Updated July 13, 2023
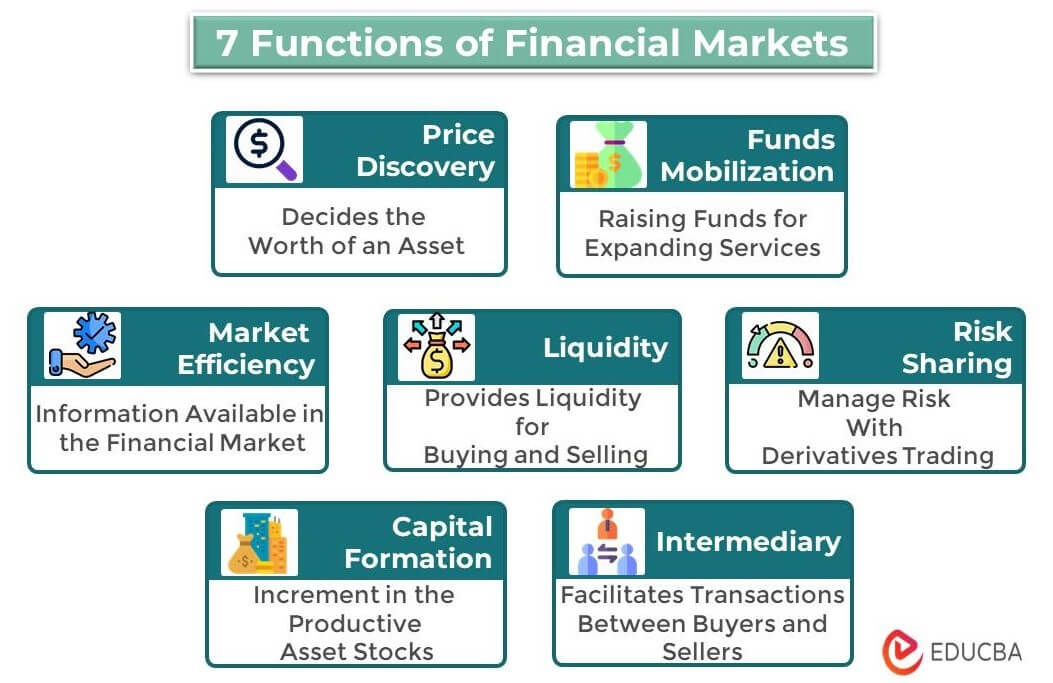
What are the Functions of Financial Markets?
The word “financial market” is a broader term used to define where buying and selling financial assets occur. In other words, the financial market refers to a virtual platform that facilitates trading financial instruments and securities. Some prominent functions of financial markets are price discovery, fun mobilization, risk sharing, etc.
All countries have financial markets, which invariably play a key role in their economic growth story. A financial market acts as the intermediary between the investors willing to invest their money and the companies needing the money to expand their business. The size of the financial markets varies across economies, wherein it is relatively smaller in developing nations but large and organized in the world’s developed economies, like NASDAQ. Nevertheless, irrespective of their size, their contribution to the economy remains the same globally.
List of Functions of Financial Markets with Examples
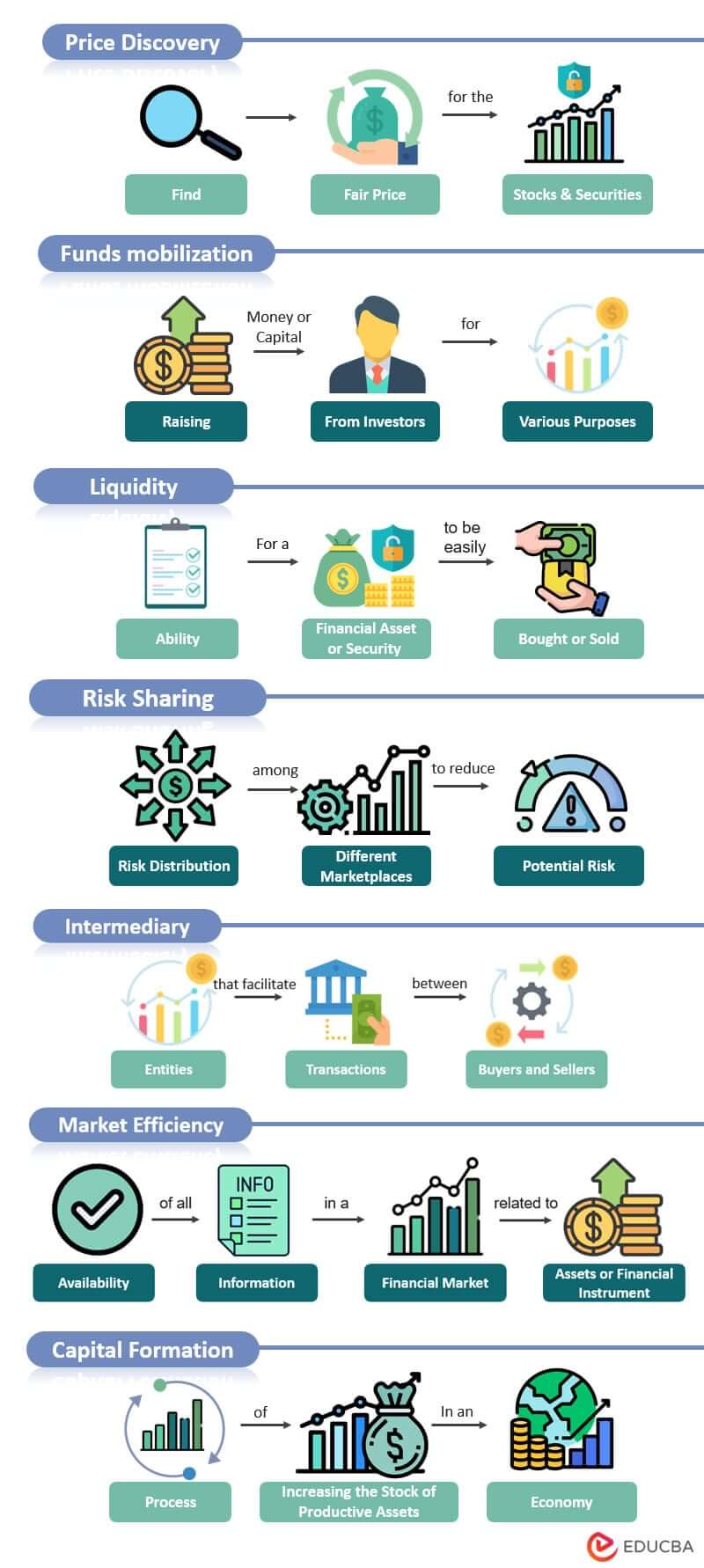
1. Price Discovery
Price discovery is a process by which people decide how much a particular product or service is worth. Imagine you have an antique clock that you want to sell. Its worth will solely rely on your assumptions and how much others are willing to pay.
The exact process applies to financial markets where prices of stocks and other securities go up or down based on how much people want to buy or sell them.
Role & Importance
| Efficient Capital Allocation | It is useful for investors to make good decisions depending on the market prices. Investors can use the market price of an asset to determine whether it is overvalued or undervalued. |
| Market Efficiency | Ensures asset prices reflect their true value, leading to productive and profitable capital allocation. |
| Risk Management | It provides information on price movements which helps investors assess and manage risk as they understand the timing of buying and selling assets. |
Example of Price Discovery
The table below shows different events for Estates Inc., contributing to the ongoing price discovery process and impact on its stock prices.
| Company Event | Stock Price Movement |
| Positive news: Successful product launch | Increase |
| Positive news: Increased profit | Increase |
| Positive news: Market expansion | Increase |
| Negative news: Decreased revenue | Decrease |
| Negative news: Lawsuit against the company | Decrease |
| Negative news: Management Fraud | Decrease |
2. Funds Mobilization
Fund mobilization is one of the functions of financial markets that refers to raising capital or money from investors or other sources for various purposes, such as funding a new project, expanding a business, or investing in financial assets.
In financial markets, funds mobilization typically occurs through various instruments such as stocks, bonds, and other securities.
When companies need funds, they have to consider the interest rates and market conditions because these factors affect the availability and cost of funds. The financial market helps decide how the money from investors is given to businesses or individuals who need it for their financial needs.
By matching investors’ savings with the capital requirements of businesses, the financial market enables the smooth movement of funds.
Role & Importance
| Capital Formation | It brings investors and borrowers together, helping businesses raise funds for growth, creating jobs, and driving economic development. |
| Diversification and Risk Spreading | Investors can invest in diversified portfolios, spread their risk, and increase potential returns. |
| Liquidity Creation | It provides investors with an easy way to buy and sell financial assets and the flexibility to convert investments into cash quickly. |
| Efficient Resource Allocation | It ensures funds for productive investments. It reflects the true underlying value of assets in the market. |
| Fosters Innovation and Growth | Supports businesses with capital for innovation, research, and development, opening new markets and opportunities for investors and fueling economic growth. |
Example of Funds Mobilization
The table below provides a step-by-step process of funds mobilization through an IPO for a startup named Fretz Inc.
| Steps | Description |
| 1. Fretz Inc. plans IPO for funding | Fretz Inc., a successful tech startup, decides to go public and raise funds through an IPO for operations and expansion. |
| 2. Fretz Inc. hires an investment bank | Fretz Inc. engages an investment bank to handle the IPO process, including due diligence, document preparation, and compliance. |
| 3. Market determines share price | The investment bank promotes shares, and investors bid based on perceived value, determining the share price through price discovery. |
| 4. Share price reflects market dynamics | High demand raises share price; low demand lowers it, with the final price driven by market forces. |
| 5. Investors purchase shares | Investors buy shares at the IPO price, providing funds to Fretz Inc. for operations, expansion, or new projects. |
| 6. Investors benefit from ownership | Investors become owners of Fretz Inc. and have the potential to earn future profits or dividends based on company performance. |
3. Liquidity
Imagine you have your money invested in bonds or shares of a company. Under normal circumstances, where the financial markets function properly, you can easily sell these investments and get your money back whenever you want.
But, without a functioning financial market, you would find it hard to sell your investments. Here, you need to wait for specific events, like the issuing company paying off the bond’s principal amount at a future date or the company shutting down.
That’s why it’s important to have a functioning market, so investors can easily buy and sell their investments whenever needed.
Roles & Importance
| Enables Easy Trading | Investors get the liberty to buy or sell at a fair price. Insufficient liquidity reduces trading and may lead to losses. |
| Enhances Price Accuracy | Due to the frequent trading of an asset, the market receives better information about its value, ensuring accurate prices. |
| Manages Risk | Quick asset selling during market stress avoids significant losses. Lack of liquidity may force selling at a loss, causing disruptions. |
| Facilitates Fundraising | Companies can raise funds by issuing securities. Confidence in easy selling attracts more investors. |
| Affects Monetary Policy | Central banks rely on market liquidity to implement monetary policy effectively. |
Example of Liquidity
Let’s examine the case of Abasin Inc., a well-established company with a large trading volume and a wide investor base, which makes its stock highly liquid. Suppose there is news about a significant change in Abasin Inc.’s financial outlook, resulting in increased buying or selling activity by investors. We will explore this situation in a highly liquid market and an illiquid market.
| Highly Liquid Market | Liquid Market |
| Easy buying and selling for investors. | Challenges in buying and selling shares. |
| Relatively stable stock prices with minor fluctuations. | Stock prices are prone to significant price swings. |
| Prompt execution of trades at fair prices. | Delays or difficulties in executing trades. |
| Market participants can confidently respond and adjust positions based on available liquidity. | Market participants may face challenges in reacting swiftly to news and adjusting positions due to a lack of liquidity. |
4. Risk Sharing
In the financial market, risk sharing refers to the distribution of risks among different market participants to decrease the impact of prospective losses. Risk sharing involves transferring risk from one party to another through various mechanisms, including insurance, hedging, diversification, and securitization.
Market participants can eliminate losses and potential risks through risk management by sharing risk. For example, a farmer can purchase crop insurance to protect against potential losses due to weather conditions.
Role & Importance
| Facilitating Investment | It facilitates investments by enabling investors to invest in projects or assets that may otherwise be too risky to undertake independently. |
| Encourages Innovation | It encourages innovation by funding new and risky ventures. Investors may invest in innovative projects if they can share the risks with others. |
| Improves Efficiency | It can also improve market efficiency by allowing investors to allocate their capital to the most efficient uses leading to increased competition, lower costs, etc. |
| Promoting Stability | It promotes financial stability by spreading risks across various investors. |
| Enhances Social Welfare | Enhances social welfare by providing access to financial markets and reducing economic inequality. |
Example of Risk Sharing
A startup tech company needs funding to develop and launch a new product. However, as a new and unproven company, it carries a high risk of failure, which makes it challenging to secure traditional financing. To mitigate this risk, the company offers convertible notes to investors. Let’s analyze the benefits and risks for both parties.
| Investor Risks | Investor Benefits | Business Risks | Business Benefits |
| Possibility of losing investment. | 1. High return on investment if the company performs well.
2. Option to convert debt into equity at a discount to the company’s valuation |
The risk of inability to pay off debt. | Access to necessary capital to develop and launch a new product. |
5. Intermediary
Companies need money to grow their businesses, and people with money (investors) want to make more money. The financial market helps these two groups connect. It provides a platform where companies can easily get the required amount to grow, and investors can find good opportunities to invest their money and seek good returns.
Role & Importance
| Information Provision | It is a useful information source for investors about the financial instruments they are trading. |
| Transaction Facilitation | It facilitates transactions between buyers and sellers by providing services, including clearing, settlement, and custody. |
| Capital Allocation | It helps allocate capital in financial markets by matching investors with borrowers seeking to raise funds. |
Example of Intermediary
Alex is an investor who wants to purchase shares in a publicly traded company. He has two options – either directly buy the shares from the company or use an intermediary like a brokerage firm to help with the transaction. Let’s explore how the second option can benefit Alex.
| Basics | Alex purchases shares directly from the company | Alex purchases shares through a brokerage firm |
| Advantages | None, except for potential cost savings. | Access to market research and analysis, transaction facilitation, custody, and settlement services. |
| Disadvantages | Time-consuming and costly. | Brokerage fees and commissions. |
| Intermediaries | None | A brokerage firm provides intermediary services between the investor and the company. |
| Market Effects | Limited impact on market efficiency, liquidity, and stability. | Promotes market efficiency, liquidity, and stability by providing investors access to various financial instruments and services. |
6. Market Efficiency
Investors need information before they invest their money. The financial market is like a big library that provides this information to investors for free. Without the financial market, investors would have to spend much time and money to get this information. But with the financial market, it’s easy to find and use the information, and this helps investors save money and make smarter investment decisions.
Roles & Importance
| Price Prediction | Market efficiency allows prices to reflect all available information, which means that prices are more accurate and reflect the actual value of a financial instrument or asset. |
| Marketplace Competition | Efficient markets promote competition by ensuring that prices reflect only genuine information. |
| Innovation & Encouragement | Encourages innovation by rewarding companies that create new and innovative financial instruments or assets which promote economic growth and development. |
Example of Market Efficiency
Ester & Co. is a publicly-traded company that recently announced the launch of a new product, expecting it to generate additional revenue. The company announced that the market would reopen the following Monday after closing on a Friday. Let’s see how we reflect this information in an efficient and inefficient market.
| Efficient Market | Inefficient Market | |
| Information | The announcement quickly affects the stock price when the market reopens on Monday. | The stock price may take days or weeks to reflect the announcement fully. |
| Investor Reaction | In anticipation of a price increase, informed investors may buy shares, while others may sell shares expecting a price decrease. | – |
| Stock Price Adjustment | The stock price adjusts to reflect the new information due to buying and selling activity. | – |
7. Capital Formation
When people save their money, it usually stays in the bank. But when investors invest their money in the financial market, they take those savings into “capital.” This capital is what businesses need to grow and become successful.
In other words, a financial market provides the channel through which the savings flow from the investors to the businesses and helps them in their capital formation.
Role & Importance
| Investment Opportunities | It allows individuals and companies to invest their savings and capital in these productive assets. |
| Innovation | It encourages innovation by providing funding for research and development. |
| More Job Creation | In a financial market, capital formation promotes job creation by funding new businesses and infrastructure projects. |
| Long-term Planning | It allows individuals and companies to make long-term plans and investments. |
Example of Capital Formation
| Scenario | A biotech company needs funds to develop a life-saving medicine |
| Financial Market Role | Acts as a platform for investors for the biotech firm |
| Investor Contribution | Investors give money in exchange for shares in the company |
| Company Benefit | The company receives funds to hire scientists and conduct research |
| Investor Benefit | Investors have the potential to earn returns as the company grows |
| Overall Outcome | The financial market connects investors to the biotech firm, enabling company growth and offering investment opportunities. |
Functions of Financial Markets Infographic
Recommended Articles
It was a comprehensive guide to the seven functions of financial markets. We discussed each type with suitable examples, importance, and roles. To learn more, you may have a look at some similar articles: