What is Financial Accounting?
Financial accounting is the process of classifying, summarizing, analyzing, and reporting an organization’s financial transactions for a specific period.
For instance, every month, Mr. X purchases goods from company ABC. In this case, the company will record all invoices and receipts concerning Mr. X to analyze sales gained from Mr. X.
Companies can consistently apply these standard rules and procedures in order to achieve reliable results. Most importantly, it is used to create financial statements, like income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. It takes a company’s raw data, like sales, revenue, etc., and performs critical computations to form valuable reports.
Key Highlights
- Financial accounting measures a company’s performance by summarizing its various financial transactions for a period. It is generally the process of recognizing and measuring business transactions through financial statements.
- The three primary financial statements are the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows. Additionally, the two types of financial accounting are accrual and cost accounting.
- A company uses it as an internal tool to analyze its performance and ability to meet future commitments. It also serves as a tool for communicating with external parties like stockholders, banks, suppliers, and regulators.
- While preparing financial statements, organizations must adhere to accounting principles like objectivity, revenue recognition, and cost principle. Utilizing the best accounting software for small businesses can help ensure these principles are followed efficiently, while also simplifying the process of financial statement preparation.
How does Financial Accounting Work?
The process of financial accounting begins with the recording of transactions in the company’s accounting system. Transactions can include sales, purchases, payments, receipts, and other financial events. These transactions are recorded using the double-entry accounting system, which ensures that every transaction has an equal debit and credit entry.
Let’s say ABC Inc. sells a product to a customer for $1,000. The sale generates revenue for ABC Inc. To record this transaction in the company’s accounting system, the following entries are made using the double-entry accounting system:
| Account | Debit | Credit |
| Accounts Receivable | $1,000 | |
| Sales Revenue | $1,000 |
In this example, the debit and credit entries are equal and opposite, as the double-entry accounting system requires. By recording this transaction, ABC Inc. has recorded an increase in its revenue and assets. This information can be used to prepare financial statements such as income and balance sheets.
Financial Accounting Principles
1. Cost Principle
- It clearly states that there should be an accurate record of all cost transactions
- It includes costs incurred to acquire goods, services, and even assets
- For instance, if an employer purchases services from employees and pays them wages. There should be a definitive salary transaction record, including the amount and the payee’s name.
2. Matching Principle
- According to this principle, companies must record income and expenses together
- It simplifies the understanding of how much a business has to spend to earn revenue
- For example, a company purchases products at the beginning of the year (January). The sales for the inventory come in till the end of March. The company has to record the purchase amount and sales together in March.
3. Revenue Recognition Principle
- It is a crucial principle as it presents a company’s current financial position
- It requires companies to file the sales amount as soon as they sell the product and not when they receive the cash
- Suppose company XYZ makes sales of $25,000 on credit. They will receive the cash amount in 90 days. However, they should document the sales amount now and not wait for the in-hand cash.
4. Objectivity Principle
- The presentation of financial documents that the company participates in without bias is an example of objectivity
- The data must be verifiable and must reflect a neutral view of the activities
- Suppose an employee incurs business expenses on the company’s account but has no receipt or bill to verify the claims. The firm cannot record transactions.
5. Consistency Principle
- This principle indicates that a business must carry uniformity in its methods through their accounting period
- An organization can change its accounting techniques only after completing the current year’s financials
- For example, a firm follows the cost method to record its transactions. Midyear, they realize its limitations and want to switch to an accrual method. However, they can do so only after finishing their current accounting year.
Types of Financial Accounting
1. Accrual Accounting Method
- This method records all sales and purchases as they happen, even if no money changes hands. For example, if a customer pays $500 on their credit card, the company will record $500 as income, even if it takes two weeks to process the transaction
- This method allows you to track the money customers owe to the business (accounts receivable) and the money the company owes to suppliers (accounts payable)
- It does a better job of matching income with expenses. However, it is difficult to apply, as to keep track of outstanding invoices, one must use additional accounts, which might increase costs and complexity
- While using this, expenses begin to accrue as soon as you receive the purchased product/service, regardless of the payment date
- It is ineffective at tracking cash as the income statement may show funds even if there’s no in-hand cash
- With high sales, using the accrual accounting method may result in a higher tax bill.
2. Cash Accounting Method
- Here, a sale does not count until you receive payment from your customer, and a purchase does not matter until you pay for the products or services. Simply put, transactions only count when cash changes hands
- This method makes it simple to track your cash flow and avoid cash shortages, benefiting people who have no accounting experience
- It is based on cash flow (sales to customers) and cash flow from operations (purchases made from suppliers)
- As sales do not record until you receive payment from your customers, it may result in a lower tax bill. However, even expenses don’t count until the final payment, so one can’t deduct expenses to save tax
- There is no income vs. expense match when using cash basis accounting. Therefore, this can be a problem if you buy products one month and sell them the next.
Financial Accounting Reporting
1. Income Statement
- The profit and loss account reports the flow of income and expenses in the company over the year. The result of an exercise can be either a profit or a loss
- When creating an accounting report, this statement helps reflect a company’s ability to generate wealth, which is the economic goal of every business
- The ratio of the balance sheet to the profit and loss account accurately represents the year’s outcome. In case of a profit, net worth increases; otherwise, the net worth decreases.
2. Cash Flow Statement
- The treasury report is another name for the cash flow statement report
- It reflects a fiscal year’s liquidity performance, both its generation & consumption
- Its interpretation can be critical in making decisions in situations of excess or scarcity of liquidity.
3. Balance Sheet
- It is unquestionably a fundamental accounting report that reflects a company’s patrimonial situation at any given time
- Provides information on accumulated wealth and its financing
- It has two parts: assets and liabilities. At the end of a financial year, a company ensures that the assets and liabilities should be equal on the balance sheet.
Examples
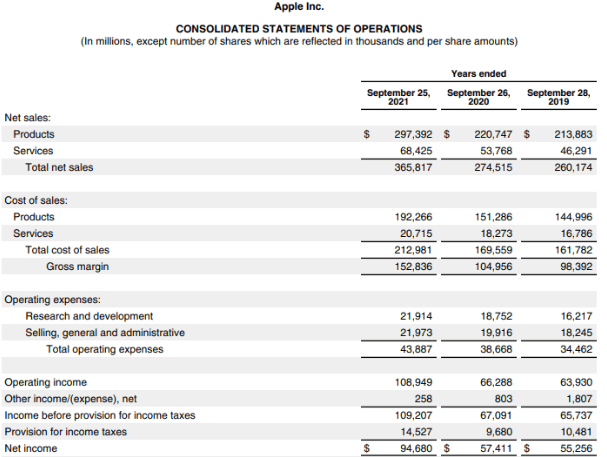
Here is an example of Apple Inc’s 2021 Consolidated Income Statement. In the image below, we can see that the Net income of Apple Inc. in 2021 was $94,680 million, whereas in 2019, it was $55,256 million.
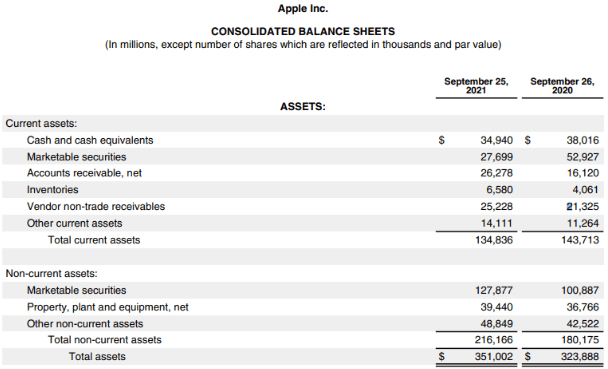
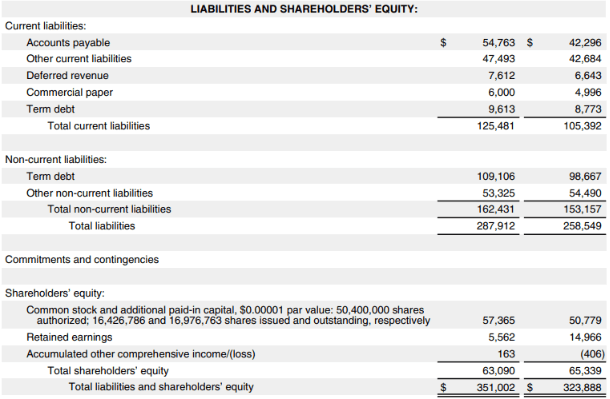
Apple’s Consolidated Balance Sheet:
- We can see that the total current assets fell from $143,713 million in 2020 to $134,836 million in 2021, while non-current assets increased by approximately $36,000 million
- The total current and non-current liabilities increased by approximately $20,000 and $30,000 million, respectively
- As for shareholders’ equity, it decreased from $65,339 million in 2020 to $63,090 million in 2021.
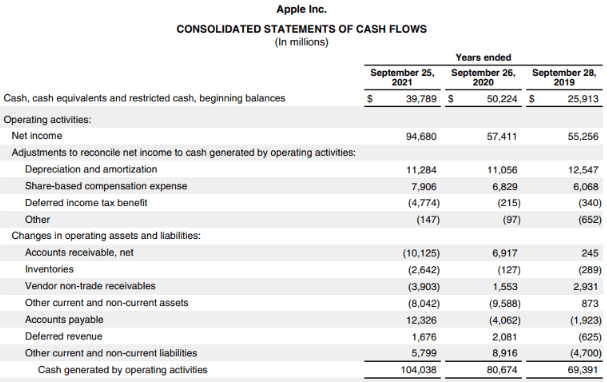
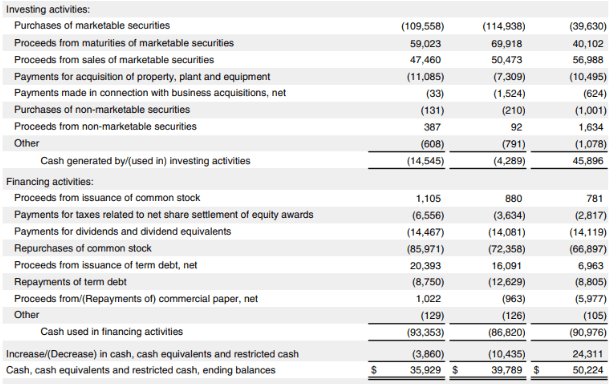
Apple’s Consolidated Cash Flow Statement:
- In comparison to the previous year, Apple’s operating income increased by 28.9% in 2021
- The company’s cash inflow through investments had abruptly fallen from $45,896 million in 2019 to $4,289 million in 2020. However, it recovered gradually by reaching $14,545 million in 2021
- In the case of the company’s financial activity cash outflow, there was an increase from $86,820 million in 2020 to $93,353 million in 2021. It was redemption after the fall from 2019
- For cash and cash equivalents, there was a slump of almost $3,860 million
Financial Accounting Journal Entry
- Journal entries are the basis of recording every business transaction efficiently. We could classify journal entries into simple and composite. While a single journal entry files single debit-credit activity, a composite journal entry may include multiple debit-credit entries
- Journal entries allow businesses to classify their transactions into manageable data. It is a chronological summary of debit and credit financial transactions and a note of the affected accounts.
Example:
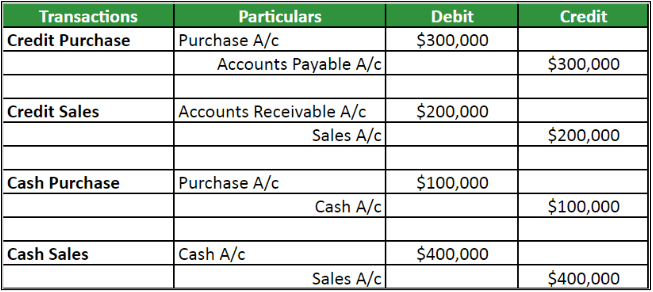
Company ABC recorded the following transactions from the business account,
- Credit Purchase = $300,000
- Credit Sales = $200,000
- Cash Purchase = $100,000
- Cash Sales = $400,000
The journal entries will be,
Financial Accounting Standards
Financial Accounting Standards were developed to unify and standardize how companies manage their accounting. These are various rules governing how to record the balances of a company’s accounts. It ensures that the financial statements accurately reflect the business’s economic situation. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Accounting Standards (IAS) are common accounting standards.
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
- Found in 1973, FASB is an independent body established by The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). It is recognized as a standard-setting body by The International Federation of Accountants
- It provides U.S. accounting standards for private enterprises and non-profits, which includes accounting for assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, and expenses
- Their standards are updated regularly through exposure drafts which allow public participation and comment before formal approval
- The focus of ASCs is on establishing accounting principles for general-purpose financial reports. The goal was that all companies in a given market, such as a country or industry sector, must apply these consistently
- It makes financial information more comparable between companies and, therefore, more useful for business and investment decisions.
Some prominent ASC standards are,
| Standard | Name |
| ASC 205 | Presentations of Financial Statements |
| ASC 210 | Balance Sheet |
| ASC 215 and 225 | Shareholder Equity and Income Statement |
| ASC 230 | Statement of Cash Flow |
| ASC 310 | Receivables |
| ASC 330 | Inventory |
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
- The IASC was established in 1973 when ten countries built this regulatory body. It later came to be known as IFRS
- They developed a set of standards for preparing and presenting financial statements. These standards are known as IAS standards
- The purpose is that companies issuing shares on different stock exchanges should present financial results using the same accounting principles.
Some prominent IAS standards are,
| Standard | Name |
| IAS 1 | Financial Statement Presentation |
| IAS 7 | Statement of Cash Flow |
| IAS 8 | Accounting Policies, Changing In Accounting Estimates, and Errors |
| IAS 18 | Revenue |
| IAS 27 | Consolidated and Individual Financial Statements |
| IAS 28 | Investments in Related companies |
Careers in Financial Accounting
People with financial accounting skills can choose various career paths in finance. Here is a list of jobs that one can pursue,
Financial Analyst
- They are responsible for analyzing the company’s financials along with the market trends and external factors
- They advise the management on future investment strategies and predict the returns on current investments
- The average salary for this role is $63,316.
Financial Controller
- Financial controller primarily oversee the various finance departments of the company
- They create and present financial reports like financial statements, performance reports, and many more
- The salary for this position averages $87,485.
Financial Accounting Manager
- The primary task for the managers is to maintain a connection with other departments and acquire the necessary information
- They also have to ensure that the records and reports adhere to accounting standards and principles
- The salary for this position is an average of $84,319.
Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
- Their principal duty is to supervise the management of budgeting, financial planning, accounting, and much more
- They are also authorized to build strategies, policies, and regulations to sustain efficiency and consistency in the company
- Their average salary is $141,223.
Finance Manager
- The critical role is to create financial forecasts, manage current & future budgets, provide valuable feedback to the staff
- They guide monthly income & expenses and track overspending or in-budget transactions
- This role’s salary is $96,516.
Role of Financial Accounting in Business
How does financial accounting support business operations?
Financial accounting is a critical aspect of business operations, as it provides essential information that helps managers and other stakeholders make informed decisions. Here are some ways financial accounting supports business operations:
- Monitoring financial performance: Financial accounting provides information on a company’s financial performance, such as revenues, expenses, profits, and cash flow. This information helps managers monitor the company’s financial health and make decisions to improve its operations.
- Planning and budgeting: Financial accounting information is used to develop budgets and financial plans for the business. By analyzing past financial performance, managers can identify areas where they must allocate more resources and plan accordingly.
- Facilitating investment decisions: Financial accounting information is used by investors and creditors to make investment decisions. A company can attract investors and secure financing to support its operations by providing accurate and reliable financial statements.
- Compliance with regulatory requirements: Financial accounting plays a vital role in complying with regulatory requirements. Companies must adhere to various accounting standards, laws, and regulations, and financial accounting ensures that they follow these rules and report their financial information accurately.
- Facilitating communication: Financial accounting provides a common language for communicating financial information to stakeholders. Financial information can be effectively communicated by companies to investors, creditors, and other stakeholders using standardized financial statements and accounting principles.
What is the role of financial accounting in budgeting?
Financial accounting plays a critical role in budgeting. Budgeting involves developing a plan for allocating resources over a specific period, typically one year. Here are some ways financial accounting supports budgeting:
- Historical financial data: Financial accounting provides historical financial data that can be used to forecast future financial performance. This data can be used to develop budget assumptions, such as revenue growth rates, expense trends, and capital expenditure needs.
- Cost analysis: Financial accounting provides cost data that can be used to analyze expenses and identify areas where cost savings can be achieved. This information is critical in developing a budget that maximizes profitability while minimizing costs.
- Revenue analysis: Financial accounting provides revenue data that can be used to analyze sales trends, customer behavior, and market conditions. This information is critical in developing a budget that maximizes revenue growth and profitability.
- Capital expenditure planning: Financial accounting provides information on the company’s capital expenditure needs, such as investments in property, plant, and equipment. This information is critical in developing a budget that includes the necessary capital expenditures to support the company’s growth and operations.
- Performance monitoring: Financial accounting provides financial performance data that can be used to monitor actual performance against budgeted performance. This information is critical in identifying variances and taking corrective action to keep the company on track to meet its financial goals.
Challenges in Financial Accounting
What are the most common challenges in financial accounting?
Financial accounting can present a range of challenges. Some of the most common include:
- Complexity: Financial accounting can be complex, involving a range of rules, regulations, and standards that can be difficult to navigate. The complexity can be further compounded by the size and nature of the organization, making it difficult to develop an appropriate accounting system
- Timeliness: Financial accounting must be done promptly, requiring accurate and up-to-date information available to key decision-makers. This can be challenging, particularly in larger organizations with complex financial structures, where information may be spread across multiple departments and systems
- Accuracy: Financial accounting requires a high degree of accuracy, with even minor errors having the potential to cause significant problems. This can be challenging when dealing with large volumes of data or complex transactions and requires attention to detail and a rigorous approach to record-keeping
- Compliance: Financial accounting must comply with various regulations, standards, and laws, which can vary depending on the jurisdiction and industry. Ensuring compliance requires an in-depth understanding of the relevant rules and regulations, which can be challenging to maintain in a constantly changing environment
- Technology: Financial accounting is becoming increasingly technology-driven, with a growing range of tools and systems available to automate and streamline processes. However, implementing new systems can be challenging, requiring significant investment in time and resources to ensure they are properly integrated with existing systems and processes.
How to address ethical challenges in financial accounting?
Addressing ethical challenges in financial accounting is crucial to maintaining the integrity and credibility of financial reporting. To address these challenges effectively, several steps can be taken.
- Establish a code of ethics: Develop a code of ethics that outlines the principles and values that guide financial accounting practices. The code should be communicated to all stakeholders and serve as a reference point for making ethical decisions
- Implement internal controls: Establish internal controls to ensure financial transactions are properly authorized, recorded, and reported. Internal controls can help prevent fraud, errors, and other unethical behavior
- Provide training and education: Provide ongoing training and education for financial accounting staff to ensure they understand the importance of ethical behavior and the consequences of unethical conduct
- Encourage whistleblowing: Establish a process for whistleblowers to report unethical behavior or concerns without fear of retaliation. This can help identify and address unethical behavior before it becomes a more significant problem
- Conduct regular audits: Conduct regular audits of financial records to ensure that they are accurate and comply with relevant accounting standards and regulations. Audits can help detect errors, omissions, or irregularities and help address them promptly
- Hold individuals accountable: Hold individuals accountable for any unethical behavior, including fraud, misrepresentation, or other violations of the code of ethics. This can help deter future unethical behavior and reinforce the importance of ethical conduct.
Financial Accounting vs. Management Accounting vs. Cost Accounting
Financial Accounting
- It concerns a company’s past data and its performance analysis
- Companies employing this accounting technique must adhere to several rules and principles set by the regulatory bodies
- It is valuable to outsiders, such as shareholders, investors, and creditors, to assess the company’s financial health.
Management Accounting
- This accounting technique tries to provide a glimpse into the company’s future. It usually focuses on the present to make decisions about future investments and strategic planning
- Companies create these reports for internal use, i.e., for information requirements of management within an organization
- This information is unregulated and not available to the public.
Cost Accounting
- This accounting approach oversees only the cost expenditures of a business
- It allows measuring of expenses to predict capital available to the company in the future and design efficient budgeting plans
- Businesses use this process to build reports for internal purposes.
Accounting vs. Financial Accounting
| Accounting | Financial Accounting |
| It records, classifies, summarizes, and analyzes transactions that occur in an organization. | It is a subset of accounting. Therefore, following the same process for specific data. |
| It deals with both internal and external transactions | It deals with only external transactions |
| This process helps prepare various kinds of statements. Example: Statement of shareholder’s equity | This process helps in creating financial statements. Example: Income statement |
| It encompasses all transactions, even non-monetary | It deals with monetary transactions |
| Accountants’ education is not as specialized. | Accountants should specialize in financial accounting. |
Why Is Financial Accounting Important?
- It is essential for regularly monitoring the company’s commercial operations and can help keep records of a company’s financial events
- One can track spending and corresponding accomplishments over time by examining the financial data. Therefore, they can assess the significance of a company’s expenses for its operations
- Additionally, it can help carry out concrete actions to determine which operations to reduce and which to prioritize
- It makes transmitting financial information to internal users of the company simple. Such as, participants or partners can view financial reports to evaluate their invested finances
- The financial statements usually provide an overall picture of the company’s profitability. Understanding these reports can be helpful in making better decisions.
Final Thoughts
Future Outlook for Financial Accounting
The future of financial accounting is dynamic and constantly evolving. Technological advancements, globalization, and regulatory reform are some of the primary drivers of change. To succeed in this rapidly changing landscape, businesses must remain informed about emerging trends and technologies. Additionally, they need to be proactive in adapting to new developments to remain competitive.
Resources for Learning more about Financial Accounting
Many resources are available for learning more about financial accounting, such as textbooks, online courses, professional organizations, industry publications, and online resources. The key is finding the best resources for you and committing to ongoing learning and development.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Who uses financial accounting?
Answer: The primary audience for financial accounting is investors, creditors, vendors, and others who need information about a business’s finances. Various other users are auditors, regulatory bodies, banks, etc.
Q2. What is financial accounting and advisory services?
Answer: Financial Accounting Advisory Services usually offers financial management advice. An individual or business in need of financial counseling often seeks experienced professionals. This type of work is known as financial advisory services and generally falls into two categories, personal and business. Accounting firms and independent financial advisory firms offer these services.
Q3. What is the objective of financial accounting? Why is it important?
Answer: Financial accounting ensures that the business is operating efficiently, on time, and in compliance with legal regulations. Moreover, financial accounting serves as a fundamental pillar by tracking income and expenses, which helps determine the available capital. Additionally, financial accounting helps to verify timely payments and invoices, prevents fraudulent activities, and prepares documents required by law, among other benefits.
Q4. Name a few limitations of financial accounting.
Answer: While financial accounting may provide insight into a business’s performance, there are a few limitations. Financial statements don’t give much information about a company’s internal operations. The classification technique can be complex and inconvenient. Moreover, companies using different ways to create their financial statements cannot effectively compare across industries.
Recommended Articles
This was a guide to Financial Accounting. To learn more, please read the following articles,