Flexible Budget Meaning
A flexible budget is an adjustable budget that companies create for different levels of activity, i.e., different output levels, revenues, or expenses for a single budgeting period.
It is unlike the static or traditional budget, which cannot be changed once created. It accurately represents expected financial outcomes in the real world by considering different scenarios and variations in income and expenses.
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- Flexible budgets are adaptable financial plans that respond to changes in income and expenses.
- They offer a more realistic view of financial performance compared to static or traditional budgets.
- It helps businesses and individuals benefit by improving financial decision-making and adjusting to unforeseen circumstances.
How to Create a Flexible Budget?
Creating a flexible budget involves several key steps:
Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
#Step 1: Identify Variable and Fixed Costs
Start by categorizing your expenses into variable costs (those that change with activity levels, like utility bills) and fixed costs (those that remain constant, like rent or mortgage).
#Step 2: Set a Base Budget
Create a baseline budget representing your expected income and expenses under normal conditions.
#Step 3: Determine Variance Factors
Identify the factors that may cause variations in income and expenses. For a business, this could include changes in demand or market conditions. For individuals, it might be fluctuations in income or unexpected expenses. Also, determine the price on a per-unit basis or as a percentage of activity level.
#Step 4: Create the Budget
Plot the variable and fixed costs for the budgeted activity level, and this will create a flexible budget.
Formula
The formula is:
Where,
- Fixed Cost: Costs that remain constant regardless of the activity level, like rent, salaries of permanent employees, and insurance premiums.
- Actual Units of Activity: Real activity or business operations during the budget period. It can be units produced, sales volume, etc.
- Variable Cost per Unit of Activity: Cost associated with each unit of activity or production, such as direct materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead.
Examples
Let us see a few examples of how to calculate flexible budgets and how to perform variance analysis.
Example #1
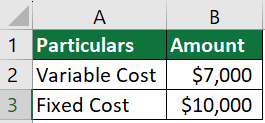
A company wants to prepare a budget based on a scheduled activity level of 70% of the production capacity, where the number of units designed is 7000. The variable costs and fixed costs are $7,000 and $10,000, respectively. Prepare a flexible budget for capacity levels of 80% and 90%.
Given:
Solution:
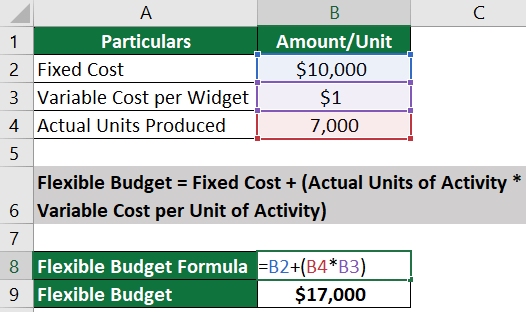
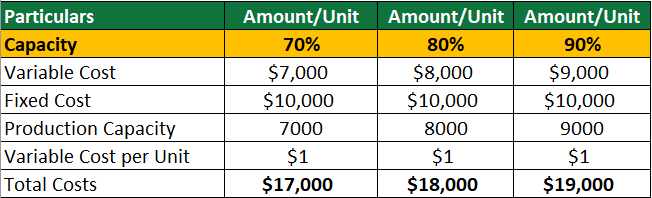
Step 1: Create an original budget at 70% capacity level (7,000 units).
Total Costs at 70% capacity = Variable Costs + Fixed Costs
= $7,000 + $10,000
= $17,000
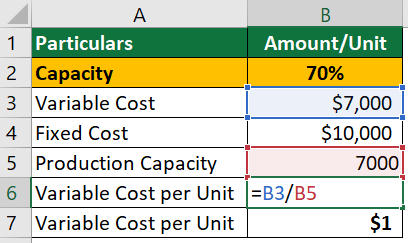
Now, let’s calculate the budgets for 80% and 90% capacity levels. For that, first, we need to find the variable cost per unit. We can calculate that as follows using variable costs for 70% capacity:
Variable Cost per Unit = $7,000 / 7,000 units = $1 per unit
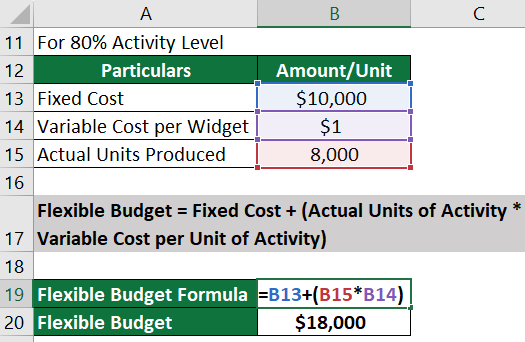
Step 2: Create a flexible budget for 80% capacity (8,000 units):
Total Costs at 80% capacity = Fixed Costs + (Variable Cost per Unit * Number of Units at 80% capacity )
= $10,000 +( $1 * 8,000)
= $18,000
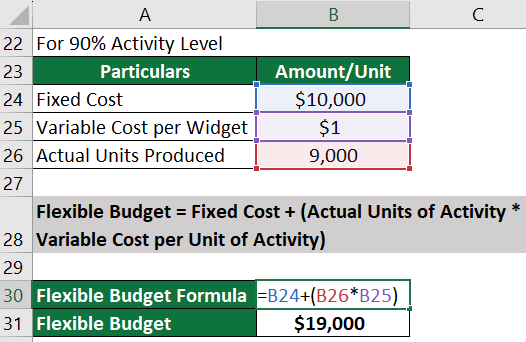
Step 3: Create a flexible budget for 90% capacity (9,000 units):
Total Costs at 90% capacity = Fixed Costs + (Variable Cost per Unit * Number of Units at 90% capacity )
= $10,000 +( $1 * 9,000)
= $19,000
Result:
An original budget at a capacity level of 70% and flexible budgets for capacity levels of 80% and 90% are as follows:
Example #2: Performing Variance Analysis
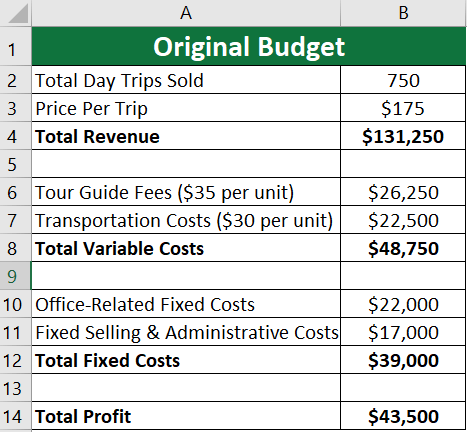
In 2022, a small travel agency in Switzerland offered guided day trips to popular Swiss destinations. Here are the financial details:
- Total Day Trips Expected Sales: 750 trips
- Price per Trip: $175
- Direct variable costs per Trip:
- Tour guide fees: $35
- Transportation costs: $30
- Fixed costs related to the office: $22,000
- Fixed selling and administrative costs: $17,000
A) Original Budget:
Based on the given information, the original budget or income statement for the travel agency for the Year 2022 will be as follows:
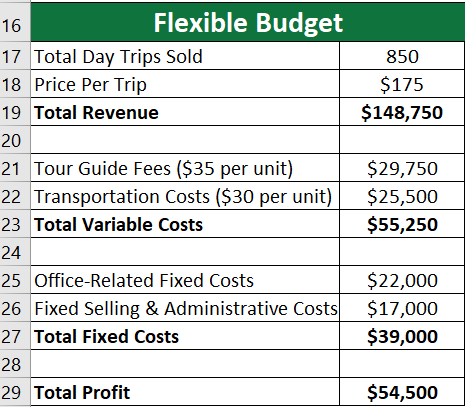
B) Flexible Budget:
The travel agency also created a flexible budget if they sold more trips than expected. They created a budget for expected day trips sold: 850.
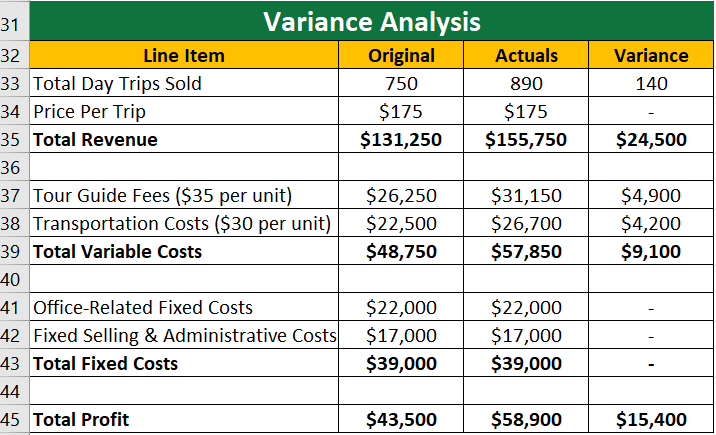
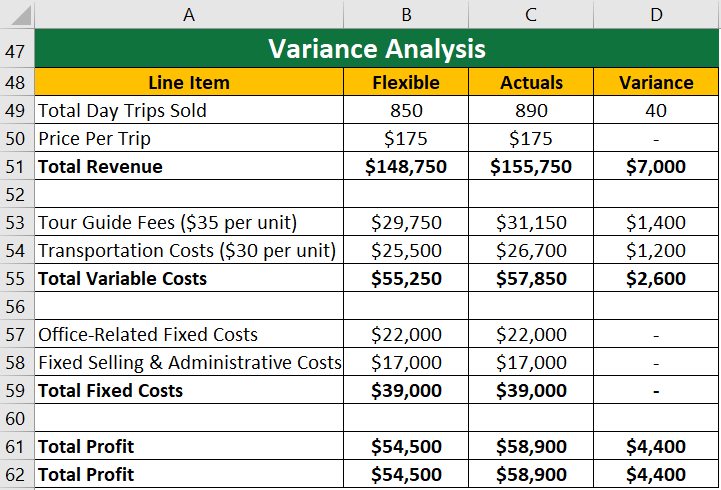
C) Variance Analysis:
At the end of the year, they actually sold 890-day trips due to higher demand. To find the variance, let us compare the original and flexible budget with the actuals.
- Variance in Original and Actuals:
- Variance in Flexible and Actuals:
As we can see above,
- The difference between the total profit from the flexible budget ($54,500) and the actual total profit ($58,900) is $4,400.
- The difference between the total profit from the original budget ($43,500) and the actual total profit ($58,900) is $15,400.
- Therefore, the flexible budgeting was more accurate than a static one.
Types
These are the three types of flexible budgets.
1. Basic
This is the simplest and most common budget for small businesses or for quick, high-level analysis. It typically adjusts the budgeted figures for one or a few key variables, such as sales volume or production levels.
2. Intermediate
Some costs do not vary with revenue. Instead, they vary based on other measures, such as electricity expenses based on consumed units. A flexible intermediate budget considers changes in costs based on such other activity measures. Thus, it provides a more accurate reflection of how costs and revenues change with fluctuations in activity.
3. Advanced
Some expenses remain the same until a particular activity level and changes after that. An advanced budget considers the cost change based on such levels, making it the most comprehensive and detailed budget. It also considers multiple variables, including changes in production volumes, sales mix, price levels, and other complex factors.
Flexible Budget Vs. Fixed Budget
Fixed (static) and flexible budgets differ in the following ways:
| Basis | Fixed Budget | Flexible Budget |
| Definition | It is static and is based on a single activity level. | It is adjustable to different levels of activity or sales volume. |
| Purpose | Planning and setting targets based on a specific sales level. | Performance evaluation and variance analysis. |
| Time Frame | Prepared at the beginning of the budgeting period. | It can be updated periodically (e.g., monthly or quarterly). |
| Flexibility | Does not adapt to changes in actual activity levels. | Adjusts to changes in activity levels. |
| Variance Analysis | Typically results in larger variances when compared to actual results. | Typically results in smaller, more meaningful variances when compared to actual results. |
| Examples | Annual budget based on a fixed sales volume projection. | Adjustable quarterly budget that adjusts projections based on actual sales. |
Advantages and Disadvantages
Following are some of the advantages and problems of a flexible budget.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It helps the management decide the output level to generate profits for the business based on budgeted costs at different activity levels. | It isn’t easy to prepare and requires experts for its preparation, especially for large organizations. |
| Businesses can allocate resources efficiently based on changing needs. | Tracking and analyzing actual performance against various budget scenarios may require more effort. |
| Variable costs can be managed better, leading to cost savings. | Some costs are not fully variable, so they require careful analysis of prices, and incorrect classification can provide inaccurate results. |
| It helps individuals adapt to unexpected financial challenges, such as medical expenses or job loss. | Requires accurate data and a good understanding of cost-activity relationships. |
Calculator
Use the following calculator to calculate a flexible budget.
| Fixed Cost | |
| Actual Units of Activity | |
| Variable Cost per Unit of Activity | |
| Flexible Budget = | |
| Flexible Budget = | Fixed Cost + (Actual Units of Activity x Variable Cost per Unit of Activity) |
| = | 0 + (0 x 0) = 0 |
Final Thoughts
In an unpredictable financial world, flexible budgets are helpful in manufacturing industries where costs change with a change in activity level. Companies must involve experts to make accurate budgets, ensuring there is less scope for error and improving variance analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Why is a flexible budget important?
Answer: A flexible budget is a crucial tool in management accounting. It helps determine what a business expects in terms of costs, income, and profits. What makes it especially valuable is that it can change based on the actual activity level. This makes it perfect for looking into the differences between what was planned and what actually happened, helping managers see how different parts of the company performed. It also helps assign responsibility within the company.
Q2. What is flexible budget variance analysis?
Answer: Flexible budget variance analysis is a technique where companies compare the actual financial outcomes to the flexible budget. This way, they can understand the reasons for any variation in the actual results. It helps firms assess the impact of changes in activity levels on their financial performance.
It provides insights into how well an organization has managed its finances in response to changing conditions and activity levels. Thus, it helps managers make informed decisions and improve budgeting processes.
Q3. Can I use a flexible budget for both short-term and long-term financial planning?
Answer: Yes, you can adapt a flexible budget for both short-term and long-term financial planning. For short-term goals, it can help individuals and businesses adjust their budgets to respond to immediate changes in income or expenses. For long-term planning, it can serve as a foundation for creating multi-year financial projections.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide on how to create a flexible budget. Here, we also discuss the definition along with its formula, examples, advantages, and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –