforcement to combat illegal activities.
- Research and Monitoring: Wildlife laws encourage scientific research on wildlife populations, habitats, and ecosystems. These provisions support ongoing monitoring efforts, helping gather essential data for informed decision-making and developing effective conservation strategies.
Animal Welfare Organizations
Numerous organizations worldwide work tirelessly to advocate for animal rights, combat cruelty, and promote the welfare of animals. Here are some prominent organizations dedicated to the cause of animal rights:
- People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals (PETA): PETA is a globally recognized animal rights organization that stands as one of the largest of its kind. It focuses on ending animal cruelty in various industries, including factory farming, clothing, entertainment, and scientific experimentation. PETA employs a combination of advocacy, public awareness campaigns, and legal action.
- Humane Society International (HSI): HSI, the Humane Society of the United States’ global arm, works in several nations to combat animal exploitation, such as the fur trade, puppy mills, and wildlife exploitation. They also work on disaster relief efforts for animals and support local animal welfare organizations worldwide.
- World Animal Protection: World Animal Protection operates globally to advance animal welfare across farming, wildlife, and disaster contexts. The organization campaigns for stronger animal protection laws encourages sustainable practices and raises awareness about animal treatment.
- Animal Legal Defense Fund (ALDF): ALDF’s mission is to campaign for animal rights and protection through the legal system. They work to strengthen animal protection laws, file lawsuits on behalf of abused animals, and provide legal resources and education to individuals and organizations fighting for animal rights.
- Mercy For Animals: Mercy For Animals dedicates itself to preventing cruelty to farmed animals. The organization conducts undercover investigations to expose animal abuse in factory farms and promotes plant-based diets to reduce the demand for animal products.
- Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (RSPCA): The RSPCA is one of the oldest animal welfare organizations founded in the United Kingdom. It works to prevent cruelty to animals through advocacy, education, and enforcement of animal protection laws. The RSPCA also operates shelters and provides veterinary care for animals in need.
- Sea Shepherd Conservation Society: Sea Shepherd focuses on marine conservation and protecting ocean wildlife. Known for its direct-action campaigns, Sea Shepherd’s efforts include combating illegal fishing, marine habitat destruction, and the exploitation of marine animals.
- Born Free Foundation: Born Free is an international wildlife charity that campaigns against animal exploitation and advocates for conserving wild animals in their natural habitats. The organization works to end captivity, rescue animals from poor conditions, and promote coexistence with wildlife.
- IFAW (International Fund for Animal Welfare): IFAW operates globally to rescue and protect needy animals. Their work includes combating wildlife trafficking, supporting animal rescue and rehabilitation efforts, and advocating for policies that enhance animal welfare.
- Animal Equality: Animal Equality is an international organization focused on ending cruelty to animals raised for food. They conduct undercover investigations, advocate for legislative changes, and work to promote a more compassionate and sustainable food system.
Success Stories and Positive Initiatives
Here are a few success stories and positive initiatives:
1. Wildlife Protection in Nepal:
- Success: Nepal has conserved its rhinoceros population, particularly in Chitwan National Park, by adopting a zero-tolerance approach to poaching.
- Initiatives: Rigorous anti-poaching patrols, community-based conservation programs, and strict law enforcement measures have contributed to the recovery of rhino populations.
2. China’s Ivory Ban:
- Success: China’s decision to ban its domestic ivory trade in 2017 marked a significant milestone in the fight against wildlife trafficking.
- Initiatives: The ban was part of a broader effort to combat illegal wildlife trade, acknowledging the role of demand reduction in curbing the killing of elephants for their ivory.
3. Tech-Based Conservation in Africa:
- Success: Conservationists are leveraging technology like drones and data analytics to monitor and protect endangered species in Africa.
- Initiatives: Drones are used for aerial surveillance, helping authorities track and apprehend poachers, while data analytics assist in identifying patterns and predicting potential poaching hotspots.
4. Community-Based Conservation in Costa Rica:
- Success: Costa Rica has succeeded in conserving its rich biodiversity by engaging local communities in conservation efforts.
- Initiatives: Community-based ecotourism projects, sustainable livelihood programs, and educational initiatives have empowered local communities to become stewards of their natural resources, discouraging illegal activities.
5. Global Collaborative Efforts:
- Success: International collaborations have played a crucial role in addressing the illegal wildlife trade, with various countries coming together to share information and resources.
- Initiatives: INTERPOL’s Environmental Security Program and CITES combat wildlife trafficking globally through international cooperation.
6. Conservation through Education:
- Success: Educational programs focused on raising awareness about wildlife conservation and the consequences of illegal wildlife trade have yielded positive results.
- Initiatives: NGOs and governmental agencies implement educational initiatives to inform communities and the public about protecting wildlife, fostering a sense of responsibility and empathy.
7. Corporate Initiatives:
- Success: Some companies have taken a stand against the illegal wildlife trade by implementing ethical sourcing policies and supporting conservation efforts.
- Initiatives: Corporate initiatives include partnering with conservation organizations, implementing sustainable supply chains, and raising consumer awareness of the impact of wildlife.
Conclusion
Cruelty towards animals remains a pervasive global issue, demanding urgent attention and concerted action. As we navigate the diverse factors contributing to such cruelty, it is imperative to emphasize education, legislation, and collective responsibility. By fostering a global culture of compassion, enforcing stricter laws, and promoting ethical treatment, we can aspire to create a world where animals are protected from harm, ensuring the well-being of both our fellow inhabitants and the delicate balance of our shared ecosystems.
Quick Tips for Responsible Human Behavior
- Stay informed about animal welfare issues.
- Treat all animals with respect and empathy.
- If you witness animal cruelty, report it to local authorities.
- Explore plant-based diets or vegan alternatives.
- Dedicate time to volunteer at local shelters or rescue organizations.
- Contribute to reputable animal welfare charities.
- Choose animal-friendly tourism options.
- Join or organize community cleanups to protect wildlife.
- Support and participate in spaying/neutering programs for stray animals.
- Advocate for more vital legislation and enforcement.
- Exercise caution in urban areas to avoid harming wildlife.
- Minimize plastic usage and dispose of it responsibly.
- Attend workshops, seminars, or fundraisers.
- Share information and resources with friends and family.