Updated July 14, 2023
Introduction of Fixed Income Funds
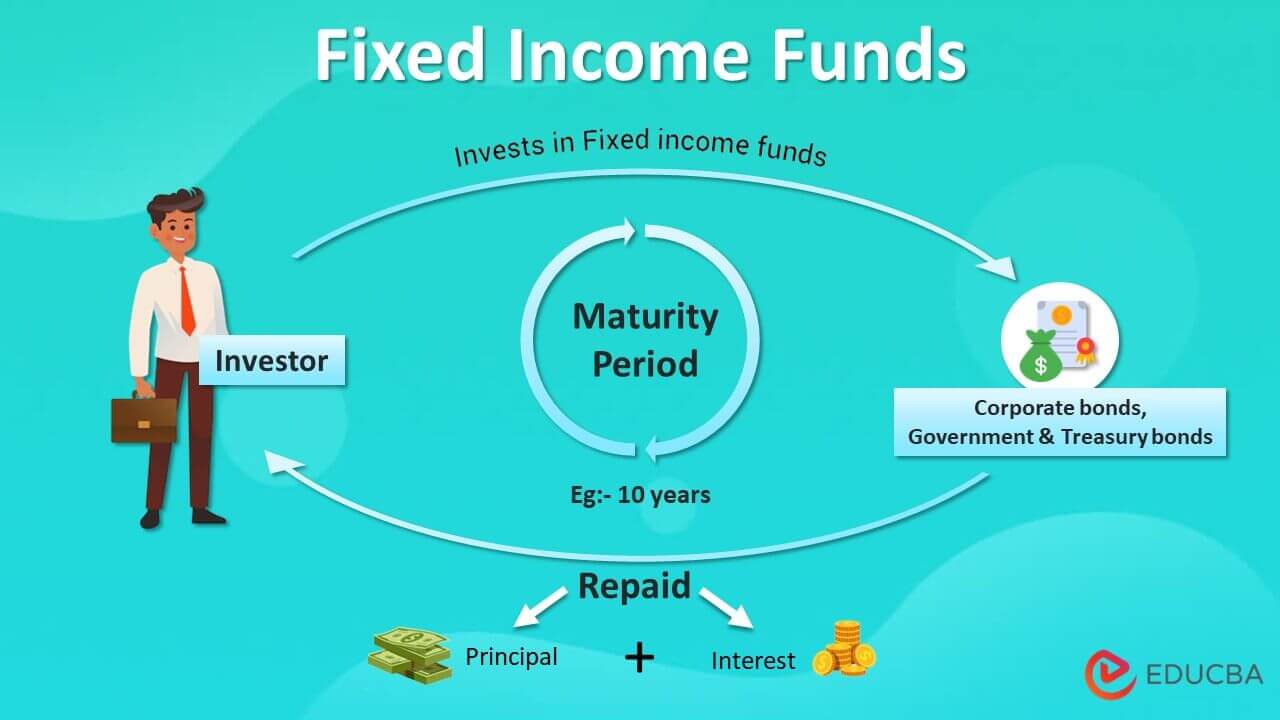
Fixed Income Funds are financial instruments or securities that give the investors a fixed income throughout the investment, and on maturity, the principal investment is repaid to the investors.
Fixed-income funds pay the investors a fixed income in interest or dividends until maturity. At maturity, the principal amount is repaid to investors along with the income component. (e.g.) Corporate bonds, Government and treasury bonds, Certificates of deposit, etc. Fixed income securities are issued to raise funds to manage corporate and government financial requirements.
Fixed income securities are more suitable for conservative investors who want to secure their capital and earn income from the investment. Even moderate risk-tolerant investors choose to invest in fixed-income securities to some level to balance their risk and returns. They predominantly invest 50% in Equities and 50% in fixed-income securities. Risk is low in these investments, so comparatively, returns are also common, and the amount of income will also be known to the investors.
Features of Fixed Income Funds
- It is a low-risk investment and secures the capital of the investor.
- It gives fixed, regular returns to the investors as interest or dividends.
- It is more suitable for conservative investors who tend to avoid risk. It is more prevalent among retirement portfolios.
- It reduces the risk in the portfolio of the investors who also invests in stocks.
How do Fixed Income Funds Work?
The government, corporates, banks, financial instruments, etc, issue fixed income funds. They are given to seek funds from investors, and in turn, they regularly pay to the investors in the form of interest or dividends.
Example:
Zen Corp floats a fixed-income bond for the expansion of the business. They issued the 5% bond with a face value of $1,000/ bond, which matures in 5 years. The company utilizes the funds to fund the new business segment.
Mr. X bought ten bonds from Zen Corp and invested $10,000 ($1,000 * 10). He will receive $500 (10,000 *5%) annually from Zen Corp as interest until maturity. (i.e.) for five years. The interest amount is fixed and paid regularly every year until maturity. Upon maturity, Zen Corp will repay the principal amount of $10,000 to Mr. X, and on this investment, Mr. X earned $2,500 ($500 * 5 years) as interest income over five years.
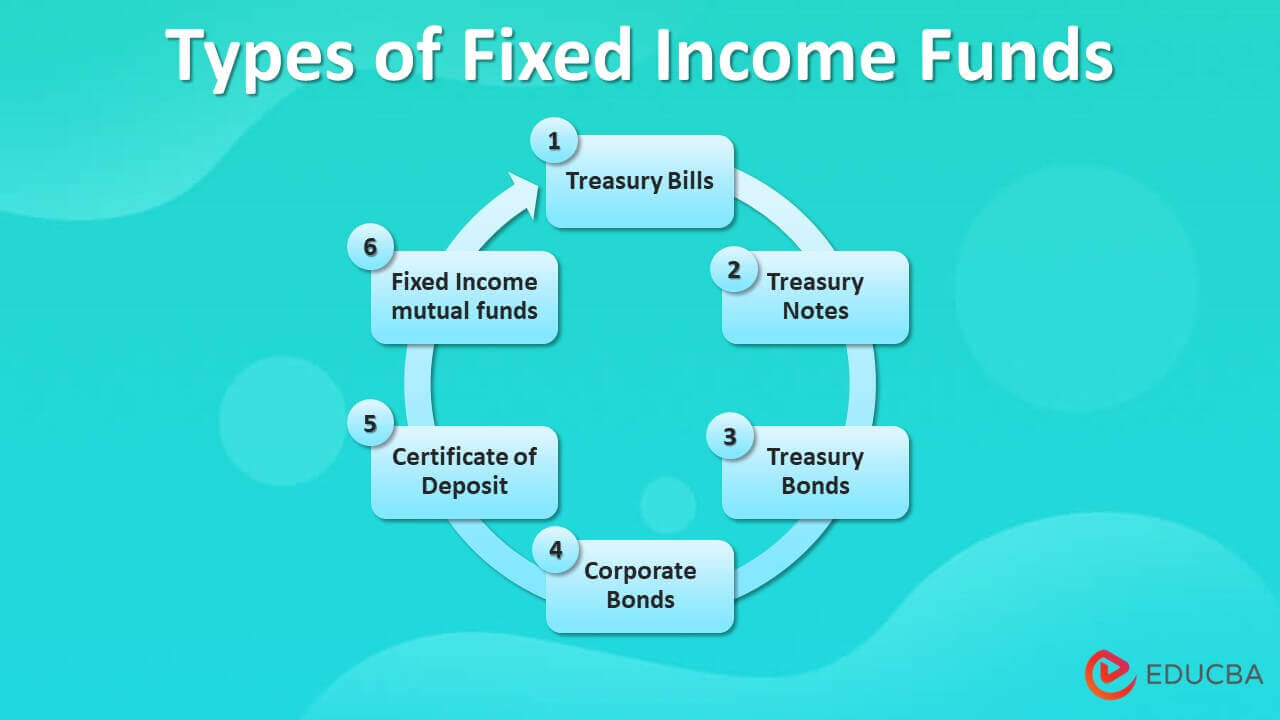
Types of Fixed Income Funds
The government and corporates usually back it. Some of the common income funds are mentioned below.
- Treasury Bills: Short-term fixed-income security usually matures within one year. It issues at a discount, and the face value is paid on maturity. The difference in the income earns from the treasury bills.
- Treasury Notes: It is a long-term investment varying from 2 to 10 years. It pays a fixed interest throughout the investment, and the principal investment is repaid to investors on maturity.
- Treasury Bonds: It is a very long-term investment with a 20-30 years maturity period. It pays a fixed income to the investors as interest, and the principal is also paid to investors on maturity.
- Corporate Bonds: Corporates issue them. The price and interest rate vary from one corporate to another. It publishes in various forms. Usually, a higher credit rating company offers low-interest rates since the investment is more secure than other companies.
- Certificate of Deposit: Banks offers fixed income instrument and financial institutions with a maturity period of less than five years. The interest rate is higher than the savings A/c interest. It is also one of the secured investments.
- Fixed Income mutual funds: A specific investment by mutual funds into bonds and debt instruments that pay fixed income in interest. The portfolio managers will charge professional fees for managing the funds, and the fixed income received will transfer to the investor.
Why Invest in Fixed Income Funds?
Fixed income funds are secured investments and suitable for risk-averse investors. The returns will be lower than equity investment, but the capital protects. Investors prefer those who seek stable income from investments and want to save money.
Benefits of Fixed Income Funds
Some of the benefits are given below:
- It offers investors a steady source of income through investment in financial instruments like bonds or debt instruments.
- It gives a more stable income than stocks.
- It is more beneficial for people at retirement age who wants to secure their retirement funds and get a decent income.
- These investments help reduce the risk in the investor’s portfolio, which also invests in some risky securities.
- It is used for diversification in the portfolio.
- It is a more secure investment like government bonds backed by the government, whereas corporate bonds may not be that secure. However, bondholders still have a higher claim on the company’s assets in liquidation or bankruptcy than shareholders.
Disadvantages
The following are some Disadvantages:
- Not all fixed-income funds are secured; corporate bonds are not secured as treasury bonds.
- Returns from fixed-income securities are lower than the returns given by stocks.
- Corporate bonds are subject to credit risk, which can even affect the valuations of the bond/ security.
- If bonds are sold even before maturity, they will be sold at market price, and there can be changes where the bond may fetch a lower value than the principal investment and can incur a loss.
- Interest rate risks associated with the investment. In certain situations, interest rates in the market can keep rising, whereas the bond still pays a lower fixed interest to the investors; in that case, it loses market value.
- The prime purpose of fixed income funds is that the investors get a fixed income from the securities. If the inflation rate increases and the income from the security are the same, the investor may not earn more gains from the investment.
Conclusion
Fixed income funds are a good investment for conventional investors and those who want to reduce their portfolio risk. They get fixed returns from the investment, and the principal investment is protected. Every investor invests some of their money in low-risk investments to balance the risk and returns. It doesn’t fluctuate much like equities and is not affected like equities due to market risk. However, the returns are comparatively lower than equities still chosen by investors for their merits.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Fixed Income Funds. We also discuss the introduction and how fixed income funds work with benefits and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –