Updated July 3, 2023
Definition
Fiscal policy is the use of government expenditures and taxes to affect or stabilize a country’s economy. Employment, wage growth, and economic expansion are a few of them.
The governments may cut tax rates or boost spending during a crisis to stimulate economic growth and the economy. On the other hand, it can increase rates or reduce spending to slow down the economy to battle inflation.
Key Highlights
- Fiscal policies are the discipline of a country’s economic policy that focuses on managing and administrating a state’s resources.
- Fiscal policy is the employment of taxation, government spending, and public debt to influence the economy. It can stabilize the economy when there is a recession or inflation is too high.
- A country with a balanced budget has more economic freedom because they have a surplus of cash to spend on things like infrastructure or social programs. Conversely, a country with an unbalanced budget has less economic freedom because it has to borrow money from other countries or cut spending to balance its finances.
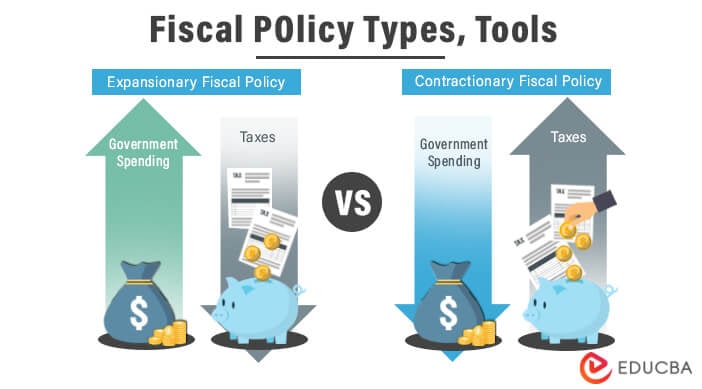
- The most common form of expansionary fiscal policy is an increase in government spending on public goods such as infrastructure, increasing aggregate demand and leading to higher levels of economic activity, output, and employment. The most common form of contractionary fiscal policy is an increase in taxes that leads to higher savings and investment levels by households, which will lead to increased aggregate supply and lower levels of economic activity, output, and employment.
What is Fiscal Policy- Explanation
- It is a type of economic policy comprising government spending, taxes, and government deficits. A country’s fiscal policies are structured to be either expansionary or contractionary. Expansionary involves increasing expenditures or decreasing tax rates, while contractionary involves lowering expenditures or raising taxes. The effects of these policies can either lead to an increase in GDP and employment rate or a decrease in GDP and unemployment rate, depending on which effect outweighs the other.
- The government can use these policies to reduce unemployment by stimulating aggregate demand through increased public spending or cutting taxes. It has a significant role in stabilizing prices when the economy experiences inflationary pressures.
Examples of Fiscal Policy
1. Tax Increases and Tax Cuts
A Tax cut occurs when a government lowers taxes on goods, income, or property. A tax increase happens when a government taxes goods, income, or property. Examples of tax cuts are: The Bush-era tax cuts reduced federal income taxes from 36% to 35%.
2. VAT should be Raised
Raising VAT would help to reduce the budget deficit. It would also make us less inclined to spend because we’ll pay more for things. The government should raise VAT by 2% to compensate for a reduction in corporation tax from 20% to 18%.
3. Increase your Export Rates
Countries can establish tariff rates lower than their import tariffs to increase export rates. This means that when an international company wants to export goods to a country, they pay a low rate of customs fees, but if they want to import goods into a country, they have to pay a high rate of customs fees.
4. Distribution of resources among the various levels of government (Nation, Province, Municipalities)
The federal government creates policies for national issues, provincial governments create policies for provincial issues, and municipal governments create policies for municipal issues. Local governments often need to depend on their respective provinces for funding because they don’t have the means to generate enough revenue from taxes or other sources like property taxes.
5. Restriction on Imports
A restriction on imports is a tax or tariff on imported goods. Such restrictions are often enacted to promote domestic industries by restricting competition outside the country. A restriction must apply to trade between two countries, typically one that imports more than it exports (called a net importer) and one that exports more than it imports (called a net exporter), to qualify as a protectionist measure.
Types of Fiscal Policy
There are two types of fiscal policies: Expansionary policies and Contractionary policies
1. Expansionary Policies
Expansionary Policies involve increasing aggregate demand, either by direct intervention or indirectly through monetary actions. It aim to reduce unemployment and increase economic output to its potential level.
-
Fiscal Policy: Effects of Expansion Policies
- Fiscal policy has the most immediate effect on aggregate demand for goods and services. A fiscal expansion, for example, boosts aggregate demand in one of two ways. First, if the government increases its purchases while keeping taxes constant, it directly increases demand. Second, lowering taxes or increasing transfer payments increases households’ disposable income, causing them to spend more on consumption. This increase in consumption will boost aggregate demand.
- It affects the composition of aggregate demand as well. When the government runs a deficit, some of its spending is by issuing bonds. In doing so, it competes with private borrowers for savers’ money. Keeping things constant, a fiscal expansion will raise interest rates and “displace” some private investment, reducing the proportion of GDP made up of private investment.
- It also influences an open economy’s exchange rate and trade balance. Rising interest rates due to government borrowing attract foreign capital during a fiscal expansion.
2. Contractionary Policies
Contractionary policies do the opposite, decreasing aggregate demand by reducing government spending or raising taxes. It aim to reduce inflation or even deflation, which can result from an overheated economy with high aggregate demand.
-
Fiscal Policy: Effects of Contractionary Policies
In order to restore order to the business cycle, a government may pursue a contractionary fiscal policy, even to the point of inducing a brief recession and other damaging expansionary symptoms. A government can accomplish this by cutting public spending and public sector salaries or laying off employees.
- When expansion leads to deficits, as usual, contractionary fiscal policy is characterized by a large budget surplus. This policy is, however, rarely used. It is considered neutral when it is neither expansionary nor contractionary.
- Along with spending and tax policy, governments can use their sovereignty to profit from printing money and selling goods as public enterprises in order to change the effects.
Tools of Fiscal Policy
- Fiscal policy is one of the two main types of economic control that a government or its agencies can exercise. Its main tools are taxes and spending. Fiscal policy instruments can achieve, or attempt to achieve, both economic and political goals. All instruments ultimately serve to answer two questions: how much a government should spend and how that spending should be funded.
- Both political and economic factors can influence the decision to spend money. In most cases, taxes are used to fund public spending. This is yet another example of how these tools can serve a social or political purpose in addition to an economic one.
- There are other ways to fund the expenses. These include borrowing money, using a previously accumulated reserve, and selling government-owned assets. These methods can result in a public deficit and, thus, a growing debt over time. This can sometimes also influence government decisions about fiscal policy tools.
- Fiscal policy instruments can be useful in conjunction with monetary policy instruments. This includes setting the base rates, which have an effect on the rates banks charge for lending to the public or to businesses in most economies. The goal of such policies is typically to manage the level of inflation, with the theory being that higher rates mean that people spend more on paying mortgages and other loans, leaving less money to spend on goods. While some governments combine fiscal and monetary policy, others delegate monetary policy to an independent monetary authority, such as a national bank.
Why is Fiscal Policy Important?
- Fiscal policy is unquestionably a state’s growth engine because it contributes to economic and social development and impacts employment, production, and market prices. It is also responsible for establishing a state’s budget with taxes and the variable of public spending, combating poverty, and generating a balance that allows equal opportunities for its citizens.
- According to data from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), most Latin American countries have improved their fiscal performance in recent years.
- These indicators show significant differences between countries due, among other things, to how they structure public revenues, the degree of decentralization of tax systems, and the quantity-quality of public services that citizens receive in exchange for their taxes. One solution is to make public spending more efficient, which includes increasing the quantity and quality of goods and public services and increasing the progressivity of public spending, allowing the most vulnerable to receive a larger proportion of spending.
Advantages of Fiscal Policy
Some of the advantages are:
a) To stimulate the economy
According to Keynesian economists, fiscal policy is a powerful tool for stimulating growth in an economy operating well below acceptable levels. A government can use this tool to boost aggregate demand in the economy. The total demand for all goods and services in a country is the aggregate demand.
b) Inflationary control of the exchange rate
Fiscal policy can help an economy combat high inflation rates. Inflation is defined as an increase in the price of goods and services without an increase in the amount of money in the economy. As a result, consumers must pay more for goods and services while having less money.
c) In response to slow times
Fiscal policy may be slow to respond to changing economic conditions. This is because fiscal policy adjustment in a government frequently involves multiple bodies making decisions with different political agendas and currents of economic thought.
Disadvantages of Fiscal Policy
It has two main disadvantages.
- The first disadvantage is that it causes unemployment because higher taxes discourage people from working. The second disadvantage is inflation. Fiscal policies cause inflation by increasing the money supply, which increases prices.
- When governments put regulations to protect workers, such as mandates on hours worked and minimum wage rates, it reduces total employment because some employers have to cut jobs to comply with the law. In contrast, others need to pay workers more than they are worth.
Conclusion
Fiscal Policy is a government’s spending, taxing, and borrowing approach. The goal is to achieve specific macroeconomic objectives like low inflation or high employment. It can be useful as an automatic stabilizer when the economy undergoes a recession. Government intervention in response to recessions has been shown to reduce the severity of these downturns by restoring output growth while keeping inflation low. Automatic stabilization of the economy is achieved through changes in government expenditures and tax revenues that occur without deliberate action on the part of policymakers.
FAQs
Q1. What are the main objectives of fiscal policy?
Answer: Economic stability, price stability, full employment, optimal resource allocation, accelerating the pace of economic development, encouraging investment and capital formation, and growth are some of the key objectives of fiscal policy.
Q2. Who uses fiscal policy?
Answer: Fiscal policy in the United States is directed by both the executive and legislative branches. The president and the secretary of the Treasury are the two most powerful positions in the executive branch in this regard. However, modern presidents frequently have a council of economic advisers.
Q3. How does fiscal policy affect the economy?
Answer: It is a set of economic tools that influence the economy. It includes a wide range of tax, spending, and regulation policies. The government employs fiscal policy to stimulate the economy in recession or slow growth. Fiscal stimulus can be achieved by lowering taxes or increasing government spending. On the other hand, it can be useful to control inflation by raising taxes or cutting spending.
Q4. Who sets Fiscal Policy?
Answer: Fiscal policy is set by the government. The government can decide to increase or decrease fiscal stimulus if they want to stimulate the economy or if they want to reduce inflation.
Q5. How is fiscal policy advantageous over monetary policy?
Answer: Monetary policy is the process of influencing the money supply in the economy by changing interest rates and buying or selling government securities. On the other hand, fiscal policy refers to changes in government spending and taxation that affect aggregate demand.
Recommended Articles
This was a guide to the Fiscal Policy. To learn more about Fiscal Policy, please read the following articles: