Introduction to Ethical Hacking Software
Ethical hacking software helps attain authorized unauthorized access to data in a system or computer. The person who carries out online hacking is a Hacker. There are three different types of ethical hacking software, which are as follows:
- White hat
- Grey hat
- Black hat
White hat hackers are people who break security for non-malicious reasons. It may be to test their own security system. These people find possible loopholes in ethical hacking software or systems report them to get them fixed. They are also referred to as “ethical hackers”. E.g., A Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) hired by a corporate firm to find flaws in the ethical hacking software. And those certified ethical hackers have CEH Certification or Ethical Hacking Certification, which one attains by clearing the CEH exam.
Black hat hackers are people who break the security of the system or ethical hacking software for malicious reasons or personal benefits. These people generally form illegal hacking groups and work to break into any secure networks in order to destroy, modify or even steal confidential data, such as credit card details, banking details, etc. They are also referred to as “crackers”.
Grey hat hackers come between white hat and black hat hackers. These people survey the system, find loopholes or any security defects, and report it to the administrator. At times the grey hat hacker reports these security flaws to the world instead of a group of people. At certain times they may offer to correct the defect for a fee. These people perform hacking without any personal gain.
So there are various ethical hacking program training or CEH training to teach these types of ethical hacking.
Let’s check more about ethical hacking software.
What is Ethical Hacking Software?
Let us see what hacking software is in detail:
A. Cyber Ethics
Cyberethics is a code of behavior for using the Internet. We have seen what hackers and their types are. Now, we will look into other terminologies related to cyber ethics.
- Phreaker: A term coined to describe a subculture’s activity that studies, experiments with, or explores telephone connection networks. Phreaking is closely related to ethical hacking basics of the computer since telephone networks have been computerized. It is sometimes called H/P culture, where H stands for Hacking and P stands for Phreaking.
- Script Kiddies: People who use scripts or ethical hacking basics developed by others to attack computer systems and networks. It is also referred to as script bunny, skiddie, or script running juvenile (SRJ).
- Hacktivists: The term Hacktivists is the combination of two words Hacker and Activists. These people carry out ethical hacking activities, such as defacing websites for political reasons. Their activities include political ideas and issues.
B. Information Gathering
Information gathering is the initial process as far as ethical hacking basics, and investigation are concerned. This involves processes such as profiling any organization, system, server, or individual using a certain defined process. This is generally used by the attacker and/or investigation agency to get additional information about the victim.
There are different ways through which ethical hacking information can be gathered. Some of them are as follows:
1. Use of Search Engine
The general understanding is that the search engine will provide certain information about the victim. The ethical hacking basics principle about using the Internet is that ‘one leaves footprints/information everywhere while surfing the Internet.’
The attacker, as well as hackers, use this principle. The attacker will gather information about the system, any loopholes in the existing system, and possible ways to exploit it. The investigator will gather information such as the approach used by the attacker to get access to the system. The most powerful search engine is Google, Yahoo Search, MSN Live Search, AOL Search, and Ask search.
2. Use of relational search engine
The relational search engine is different from the normal search engine. It gets results from different search engines and makes the relation between those results.
i. Whois Lookup: WHOIS which is pronounced as “who is”, is a query protocol that is widely used for querying the official database in order to determine details such as the owner of a domain name, IP address, etc.
ii. Maltego: It is an open-source intelligence and forensics application that allows the mining and gathering of information as well as the representation of this information in a meaningful way. The graphing libraries allow you to identify key relationships between information.
iii. Reverse IP Mapping: This method is used to find a number of websites hosted on the same server where your software/function is hosted
iv. TraceRoute: It gives useful information, such as the number of servers between your and remote computers. This is useful for investigation as well as different types of attacks. You can see the route between your system and the attacker system using NeoTrace, which gives MAP view or NodeView of all nodes between attacker and victim.
v. Email Spider: These automated ethical hacking programs capture email ids using spiders and store them in the database. Spammers (people who send junk emails to a large number of people) are using email spiders to collect a thousand emails for spamming purposes.
C. Scanning
Scanning is discovering any open or closed ports, and any loopholes in the remote system, servers, and networks. It helps in getting details of the victim, such as IP addresses,
Operating System used as well as services running on the remote computer.
There are three different types of scanning. These are Port scanning, Network scanning, and Vulnerability Scanning.
Port scanning is most commonly used in the ethical hacking program by attackers to find loopholes. All systems connected to a LAN (Local Area Network) or an Internet using a modem run many ethical hacking services that listen at well-known and not well-known ports. There are a total of 1 to 65535 ports available on the computer. The port scanning allows the attacker to find which ports are available.
Open scan (TCP scan) is normally used to program sockets. This is quite an old ethical hacking technique and works more correctly to connect with the server fully. In order to establish the connection, it makes an authentication using three packets. This mechanism of authentication is called a three-way handshake.
For open port :
Client –> SYN –>
<– SYN/ACK <– Server
Client –> ACK –>
For close port :
Client –> SYN –>
<– RST <– Server
The advantage of this open scan is that it is easy to program. However, the limitation is that detecting and making logs on each connection is very easy.
TCP connect() :
- The connect() system call provided by an ethical hacking operating system is used to open a connection to every interesting port on the machine.
- If the port is listening, connect() will succeed; otherwise, the port isn’t reachable.
SYN scan :
- This scanning technique is called half-open scanning because a TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) connection is not completed.
- An SYN packet is sent to remote computing.
- The target host responds with an SYN+ACK packet which indicates the port is listening, and an RST indicates a non-listener
NULL scan :
- NULL scan used no flags of TCP header, and it sent to the target host
- Closed ports reply to packets with RST
- Open ports ignore packets
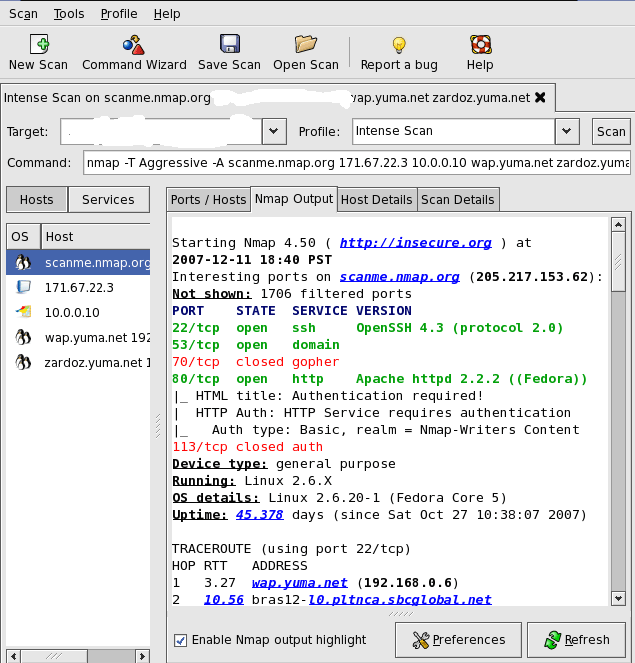
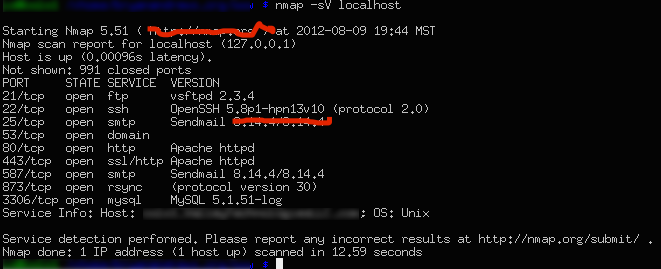
NMAP (a port scanner):
- NMAP is a powerful utility for scanning a large number of ethical hacking tools
- Available with GUI (Graphical User Interface) and Command Line Interface
- Supported by a wide range of Operating Systems such as Linux, Mac OS, Windows
- Can carry out SYN scans, FIN scans, Stealth scans, Half-open scans, and many other types.
D. Virus, Worms, Trojans, and Virus Analysis
VIRUS (particularly stands for Vital Information Resource Under Siege) is an application or piece of code that replicates itself by injecting its code into other data files or an ethical hacking program and has a detrimental effect, such as corrupting the system or destroying data.
Worms are a standalone malware computer program that replicates themselves over ethical hacking basics. Compared to the virus, it does not need to attach itself to an existing program.
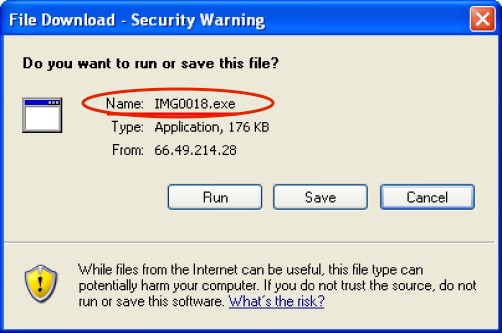
A Trojan (in the context of computing) is any malicious computer program representing itself as useful to persuade a victim to install it on his/her system.
There are several different modes of transmission for these viruses, worms, or trojans into your system. Some of them are listed below:
- IRC (Internet Relay Chat)
- ICQ (I Seek You – Instant Messaging Program)
- Email attachments
- Physical access (such as connecting an infected USD drive or hard disk)
- Infected Browsers
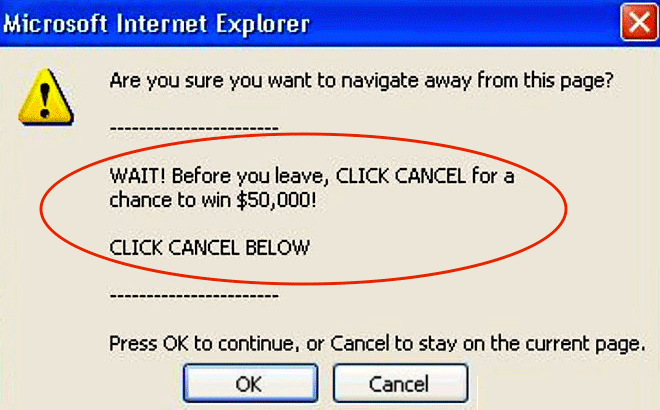
- Online advertisements (such as banners that claim you won the lottery)
- NetBIOS
Properties of Virus
Following are some of its properties:
- Your computer or system can get infected even if files are only copied.
- It can be polymorphic.
- Can be a memory or non-memory resident.
- It can be a stealth virus.
- Most times, viruses carry another virus.
- It can even make your system never show outward signs.
- It can even stay on your system even though it is formatted.
Virus operation phase
Most virus operates in two phases, i.e., infection phase and attack phase.
- Infection phase
- In this phase, the virus determines when and which programs to infect.
- Some viruses infect the system as soon as a virus file is installed on the system.
- Some viruses infect the system at a specific date, time, or the particular event.
- TSR viruses are loaded into memory and later infect the systems.
- Attack phase
- In this phase, the virus will delete files, replicate itself to other systems, and corrupt targets only.
Symptoms of virus-infected system
The symptoms of a virus-infected system are as follows.
- Files/Folder have a strange name than the normal (e.g. %$#%% as the file name).
- File extensions can change as well.
- The program takes longest time to load than normal.
- Systems hard drives constantly run out of free space.
- You will not be able to open some programs.
- Programs get corrupt without any reasons.
- The system works very slowly and sometimes reboots unexpectedly.
Types of Virus
– Macro virus: spreads and infects database file
– File virus: infects executable
– Source code virus: effects and damage source code
– Network virus: spreads via network elements and protocols
– Boot virus: infects boot sectors and records
– Shell virus: forms a shell around the target host’s genuine program and host it as the subroutine
– Terminate virus: remains permanently in the memory during the work session
Methods to avoid detection of the virus in Ethical Hacking Software
Below we have listed some useful methods to avoid virus detection.
-
Keep the same “last modified” date.
i. To avoid detection by anti-virus software and users, some viruses use different kinds of deception, such as they have the same last modified date as other genuine files or folders.
ii. Some viruses (especially on the MS-DOS system) ensure that a host file’s “last modified” date stays the same when the virus infects the file.
-
Avoiding Bait files
i. Bait files (or goat files) are specially created by anti-virus software or by anti-virus professionals to be infected by the virus.
ii. Many anti-virus programs perform an integrity check of their codes using Bait files.
iii. Infecting such programs will increase the chances of the virus detection.
-
Killing activity of anti-virus software
There are some viruses that avoid detection by anti-virus software by killing the task associated with anti-virus software.
-
Making stealth virus
i. There is some strong virus that tricks anti-virus software by intercepting its requests.
ii. The virus can then return an uninfected version of the file to anti-virus software so that it assumes that the file is “clean”.
Virus analysis
Here we have discussed two major virus analyses in detail.
-
IDA pro tools
– IDA pro ethical hacking tools are dissembler and debugger tool
– It can run on multiple operating systems such as Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, etc.
– It can have uses in source code analysis, vulnerability research as well as reverse engineering
-
Autorun virus remover
- Autorun is the built-in feature of Windows OS that allows the application to run automatically from USB/CD drives as soon as they connect to the system.
- Viruses often exploit this feature to spread from one system to another.
- Autorun virus remover helps remove the virus that comes with external storage, such as USB/CD drives.
Related Articles
This has been a guide to Ethical Hacking Software. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more: