What is the Difference Between Fixed Cost Vs Variable Cost?
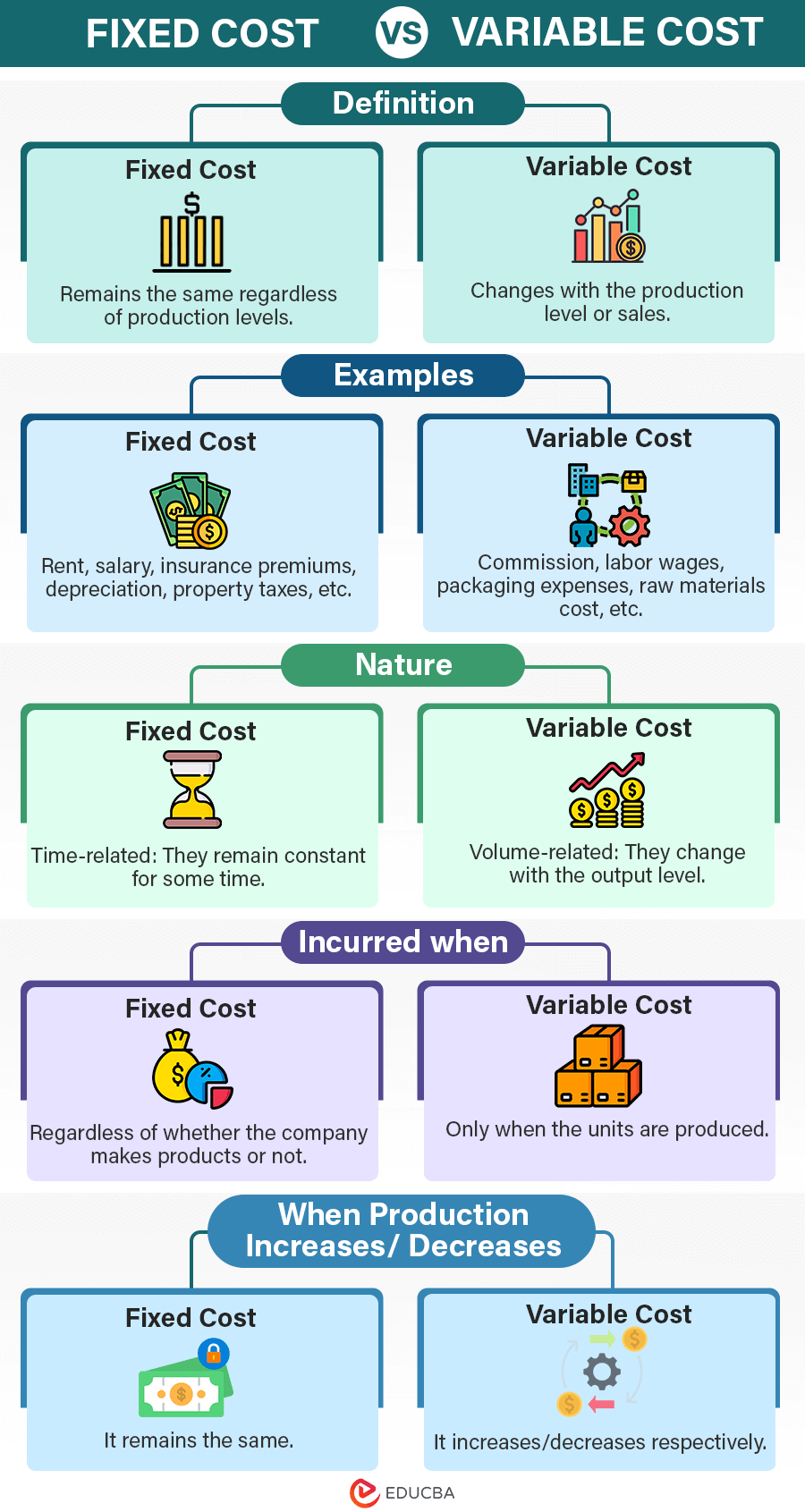
Fixed costs remain constant regardless of production or sales levels, whereas variable costs change with production level.
Consider a software company with a monthly rent cost of $2,000, which stays the same whether they sell 100 or 500 software products. This cost is known as the fixed cost. Suppose a software product costs $10 per unit, and it varies with the production volume. This cost is known as the variable cost. If the company produces 100 units, the variable cost will be $1,000 ($10 x 100); for 500 units, it will be $5,000 ($10 x 500). This explains how fixed costs remain constant, whereas variable costs fluctuate based on production levels.
Table of Contents
- What is the Difference Between Fixed Costs Vs. Variable Costs?
- What is Fixed cost? (with Example)
- What is Variable cost (with Example)
- Key Differences
- Infographic on Fixed Cost Vs Variable Cost
- Why is it important to distinguish between fixed cost and variable cost?
What is Fixed Cost?
Fixed costs are expenses that do not vary with changes in production or sales levels over a specific period. The company has to pay fixed costs even if they don’t produce any units. It is also known as overhead, indirect, or supplementary costs.
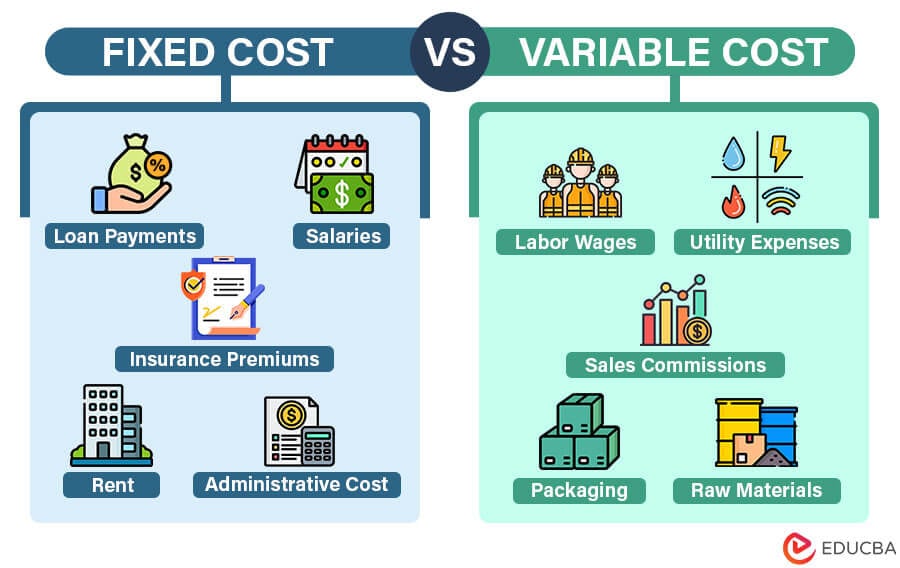
These costs include:
- Rent
- Salaries
- Loan payments
- Insurance premiums
- Administrative costs
Example:
Sarah’s company, TechGear Innovations, has monthly fixed costs. These include:
- Rent of manufacturing facility: $5,000
- Salaries of staff: $3,000
- Insurance for the equipment: $1,500
So, the fixed cost for each month will be:
Total Fixed Costs = Rent ($5,000) + Staff Salaries ($3,000) + Insurance ($1,500)
= $9,500 per month
Therefore, the fixed cost of $9,500 per month remains constant and won’t change with the production level.
What is Variable Cost?
Variable costs are expenses that change with changes in production or sales volume. Like, if a company produces more or sells more products, variable costs will increase, and vice versa. In addition, the company only incurs variable costs when it does some production. It is also known as direct costs or prime costs.
These costs include:
- Labor wages
- Raw materials
- Packaging
- Utility expenses
- Sales commissions
Example:
Suppose an AromaGlow company manufactures fragrance candles. Manufacturing one candle costs $3.50 (including ingredients like wax, fragrance oils, wicks, and packaging materials). Let’s calculate the monthly variable costs if they plan to produce 500 candles.
For 500 candles, the variable cost will be:
Total Variable Costs = Cost Per Unit x Total Number of Units
= $3.50 x 500
= $1,750
This cost will change depending on the production level. If it makes 1000 candles, the variable costs will be $3,500 ($3.50 x 1000).
Key difference between Fixed Cost Vs Variable Cost
The following is the key difference between fixed costs and variable costs.
1. Profitability
- Fixed cost: It is affected by profitability, indicating that a higher productivity level leads to a reduced fixed cost per unit.
- Variable cost: It is not affected by production levels and does not influence profitability.
- Example:Let’s say you start a bakery. The fixed costs will include rent and equipment costs, which you can track efficiently using Rental Invoice Receipt Templates. As you sell more pastries, these costs will spread out, reducing the cost per pastry. However, your variable costs, such as ingredients like flour and eggs, will remain constant per pastry, regardless of how many you bake.
2. At Per-unit Level
- Fixed cost: It decreases as the company produces more units of a particular product.
- Variable cost: It stays the same for each unit that the company makes.
- Example: A company’s variable cost is $3 per unit, and its fixed cost is $10,000 monthly. If it produces 1,000 units, the fixed cost per unit is $10 ($10,000/1,000). If it produces 2,000 units, it will become $5 ($10,000/2,000). However, the variable cost of $3 will remain the same whether the company produces 1,000 or 2,000 units.
3. Financial Planning
- Fixed cost: It remains constant and is crucial for long-term planning,
- Variable cost: It varies with the production level and impacts short-term decisions and production planning.
4. Risk Associated
- Fixed cost: It is risky during low production and economic downturns.
- Variable cost: It is risky when the cost increases with higher production levels.
5. Level of Control
- Fixed cost: It requires less monitoring.
- Variable cost: This cost can be controlled by managing the product output number, raw material costs, labor costs, etc.
Infographic on Fixed Cost Vs Variable Cost
The following is the infographic showing the difference between fixed cost vs. variable cost.
Why is it important to distinguish between fixed cost vs variable cost?
Distinguishing between fixed and variable costs is crucial in business and financial management for the following reasons.
1. Cost Control
It helps companies understand their cost structure and set pricing strategies. Companies can contribute to overall cost efficiency by identifying areas for cost reduction.
2. Economies of Scale
Economies of scale refer to the concept that the cost per unit decreases as a business produces more units or expands. By optimizing production, businesses can reduce per-unit costs, identify areas for improvement, and enhance their competitiveness in the market.
3. Break-Even Analysis
Break-even analysis helps to identify the point at which total revenue equals total costs. As a result, companies can determine the minimum sales level required to cover fixed and variable expenses and set a profitable price that will cover production costs.
4. Profitability Analysis
Businesses can make strategic decisions and pricing strategies by assessing the impact of changes in production or sales on overall profitability. In addition, the higher production level reduces the fixed cost per unit, thereby improving profitability.
5. Risk Management
Identifying fixed and variable components is key to effective risk management. Businesses can develop better risk mitigation strategies by assessing their financial stability and susceptibility to market fluctuations.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the fixed costs, which remain constant regardless of production levels, and variable costs, which fluctuate with production, is crucial for financial management. For example, fixed expenses, like rent or insurance, stay the same for a longer period, while variable costs, like raw materials, change with the output number. This knowledge is crucial for businesses for budget planning and making informed pricing decisions to control expenses. Moreover, companies can also deal with economic challenges, maximize production, and maintain financial stability.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on fixed cost vs variable cost was informative. For further guidance on related topics, we recommend the following articles: