Updated April 7, 2023

Difference between F# vs Haskell
F# vs Haskell is a comparison between F# and Haskell. F# is a multi-paradigm language, imperative by nature and is object oriented. Haskell is a pure functional language. All the functional languages are not defined in terms of operations on the global state. They provide a high degree of F#, makes it easy to code in the functional style, lets the user copy objects instead of changing their form. Haskell is a lazy functional language which gives no side effects; it has tuples, pattern matching and algebraic data. Functional languages provide a high degree of expressiveness and abstractions, which enables parallel programming. Likewise, we shall look into the key differences and list out similarities and differences of F# vs Haskell.
Head to Head Comparison Between F# vs Haskell (Infographics)
Below are the top differences between F# vs Haskell
Key Differences F# vs Haskell
- Haskell is pure Functional, whereas F# is both imperative and object oriented.
- Even though h Haskell is one of the amazing Programming languages, F# has a major benefit e. it acts on top of CLR.
- Haskell has its own runtime environment, whereas F# uses .NET
- Haskell has type classes which let the user do similar to Object-Oriented programming, whereas F# is automatically implemented in Object-Oriented Programming
- Haskell is lazy, whereas F# is not. This laziness enables some tricks which looks actually slow but executes fast.
- Syntactically, Haskell’s syntax looks much better comparatively
- F# has excellent integration with Visual Studio, whereas Haskell too has integration with an older version of Visual Studio
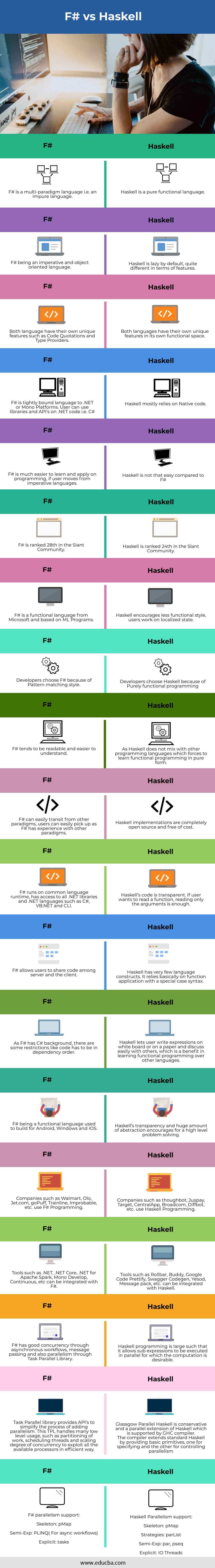
Comparison Table: F# vs Haskell
| F# | Haskell |
| F# is a multi-paradigm language, i.e. an impure language | Haskell is a pure functional language |
| F# being an imperative and object oriented language | Haskell is lazy by default, quite different in terms of features. |
| Both languages have their own unique features, such as Code Quotations and Type Providers. | Both languages have their own unique features in their own functional space. |
| F# is a tightly bound language to .NET or Mono Platforms. User can use libraries and API’s on .NET code, i.e. C# | Haskell mostly relies on Native code. |
| F# is much easier to learn and apply to programming if the user moves from imperative languages. | Haskell is not that easy compared to F# |
| F# is ranked 28th in the Slant Community | Haskell is ranked 24th in the Slant Community |
| F# is a functional language from Microsoft and based on ML Programs | Haskell encourages a less functional style; users work in a localized state. |
| Developers choose F# because of the Pattern matching style. | Developers choose Haskell because of Purely functional programming |
| F# tends to be readable and easier to understand | As Haskell does not mix with other programming languages, which forces to learn functional programming in pure form |
| F# can easily transit from other paradigms; users can easily pick up as F# has experience with other paradigms. | Haskell implementations are completely open-source and free of cost. |
| F# runs on common language runtime, has access to all .NET libraries and .NET languages such as C#, VB.NET and CLI. | Haskell’s code is transparent. If the user wants to read a function, reading only the arguments is enough. |
| F# allows users to share code among server and the client | Haskell has very few language constructs. It relies basically on function application with a special case syntax |
| As F# has C# background, there are some restrictions like code has to be in dependency order | Haskell lets the user write expressions on white board or on a paper and discuss easily with others, which is a benefit in learning functional programming over other languages |
| F# being a functional language used to build for Android, Windows and iOS. | Haskell’s transparency and a huge amount of abstraction encourage for high-level problem-solving. |
| Companies such as Walmart, Olo, Jet.com, goPuff, Trainline, Improbable, etc., use F# Programming. | Companies such as thoughbot, Juspay, Target, CentralApp, Broadcom, Diffbot, etc., use Haskell Programming. |
| Tools such as .NET, .NET Core, .NET for Apache Spark, Mono Develop, Continuous, etc. can be integrated with F# | Tools such as Rollbar, Buddy, Google Code Prettify, Swagger Codegen, Yesod, Message pack, etc., can be integrated with Haskell. |
| F# has good concurrency through asynchronous workflows, message passing and also parallelism through Task Parallel Library. | Haskell programming is large such that it allows sub-expressions to be executed in parallel for which the computation is desirable. |
| Task Parallel Library provides API’s to simplify the process of adding parallelism. This TPL handles many low-level usages, such as partitioning of work, scheduling threads and scaling degree of concurrency to exploit all the available processors in an efficient way. | Glassgow Parallel Haskell is conservative and a parallel extension of Haskell, which is supported by the GHC compiler.
The compiler extends standard Haskell by providing basic primitives, one for specifying and the other for controlling parallelism. |
| F# parallelism support:
Skeleton: pMap Semi-Exp: PLINQ( For async workflows) Explicit: tasks |
Haskell Parallelism support:
Skeleton: pMap Strategies: parList Semi-Exp: par, pseq Explicit: IO Threads |
Conclusion
With this, we conclude our topic ‘F# vs Haskell’. We have seen F# vs Haskell’s means and have seen their similarities and differences in a comparison table above. Some of the key differences or features are also listed to get an overview of F# and Haskell. In the Developer’s opinion, Haskell is much more advantageous and disadvantageous both, but the most commonly used programming among both is Haskell. There are less disadvantages to F# comparatively. Thanks! Happy Learning!!
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to F# vs Haskell. Here we discuss the F# vs Haskell key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –