Updated July 7, 2023
What Is Fire Insurance?
Fire insurance aims to protect homeowners against the damage that a fire can cause to their property and assets. For example, suppose Emily purchases a fire insurance policy for her new house. Due to some unfortunate event, a fire causes damage to her property.
According to the policy coverage, she can claim up to $270,000 and be reimbursed for her loss. It typically includes various coverage sections for homes, cars, clothing, furniture, etc. It also entails coverage for liability, legal costs, and living expenses.
Key Highlights
- Fire insurance is a protection providing support to the insured in case of damages/loss because of a fire or even lightning.
- It is of numerous types, like basic, comprehensive, valued, and many more
- Its primary features are a written contract, the coverage amount, the period, and the premium payment by the insured
- This policy follows the principles of good faith, indemnity, insurable interest, and more.
How Does Fire Insurance Work?
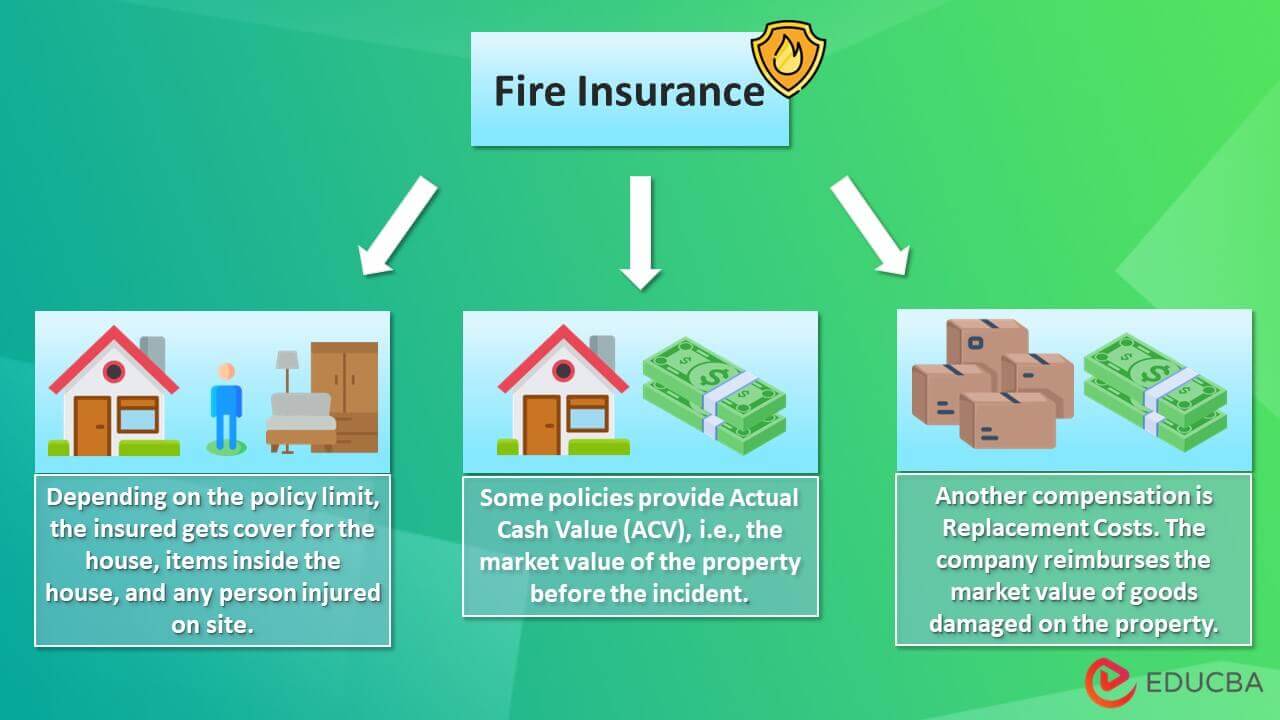
- Fire insurance policy insures the person’s property, its possessions, and anyone present on the property during the fire
- Most policies cover fires starting both inside or outside the property and reimburse in the actual cash value of the damages or replacement costs
- In case of a total loss, the company may compensate for the property’s current market value, or they typically pay for the market value of lost goods
- For example, if a policy covers a $350,000 home, the contents are usually protected for at least 50-70% of the policy’s value. Many policies limit compensation to luxury items like paintings, jewelry, gold, fur coats, etc
- The coverage limit depends on what caused the fire. It mainly covers fires due to faults in electric cables or natural causes like lightning
Fire Insurance Claiming Process
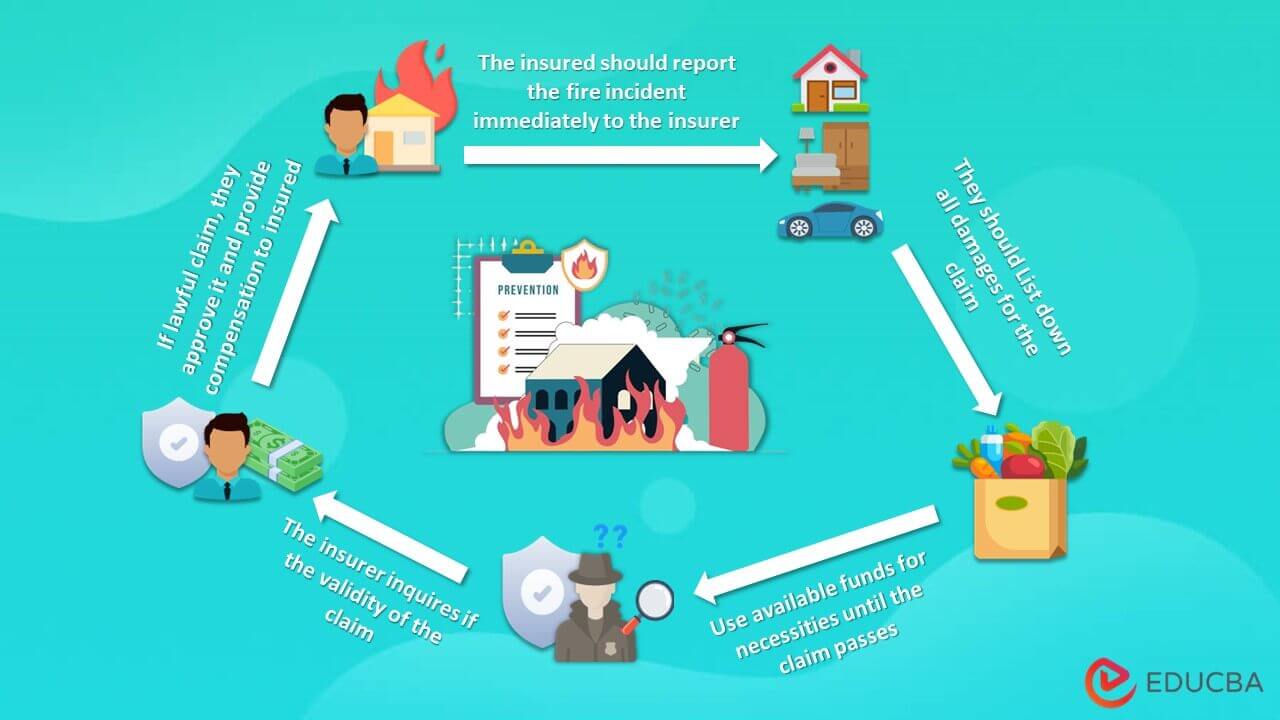
Step 1: Contact the Insurance Provider
- Contact the insurer and report the incident after authorities have put out the fire
- Insurers urge policyholders to submit an insurance claim once an accident occurs. For instance, to file a claim in North Dakota, one can fill out the form at the insurance department.
Step 2: List Losses/Damages
- Keep track of all losses incurred following the fire accident and assess the damage
- Submit a “Proof of Loss Claim” to the insurance provider, which details the lost or damaged items and their associated values.
Step 3: Use Currently Available Funds
- Use in-hand resources to avail any necessities until the insurer passes the claims
- If you don’t have enough for your needs, you can ask the insurer for the necessary portion of the sum insured.
Step 4: The Insurer’s Approach to Making a Claim
- The company sets up an inquiry as they receive the claim. If the reason for the fire is under the policy coverage, you’ll receive the benefits
- However, due to various reasons, the company can also decline the claim.
Step 5: Obtain Costs
- When the agency approves the claim, you get compensation for your home and possessions
- Please keep the original receipts and repair estimates to give to the insurance provider.
Types of Fire Insurance Coverage
- Property policy covers the building, its contents, and other structures on the property.
- A dwelling policy is similar to a property policy, but it is for premises that the holder owns but rarely lives, like guest houses, farmhouses, etc.
- Specialty coverage is for high-risk properties such as churches, hospitals, and schools.
- Additional living expenses pay for accommodations if the home is uninhabitable due to fire damage.
- Homeowners Insurance covers one’s home and the belongings inside it
- Commercial Property Insurance is for buildings that are not a residential property
- Business Interruption Insurance helps cover the cost of lost income in the event of business closure for an elongated period
- Apartment Building Insurance protects buildings with four or more units in them
- Renters Insurance provides coverage for personal belongings damaged by fire on a rented property.
Fire Insurance Examples
Example 1:
In a fire breakout on November 5, 2022, in an apartment building in Manhattan, two were critical, and dozens were injured. The cause was faulty lithium batteries that started the fire at the 20th-floor apartment.
Considering this scenario, suppose the person living on the 20th floor has fire insurance. Thus, they can easily cover all damage-related expenses. However, if no such insurance was in place, they might suffer the loss and bear the liability expenses for others’ injuries.
Example 2:
An organization builds a new factory and purchases fire insurance as the equipment poses a fire danger. In such an event, the overheating of the machinery leads to fire in the factory. As the property has business interruption coverage, the organization receives compensation for the period when the factory is not in use due to the incident.
Fire Insurance Features
Agreement
- It is a contract between the insurer (a company) and the policyholder (an individual), which contains all necessary information regarding the policy
- This signifies that the individual will pay a certain amount in exchange for a promise from the insurer to protect against fire.
- It can be helpful if the insurer declines to pay or the insured raises incorrect claims.
Premium
- An insurance premium is a set amount the policyholder pays to ensure that the policy stays active.
- The amount is subject to the type of coverage; the more comprehensive the coverage, the higher the premium.
- The basic level includes protection from damage to a building and its contents up to a certain amount. Comprehensive coverage includes replacement costs for items such as furniture and appliances.
Covered Amount
- It is the amount that the insurance company pays for the loss of your home or belongings
- The first type of coverage is actual cash value (ACV), which only pays as per the property’s current market worth. It considers the property’s condition just before the fire for the amount calculation.
- Replacement cost coverage is another type that pays to replace damaged possessions at their current price. It is a better option than ACV.
Insurance Period
- It is the validity term of the insurance. The insured can claim the coverage if any fire incident occurs within this timeframe.
- The general period for fire insurance is one year. The holder can renew the coverage every year as per the requirement.
- However, in some cases, like dwelling insurance, the period can vary as it is not a primary residence, thus, carries lower risks.
Fire Insurance Types
Basic Insurance
- Under this, the insured party gets the compensation only if the cause of the fire comes under the obtained policy
- The policyholder generally has to pay for the damages themselves before filing a claim with their insurer
- One would have to purchase other coverages to protect against the risk of injuries, liability claims, and so on.
Valued Insurance
- The company decides the coverage amount for this policy while issuing the insurance by surveying the market and determining the property’s current value.
- These are more expensive than basic but less costly than comprehensive
- For example, Lily purchases a house at $1,500,000 and immediately buys fire insurance. After a few years, the house catches fire, and she claims the insurance. Even if the property’s current value is $1,000,000, the company must pay her $1,500,000 if she claims the amount.
Comprehensive Insurance
- It reimburses for the property, its belongings, and harm to any person on the property.
- It is one of the costliest policies as it provides overall protection to the insured property.
- People who build houses with numerous valuables (paintings, antiques, etc.) should opt for this policy.
Average Insurance
- It is primarily a clause that applies if the insured buys the property’s insurance for half its value.
- In this policy, while claiming the insured amount, the policyholder will receive half of the damage cost as they insured only half value.
- For instance, the property’s value is $2,000,000, but the insured buys fire insurance for $1,000,000. Thus, if there are losses of $800,000, the insured will only get $400,000.
Floating Insurance
- It is mainly for companies that trade goods from around the world, as they need to store inventories at various locations and even indulge in goods transportation
- This policy insures all goods – from warehouses to ones in transit – and promises to pay in case of damages
- The coverage is the total value of these goods, while the premium is the average value for all goods.
Principles of Fire Insurance
Principle of Indemnity
- It specifies that the insurer must ensure that the insured gets reimbursed in total quantity as per the contract
- The insurer agrees to hold the policyholder harmless against any loss or damage a fire may cause.
Warranties in Fire Insurance
- They are certain conditions that the insurer levies on the policyholder. If these conditions qualify, only then can the holder claim the insurance
- Primary conditions include annual maintenance and fire extinguishing appliances. Additionally, the property should be concrete and not have an ineffective structure.
Complete Trust
- The insured and the insurer should maintain honesty and good faith toward one another
- The insured must exercise reasonable care for protecting the property, and there should not be a breach of contract or negligence on behalf of the insurance company.
Insurable Interest
- Insurable interest specifically defines the policy buyer must have a financial or personal interest in the insured object.
- It can either be direct or indirect. For example, a person who owns an apartment is interested in it. Suppose it is a rental property. Then the one living in it has an indirect interest as it is their residence.
Compensation Principle
- It means the insurer is liable to compensate the insured for damage to the property due to a fire.
- Also, the company should only pay for direct and actual costs related to property damage. The insured cannot claim unrelated expenses.
Conclusion
Fire insurance buyers should be aware of fires that are covered and not covered in the policy. For example, it may exclude a fire caused by an earthquake. It is critical to read the policy terms and seek clarification carefully. It also is necessary while applying for mortgages, as lenders favor properties with proper insurance.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. Does fire insurance cover negligence?
Answer: It depends if the negligence causing the fire was intentional or accidental. For instance, the policy may cover fire due to an accidentally left burning candle. However, if someone intentionally sets the property on fire to collect money, it is deliberate negligence, which the fire insurance would not cover.
Q2. Can a fire insurance policy be assigned?
Answer: A homeowner can assign their fire insurance policy to another person. However, the insured must have written authorization from the insurer and the insurable interest of the assignee in the property; otherwise, it is illegal.
Q3. How are claims settled in fire insurance?
Answer: The process begins with an investigation. The agency appoints a team to inquire about the cause of the fire. Suppose the reason was intentional or due to negligence. The claim can be denied. However, the company will pass the claim if the legitimate source comes under fire insurance coverage. Therefore, the insured will get the required benefits.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Fire Insurance. We discuss its definition, types, coverage, and more. To learn more, please read the following articles,