Updated July 24, 2023
Difference Between Futures vs Forward
Future is a traded contract on the future exchange, while forwards are customized private agreements that are privately traded over the counter and not on the future exchange. A futures contract is publically quoted and traded on the futures exchange, whereas the customer and the supplier directly negotiate a forward contract. A futures contract is standardized, and it is generally used for the purpose of speculation, whereas a forward contract is customized as per the needs of the buyers and is generally used for the purpose of hedging. The government regulates a futures contract. CFTC (the Commodity Futures Trading Commission) governs the futures contract market, whereas the government or any governing body does not regulate forwards contract. A futures contract has a lower rate of counterparty risk, whereas a forward contract has a higher rate of counterparty risk.
The expiry date and the contract size of a futures contract are standardized, whereas the expiry date and the contract size of a forwards contract completely depend on the financial transaction as well as the requirements quoted by the parties to a particular transaction. Futures contracts are standardized, whereas forwards contracts are over-the-counter (OTC) contracts. Futures contracts are settled on the maturity date, whereas forwards contracts are settled on a daily basis. Futures contracts are highly liquid as compared to forwards contracts. In a futures contract, the settlement is made on a daily basis, whereas, in a forwards contract, the settlement will take place at the end of a particular period.
Head To Head Comparison Between Futures vs Forward (Infographics)
Below are the top 19 differences between Futures vs Forward
Key Differences Between Futures vs Forward
The key differences between a futures and forwards contract are provided and discussed as follows-
- A futures contract is publically traded on the futures exchange, whereas forwards contract is privately traded between the participants of an agreement.
- Futures contracts are less expensive whereas forwards contract is more expensive.
- The size of future contracts is fixed, whereas the size of a forwards contract depends on the transaction as well as the terms of the contracting parties.
- The payment date of future contracts is fixed, whereas the payment date of a forwards contract depends on the transaction as well as the terms of the contracting parties.
- Futures contracts are less risky as compared to the forward’s contract.
- Futures comprise of the delivery mechanism, contract size and dates, whereas forwards are tailor-made contracts.
- Futures are publically traded, whereas forwards are privately traded.
- Futures are traded on the futures exchange, whereas forwards are traded over the counter (OTC).
- Futures are highly liquid in comparison to forwards.
- Futures are regulated by the CFTC (the Commodity Futures Trading Commission), whereas forwards are unregulated.
- There is a need to make an initial margin payment in the future, whereas there is no need to make an initial margin payment in the forwards.
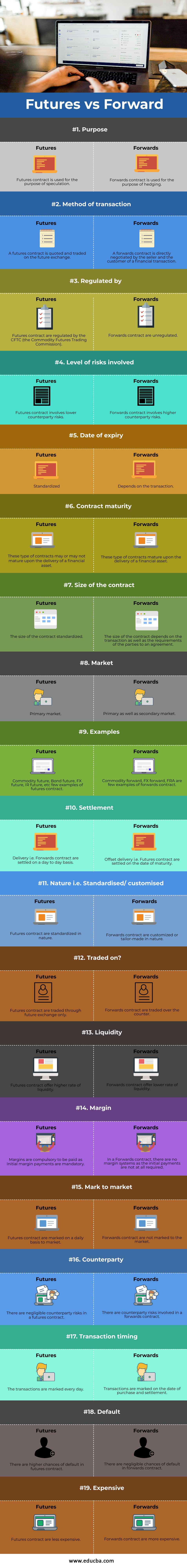
Futures vs Forward Comparison table
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Futures vs Forward:
|
Basis of Comparison |
Futures |
Forward |
| Purpose | A futures contract is used for the purpose of speculation. | Forwards contract is used for the purpose of hedging. |
| Method of transaction | A futures contract is quoted and traded on the futures exchange. | A forwards contract is directly negotiated by the seller and the customer of a financial transaction. |
| Regulated by | Futures contracts are regulated by the CFTC (the Commodity Futures Trading Commission). | Forwards contract are unregulated. |
| Level of risks involved | Futures contract involves lower counterparty risks. | Forwards contract involves higher counterparty risks. |
| Date of expiry | Standardized | It depends on the transaction. |
| Contract maturity | These types of contracts may or may not mature upon the delivery of a financial asset. | These types of contracts mature upon the delivery of a financial asset. |
| Size of the contract | The size of the contract standardized. | The size of the contract depends on the transaction as well as the requirements of the parties to an agreement. |
| Market | Primary market. | Primary as well as the secondary market. |
| Examples | Commodity future, Bond future, FX future, IR future, etc. few examples of a futures contract. | Commodity forward, FX forward, FRA are few examples of forwards contract. |
| Settlement | Delivery, i.e. Forwards contract, is settled on a day to day basis. | Offset delivery, i.e. Futures contract, are settled on the date of maturity. |
| Nature i.e. Standardised/ customised | Futures contract are standardized in nature. | The forwards contract is customized or tailor-made in nature. |
| Traded on? | Futures contracts are traded through futures exchange only. | Forwards contract are traded over the counter. |
| Liquidity | Futures contract offer a higher rate of liquidity. | Forwards contracts offer a lower rate of liquidity. |
| Margin | Margins are compulsory to be paid as Initial margin payments are mandatory. | In a forwards contract, there are no margin systems as the initial payments are not at all required. |
| Mark to market | Futures contracts are marked on a daily basis to market. | Forwards contracts are not marked to the market. |
| Counterparty | There are negligible counterparty risks in a futures contract. | There are counterparty risks involved in a forwards contract. |
| Transaction timing | The transactions are marked every day. | Transactions are marked on the date of purchase and settlement. |
| Default | There are higher chances of default in futures contracts. | There are negligible chances of default in a forwards contract. |
| Expensive | Futures contract are less expensive. | Forwards contract is more expensive. |
Conclusion
A futures contract can be defined as a contract in which there is an agreement between the parties for the purpose of exchanging a financial asset against cash at a pre-determined price and at a specified date in the nearing time. On the other hand, forwards contracts can be defined as a contractual agreement between the parties to buy and sell the underlying financial assets at a mutually agreed rate and at a future specified date. A futures contract is traded publically on the exchange, whereas a forward contract is privately traded over the counter. Futures contract are fixed and highly liquid, whereas forwards contracts are customized and offer a lower level of liquidity in comparison to the former. A futures contract involves lower counterparty risks, whereas forwards contract involves higher counterparty risks.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the top difference between Futures vs Forward. Here we also discuss the Futures vs Forward key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –