Updated December 21, 2023
Expansionary Monetary Policy Definition
Expansionary monetary policy is a macroeconomic policy, like reducing the interest rate to increase the money supply and boost economic activity during economic downturns or recessions.
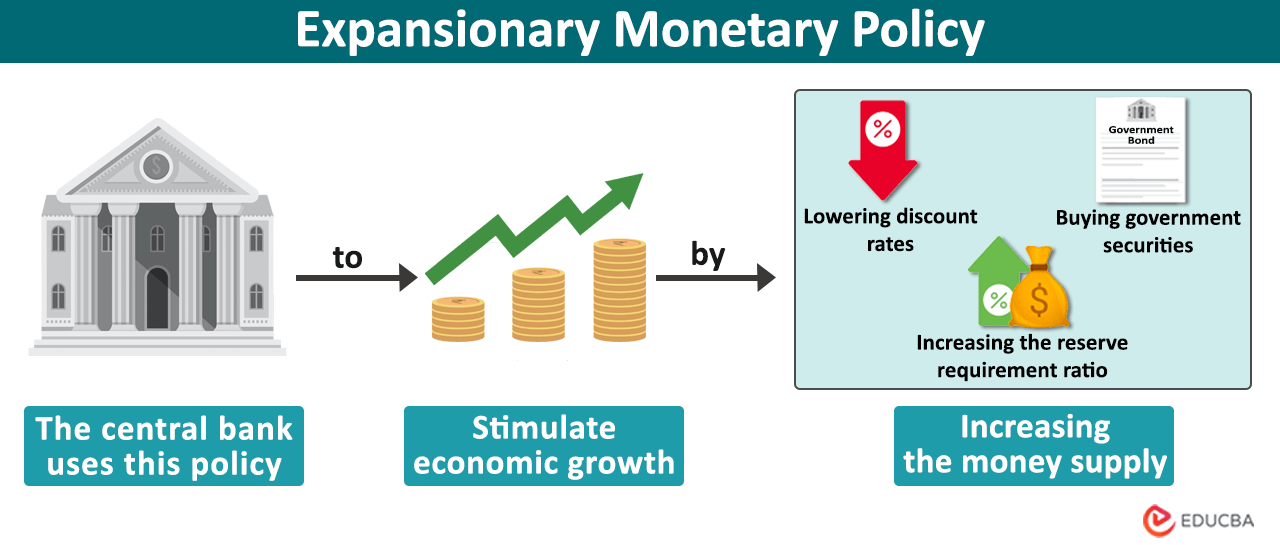
Table of Contents
How Does it Work?
The central bank of a country manages the economy and ensures financial stability. It considers inflation, employment, and economic growth to make decisions.
If the economy is not doing well, the central bank boosts activity and creates jobs while keeping prices stable. The central bank encourages borrowing, spending, and investment to help achieve these goals. They might lower interest rates, buy government bonds, or increase bank reserves to stimulate spending and investment.
However, if these measures are not controlled properly, it can lead to negative effects like budget deficits and inflation. The central bank carefully monitors the economy and adjusts policies to prevent these negative effects.
Tools
Let’s see the following tools or measures the central bank implements to boost the economy.
1. Lowering the discount rate (bank rate)
One of the primary tools the central bank uses is lowering the discount rate. It sets this rate. Commercial banks can borrow money from the central bank at this rate for their operations and to lend more money.
Also, banks can then lower their interest rate, encouraging people and businesses to take loans from banks to buy homes, start new projects, etc.
2. Open market operations
This involves the central bank buying government bonds or government-issued securities on the open market. When the central bank buys these bonds or securities, it adds money into the banking system, encouraging banks to lend more. Thereby, it increases the money supply and boosts economic growth.
3. Increasing the reserve requirement ratio
The central bank makes it mandatory for commercial banks to maintain a minimum amount of reserves within their vaults. Commercial banks cannot use this money for lending loans or for investment. However, to increase the money supply, the central bank can lower the reserve requirement so that banks can have more money to lend to their customers.
4. Forward guidance
Forward guidance involves the central bank publicly discussing changes regarding interest rates and other policies in the future. By giving clear guidelines about their plans, they shape how people borrow, spend, and invest even before making any changes. For instance, lowering interest rates in the future could allow people to borrow and spend more at present, expecting better returns on their investments in the future.
Examples
The following table shows a list of countries and the measures they took.
| Country | Year | Measures |
| United States | 2020-2022 | The Federal Reserve reduced the federal funds rate and introduced quantitative easing. |
| India | 2020-2022 | The Reserve Bank of India implemented repo rate cuts. |
| United Kingdom | 2020-2022 | The Bank of England reduced the Bank Rate. |
| European Union | 2020-2022 | The European Central Bank lowered its main refinancing rate. |
| Japan | 2020-2022 | The Bank of Japan maintained a low policy interest rate. |
Benefits
The following are the expansionary monetary policy benefits.
1. Stimulates economic growth
Measures such as encouraging borrowing and investment boost economic activity. It makes it cheaper for businesses and individuals to spend more, which increases the money supply in the economy.
2. Reduce unemployment
Lower interest rates make businesses invest in new projects and technologies and expand their business in new regions. This investment often leads to job creation by hiring more workers and reducing unemployment rates.
3. Controls deflation
An increase in money supply reduces the value of the country’s currency compared to other currencies in the foreign exchange market. This boosts the export industry because a weaker currency makes the products produced in that country cheaper for foreign buyers. This potentially boosts demand for those products and increases export revenues.
Risks
The following are the risks associated with implementing expansionary monetary policy.
1. Inflation
When the spending capacity increases, people buy more products and services, increasing the demand for those products and services. Increasing demand will cause the price to increase. The continual rise in prices leads to inflation and disrupts economic stability.
2. Asset bubbles
With low interest rates, individuals and businesses borrow more money to purchase assets like houses, properties, or stocks. The increased demand for these assets will increase asset prices, and people will still buy as a future investment. If the market changes and there is a sudden drop in prices, it can cause investment losses and financial instability.
3. Excessive debt burden
The lower rate will encourage corporations and individuals to borrow more and more money, resulting in high debt levels. If economic conditions change, like high interest rates or recession, the ability to repay the debt amount will decrease. It can lead to financial stress for borrowers and lenders or even bankruptcy.
Expansionary Vs. Contractionary Monetary Policy
The following is the difference between expansionary and contractionary monetary policy.
| Particulars | Expansionary Monetary Policy | Contractionary Monetary Policy |
| Purposes | To increase economic growth by lowering interest rates and increasing the money supply. | To slow down economic growth by increasing interest rates and decreasing money supply. |
| Impact on Employment | Can reduce unemployment. | May lead to higher unemployment. |
| Impact on Inflation | It may increase inflationary pressure. | It may reduce inflationary pressure. |
| Government Securities | It involves buying government securities on the open market. | It involves selling government securities on the open market. |
Final Thoughts
The central bank uses expansionary monetary policy tools like discount rate cuts, open market operations, and adjustments to reserve requirements to boost economic growth. However, global financial conditions can influence its impact, and central banks must carefully observe all factors and adapt flexible policies to ensure effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How long does expansionary monetary policy take to work?
Answer: The timeline for the policy to impact the economy varies. Some effects can be immediate or happen within months, like increasing borrowing and spending with changes in interest rates. However, the full impact on economic growth might take longer. Businesses might take time to plan and execute new projects or investments, and the results of these investments may take time to show profit.
Q2. What are the scenarios that indicate an expansionary monetary policy is needed?
Answer: When a country’s economy is weak due to scenarios like low inflation, slow growth, or natural disasters, the central bank can use this policy to increase the liquidity (amount of money) in the economy.
Recommended Articles
For further guidance on policy-related topics refer to our below-recommended articles:

