What is a Financial Instrument?
A financial instrument is a legal contract between two parties with a monetary value. These contracts can be created, traded, or modified according to the parties’ needs.
Financial instruments are assets that one can trade in the financial markets. Their primary objective is to facilitate the efficient flow of capital among investors worldwide. Examples of financial instruments include equity stocks, bonds, and derivative contracts.
Key Takeaways
Some key takeaways from this article are:
- A financial instrument is a contractual agreement between two parties exchanging an asset with monetary value.
- Financial instruments are of three broad types: cash instruments, derivative instruments, and foreign exchange instruments. One can also classify them into two major asset classes: equity instruments and debt instruments.
- They facilitate the flow of capital among investors in an efficient manner.
- One can purchase financial instruments through brokers directly from the issuing company, banks, and individual investors.
Examples of Financial Instrument (With Excel Template)
Below are various examples of financial instruments:
Example #1
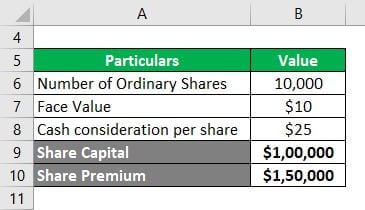
Assuming that XYZ Inc. issued 10,000 ordinary shares with a face value of $10 and a cash consideration of $25 each, the entity has raised funds by issuing a certain type of financial instrument. Identify the financial instrument type and explain the transaction.
Since the entity has issued ordinary shares to raise funds, there is no obligation to repay the money. Hence, the issuance of ordinary shares results in creating an equity-type financial instrument.
In this case, one would record $1,00,000 (= 10,000 × $10) as ordinary share capital, while the remaining $1,50,000 (= 10,000 × ($25 – $10)) as the share premium in the balance sheet.
Example #2
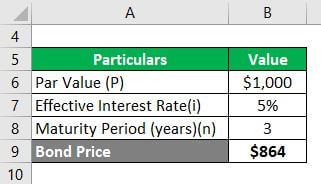
Let’s assume that ABC Inc. raised funds by issuing zero-coupon bonds with a par value of $1,000 on the first day of the current year. The bonds will mature after three years, and the effective interest rate is 5%. First, identify the financial instrument type and determine the value of the bonds today.
Since ABC Inc. received funds with a repayment obligation, it is classified as a financial liability. The bonds are issued at a discount on the par value. Thus, one can determine the value of the bonds today as:
Hence, the price of the zero-coupon bond today is $864.
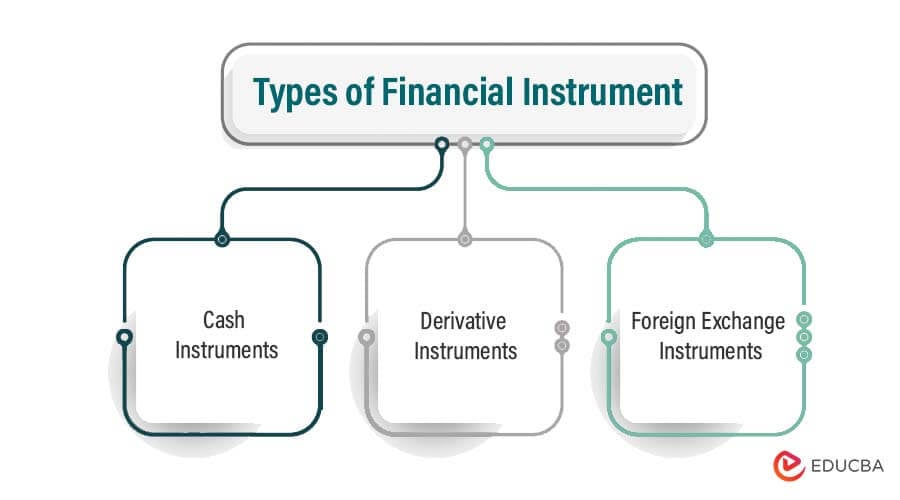
Types of Financial Instruments
Financial instruments are of three major types: cash, derivative, and foreign exchange.
1. Cash Instrument
In this financial instrument, the market condition directly influences the value. There are two types of cash instruments – securities and deposits & loans.
The market conditions directly influence this type of financial instrument. There are two types of cash instruments: securities and deposits & loans.
- Securities: These financial instruments represent ownership of a portion of a publicly-traded company and are traded on the stock market.
- Deposits & loans: These financial instruments are monetary assets that represent a contractual agreement between the parties involved.
2. Derivative Instrument
This financial instrument derives its value from underlying assets, such as stocks, currency, or bonds. Examples of derivative instruments include:
- Forward: A contractual obligation between two parties in a derivative transaction in which the underlying exchange occurs at the end of the contract at a particular price.
- Future: A derivative transaction that facilitates the exchange of the underlying on a pre-decided future date at a predetermined exchange rate.
- Option: An agreement in which the buyer of the option enjoys the right to exercise the option of either purchasing or selling the underlying at a predetermined price within a particular period.
3. Foreign Exchange Instrument
This type of financial instrument deals primarily with currency agreements in the foreign market, and one can divide it into three categories:
- Spot: The exchange of currency takes place no later than the second working day from the date of the agreement.
- Outright forward: The currency exchange occurs before the actual date per the agreement.
- Currency swap: Involves simultaneous purchasing and selling of currencies with different value dates.
Buying Financial Instrument
There are a lot of benefits to buying these financial instruments. However, it is important to know that buying these financial instruments also involves many risks. Hence, looking out for potential risks before buying these instruments is advisable. One can buy them in various ways, some of them are:
- Brokers
- Directly from the issuing company
- Banks
- Individual investors
How to Record a Financial Instrument?
In addition to the classifications mentioned earlier, financial instruments can be classified into two asset classes: equity and debt. Let’s look at how one records these two categories in financial statements.
- Equity Instruments: These are measured at their fair value minus any issue costs. Equity shares are often recorded at their face value, while any excess consideration is recorded as a share premium. Any issue costs deduct from the share premium.
- Debt Instruments: These are recorded at the cost of acquisition, while any discount or premium over the par value is amortized over the asset’s life. Transaction costs are capitalized.
Conclusion
Financial instruments are contractual agreements between parties that capture the monetary value of the underlying asset. Each type of financial instrument has its own benefits and potential risks. Therefore, it is essential to understand the details of these instruments before buying them.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles for expanding understanding: