Updated July 15, 2023
Introduction to Estate Tax
Estate tax refers to the tax applicable to the transfer of assets after the death of the person to his legal heirs. There are specific categories of Assets over which Estate Tax is applicable, and only this tax is applied beyond a threshold limit. Also, certain tax deductions are applicable while determining the liability.
The US Tax Administration IRS Form 706 provides details of the exact calculation of assets and computation of tax liability. Apart from certain exemptions over this tax levy, this tax rate and its applicability vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction. Despite its applicability to a limited number of people due to a higher threshold, the estate tax is an essential direct tax and a revenue source for the government.
Explanation
Estate Tax is a tax applicable to the legal heirs of the deceased who inherit the deceased’s assets. This tax is applicable only if the amount of Estate inherited is beyond the threshold limit. Various eligible deductions are made available to reduce the Taxable asset for computing ET.
Let’s understand the same with the help of a simple example:
Mr. Alex, a US citizen with taxable assets following guidelines laid down in ET amounting to 20 million dollars, died in March 2020. Accordingly, the rules for 2020 will apply. Form 706, United States Estate Tax return, must be filed as gross estate plus any adjusted taxable gifts he has given during his lifetime valued at more than $11.58 million in 2020. The legal heir of Mr. Alex will have to file Form 706, and the tax applicable is to be paid within nine months from his death, i.e., Dec 2020.
Important Points About Estate Tax
- Estate Tax is not applicable in cases where the deceased’s surviving spouse has inherited assets.
- It is not uniform across different countries. Further, many countries do not levy this tax at all, which results in many wealthy individuals changing their residency status to take advantage of such an anomaly. This results in the migration of wealthy individuals.
Example of Estate Tax (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Xavier is a US citizen who died in January 2020 and holds net assets for ET amounting to 25 million US dollars. His family has furnished the following details for the computation of gross estate tax. Based on the applicable tax rate for 2020, let’s compute the Estate Tax.
|
Particulars |
Amt in USD |
| Gross Estate | 25000000 |
| Permission State and Federal deductions | 1100000 ( Federal) and 1200000 (State) |
| Adjusted Taxable gifts | 2700000 |
| Total gift tax already paid | 540000 |
Computation of Estate Tax liability is as follows:
|
Particulars |
Amt in USD |
| Total Gross Estate net of exclusion | 25000000 |
| Allowable deductions | 1100000 |
| Taxable Assets-Tentative | 23900000 |
| State Death Tax Deduction | 1200000 |
| Taxable Asset after State Death Tax Deduction | 22700000 |
| Adjusted Taxable gifts | 2700000 |
| Net Taxable Assets | 25400000 |
| Tentative Tax^ | 10105800 |
| Total gift tax already paid | 540000 |
| Gross Estate Tax | 9565800 |
As per the Tax slab for 2020, the tax liability of $345800 is applicable for taxable assets up to $1000000, and beyond that, the excess is taxable at a flat rate of 40%.
Estate Tax Rate
- The ET state Tax rate ranges from 18%-40% in the united states of America, and it is the same whether one is a citizen, domiciliary, or not of the united states of America.
- The tax rate of 18%-40% is a progressive tax rate that increases as taxable income increases, with the highest tax rate of 40% applicable in the case of taxable income over 1 million dollars.
- As of 2020, ET exemption, as determined by the internal revenue service, is 11.58 million dollars for individuals. In short, ET is not applicable if the eligible assets of the deceased are below this amount. The value of the assets is based on the fair market value
- The estate tax exemption limit is indexed annually for inflation and increases year on year based on incremental changes in inflation.
An important point to note is that in the USA, apart from federal tax, the ET is applicable at the state level, with the threshold minimum taxable assets varying from 1 million dollars in some states to as much as 6 million dollars in some states and even more.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Let’s look at a few prominent benefits and drawbacks.
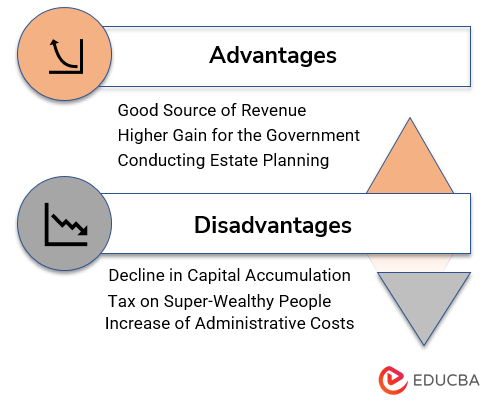
Advantages
- It is a good source of revenue for the government and enables the government to tax rich people, thereby reducing the economic disparity between the poor and the rich.
- It results in a higher gain for the government as tax is applied on fair market value and not on the cost of acquisition of eligible assets on which ET is eligible.
- Individuals can safeguard their tax liability by conducting estate planning in accordance with the relevant regulations.
Disadvantages
- An important disadvantage is that it leads to a decline in capital accumulation and unnecessary consumption as wealthier individuals subject to this estate tax prefer consumption over investment.
- It is criticized across different jurisdictions for being anti-superrich as it is a tax on super-wealthy people to bring economic disparity.
- It increases the overhead and administrative costs of the government and provides little benefit vis-à-vis cost.
- Due to this tax, many super-wealthy individuals create shell companies as well as trusts to avoid tax liability
Conclusion
Estate tax or death tax, or inheritance tax, is a tax on the super-wealthy. It is intended to bridge the income inequality between the poor and the rich and bring tax revenues for the government. Known by different names in different jurisdictions, the ultimate objective is the same to levy tax beyond a threshold limit. The ET rate varies from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, with many countries, like India, not having this tax.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Estate Tax. Here we discuss the definition, important points about estate tax, and its advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –