Updated March 21, 2023
Difference Between ETL vs ELT
The following article provides an outline for ETL vs ELT. ETL stands for Extract, Transform & Load, and ELT stands for Extract, Load & Transform, and so in ETL, Transforming the data into a common format is done before loading. However, in ELT, loading the data to the destination is performed first, and then the transformation is applied based on the destination format. ETL is time-consuming compared to ELT, as the ETL is implemented in the staging area, and ELT doesn’t have the need for a designated staging process.
What is ETL?
The ETL process involves extracting the data from classified data sources and then transforming and tethering the data in a suitable manner; lastly, the data has been loaded into data warehouse systems. This Technique is sensible until many dissimilar databases are implicated in the data warehouse landscape. Here moving data from one place to another has to happen in any way, so ETL acts as the best practice in these situations to do transformations since the transfer of data is anyhow happening instance here.
What is ELT?
It is a slightly different process; the same technique of extract is used here, next the data is loaded into the target systems directly. At the preceding end, the objective systems are accountable for applying the transformations at the loaded data. The major disadvantage here is it usually takes a larger time to get the data at the data warehouse, and hence with the staging tables, an extra step is added in the process, which makes in need for more disk space to be available.
Head to Head Comparison Between ETL vs ELT (Infographics)
Below are the top 7 differences between ETL vs ELT:
Key Differences Between ETL vs ELT
There are major key differences between ETL vs ELT are given below:
- ETL is an older concept and has been there in the market for more than two decades; ELT is relatively new and comparatively complex to implement.
- In an ETL case, a large number of tools have only one of its kind hardware requirements that are posh. In the case of an ELT, Since this falls under Saas, hardware cost is not a concern.
- ETL operates row by row pattern to map a fact-value with its dimension key element from a different table to carry out a lookup. Thus, in ELT, we can directly map fact-value with dimension key elements.
- In ETL, Relational data is prioritized here, whereas ELT Readily supports unstructured data.
Comparison Table Between ETL vs ELT
Let’s discuss the top 7 differences between ETL vs ELT
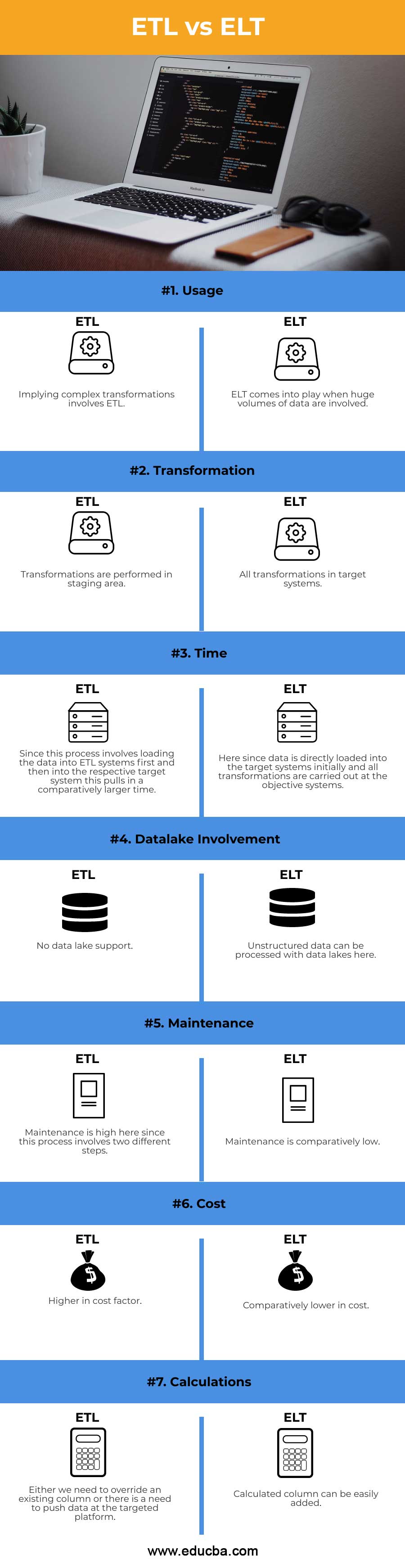
| Basis of Comparison | ETL | ELT |
| Usage | Implying complex transformations involves ETL. | ELT comes into play when huge volumes of data are involved. |
| Transformation | Transformations are performed in the staging area. | All transformations in target systems. |
| Time | Since this process involves loading the data into ETL systems first and then into the respective target system, this pulls in a comparatively larger time. | Since data is directly loaded into the target systems initially, all transformations are carried out at the objective systems. |
| Datalake Involvement | No data lake support. | Unstructured data can be processed with data lakes here. |
| Maintenance | Maintenance is high here since this process involves two different steps. | Maintenance is comparatively low. |
| Cost | Higher in the cost factor. | Comparatively lower in cost. |
| Calculations | Either we need to override an existing column, or there is a need to push data at the targeted platform. | The calculated column can be easily added. |
Conclusion
Every company that complied with the data warehouse will be using ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) or ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) to push data into the data warehouse, which is emerging from different sources. Based on the industry and technical wants, one of the above procedures is widely deployed.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to ETL vs ELT. Here we have discussed the ETL vs ELT key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –