What Is A Flipped Classroom?
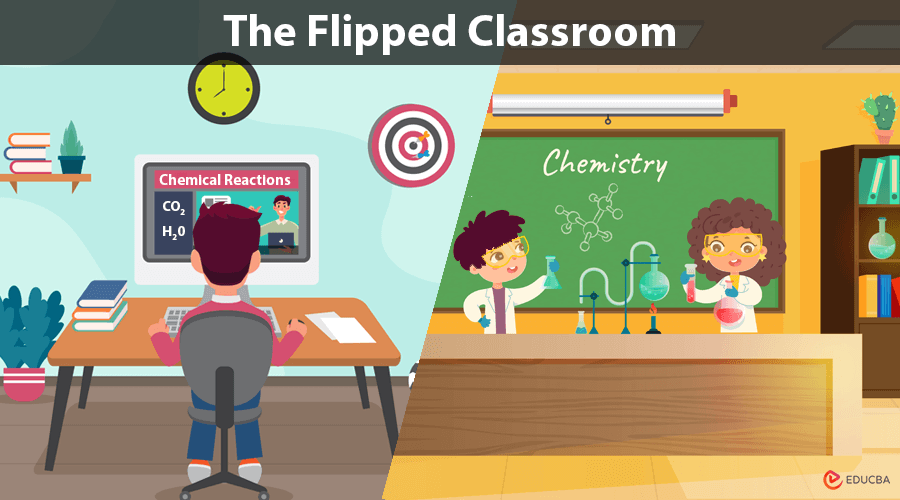
A flipped classroom is an educational model where students learn content at home through videos and engage in interactive activities in the classroom.
As education continues to evolve, traditional teaching methods are being replaced by new and innovative approaches. One such method gaining traction in both K-12 and higher education is the flipped classroom.
A classroom where traditional learning environments are “flipped.” In this model, students first engage with new content at home, usually through video lectures, readings, or online quizzes. Then, during in-class time, students apply what they have learned through discussions, problem-solving, collaborative projects, or practical exercises.
Key Features of the Flipped Classroom
The flipped classroom model incorporates several distinctive elements that differentiate it from traditional teaching methods, which are:
- Pre-Class Learning: Students watch recorded lectures or review reading materials before attending class. This enables them to learn at their own pace and revisit the material whenever necessary.
- In-Class Collaboration: Classroom time is used for group activities, peer discussions, and teacher-guided problem-solving. This promotes deeper understanding and critical thinking.
- Student-Centered Approach: The focus shifts from teacher-led instruction to student-driven learning, encouraging responsibility and independent study.
- Use of Technology: The flipped classroom often relies on educational technology, such as video lectures, learning management systems (LMS), and interactive tools, to facilitate content delivery and collaboration.
Steps to Implement the Flipped Classroom Model
Implementing a flipped classroom requires thoughtful planning, preparation, and the right resources. Here are steps to guide you through the process:
- Select Appropriate Content: Choose instructional content suitable for out-of-class learning. This could include videos, podcasts, articles, or online tutorials. Ensure the material is engaging, well-structured, and aligned with the learning objectives.
- Create Engaging Learning Materials: Prepare videos, quizzes, and assignments that keep students engaged while studying outside class. Use visuals, animations, and interactive features to make the content more dynamic.
- Utilize Digital Tools: Integrate platforms like Google Classroom, Edmodo, or Moodle to share materials, track student progress, and foster communication. Interactive tools like Kahoot! or Padlet can be used to encourage student participation during in-class activities.
- Design Interactive In-Class Activities: Emphasize activities that enable students to apply the knowledge they acquired during pre-class learning. These could include group discussions, debates, peer teaching, role-playing, and hands-on experiments.
- Monitor and Provide Feedback: Ensure that you are actively involved in guiding students through their learning process. Provide regular feedback, answer questions, and encourage discussions to clarify doubts.
Traditional Classroom vs. Flipped Classroom
Below is a table comparing traditional classroom methods with the flipped classroom approach to highlight the key differences:
| Aspect | Traditional Classroom | Flipped Classroom |
| Learning Style | Teacher-centered, lectures during class | Student-centered, pre-class learning and active class time |
| Use of Technology | Limited, mostly for research or presentations | Extensive, utilizes videos, quizzes, and online platforms |
| Classroom Time | Used for lectures and note-taking | Focused on discussions, problem-solving, and collaboration |
| Homework | Assigned after class, reinforcing material learned | Pre-class learning, engaging with instructional content at home |
| Student Engagement | Passive, listening to lectures | Active, engaging in collaborative and hands-on activities |
| Teacher’s Role | Delivering content, managing class time | Facilitating learning, guiding discussions and activities |
Challenges of the Flipped Classroom
While the flipped classroom offers several advantages, it also presents specific challenges that educators and institutions must address:
- Access to Technology: Every student cannot access the technology required to engage with pre-class materials. Institutions must ensure all students have access to necessary devices and reliable internet connectivity.
- Increased Preparation Time for Teachers: Teachers need to create or curate high-quality, engaging pre-class materials. Producing video lessons, quizzes, or other resources that align with the course content may require a significant upfront time investment.
- Student Resistance: Some students may resist the flipped model, especially if they are used to traditional lectures. Helping students adjust to the self-paced learning approach and encouraging active class participation may take time.
- Time Management: To ensure the flipped model’s effectiveness, students and teachers must be organized. Students must complete pre-class learning materials on time, and teachers must ensure that class activities are appropriately designed to maximize the interactive learning time.
Real-World Examples
Many educational institutions around the world have successfully implemented the flipped model. For example:
#1. Lynn University (Florida, USA)
Lynn University, located in Florida, is known for being one of the first institutions to fully implement the flipped classroom model across all its undergraduate courses. The university’s faculty embraced flipped learning to enhance student engagement and maximize in-person class time.
- Implementation: Instead of traditional lectures, Lynn University uses video lectures and online discussions as the primary content delivery method. This allows in-class time to focus on interactive activities like debates, group work, and hands-on exercises.
- Results: The university saw improved student engagement and better retention of material. Faculty and students reported that the model facilitated more meaningful classroom interactions and a deeper understanding of the course content.
#2. Khan Academy (Global)
Khan Academy, a widely used online platform offering educational videos, has contributed significantly to the rise of the flipped classroom model. Educators worldwide use Khan Academy’s video lessons to introduce new topics before classroom instruction, allowing for more effective in-class problem-solving.
- Implementation: Teachers assign Khan Academy videos for homework, where students learn the concepts. In class, students work through problems with teacher support, engage in discussions, and collaborate on activities.
- Results: This method has helped students gain a more comprehensive understanding of complex topics like mathematics, science, and history, as they have more time to interact with the teacher and peers during in-class sessions.
#3. The College of New Jersey (TCNJ)
At the College of New Jersey, Dr. Rachael Heller, a biology professor, taught a large introductory biology class using a flipped classroom approach. This approach combines videos, readings, and quizzes as pre-class materials, followed by problem-solving and peer collaboration during in-class time.
- Implementation: Students watch pre-recorded lectures and complete quizzes at home. In class, Dr. Heller uses active learning techniques, such as collaborative group projects and peer discussions, to apply the concepts from the videos.
- Results: This shift improved student performance, particularly in terms of retention and application of knowledge. The students reported feeling more prepared for class and better equipped to participate in discussions and group projects.
#4. The University of Colorado Boulder (USA)
The University of Colorado Boulder has advocated for flipping the classroom in its engineering courses. Professor Carol N. D. G., who teaches mechanical engineering, switched from traditional lecture methods to flipped learning to give her students more opportunities for hands-on learning.
- Implementation: Students watch lectures and engage with interactive simulations on the course website before class. They apply their knowledge during class by designing models, conducting experiments, and collaborating in teams.
- Results: The flipped model improved students’ problem-solving and critical thinking skills, as they could actively apply the theoretical concepts they had learned at home to practical, real-world scenarios.
Final Thoughts
The flipped classroom model signifies a fundamental change in how we approach teaching and learning. By prioritizing active learning, collaboration, and personalized education, the model empowers students to take charge of their learning while still receiving the guidance and support they need from their instructors. While challenges exist, the potential for improved engagement, understanding, and academic performance makes the flipped classroom an exciting and effective method for modern education.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on the flipped classroom helps you understand how this innovative teaching approach enhances student engagement and learning outcomes. Check out these recommended articles for more strategies and insights into effective classroom techniques.

