Introduction to AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are popular cloud computing platforms with their unique offerings in infrastructure, networking, and machine learning services. The following article outlines the differences between AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud.
AWS, or Amazon Web Services, is a cloud computing platform that was launched in 2002 and re-launched in 2006. It offers different services, such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). It also offers public and private cloud networks, with the ability to isolate networks in a virtual private cloud. Furthermore, AWS allows the creation of subnets, private IP addresses, network gateways, and route tables.
Microsoft’s cloud computing platform, Azure, was initially released in 2010 and supports Linux and Microsoft Windows operating systems. It provides IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS services and allows for building, deploying, testing, and managing applications. Azure allows users to select the Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) machine that can be configured by Microsoft, the user, or a third party.
Google Cloud is a cloud computing platform released by Google in 2008. It offers IaaS, PaaS, and serverless platforms. Google Cloud is categorized into different platforms, such as Google App Engine, Google Compute Engine, Google Cloud Datastore, Google Cloud Storage, Google BigQuery, and Google Cloud SQL. Users can select their desired configuration, and Google Cloud provides temporary storage, various frameworks, programming languages, and databases.
Head-to-Head Comparison (Infographics): AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud:
Below are the top 14 differences between AWS and Azure and Google Cloud:
Key Differences: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
- AWS provides instances of virtual servers and virtual machines, while Azure provides virtual hard disks, and Google Cloud provides virtual machine instances.
- AWS instances can be purchased in any of the following models: On-demand, Reserved, and Spot. An Azure instance can be bought in any of the models: On-demand and short-term commitments. For Google Cloud, it can be purchased in On-demand and sustained-use models.
- AWS charges its users per hour using a pay-as-you-go model. Azure charges its customers per minute, and Google Cloud charges its customers per minute as well.
- In AWS, ECS is used for Docker management, while Azure uses Container Service for the same purpose. Google Container Engine is used for Docker management in Google Cloud.
- For archive storage, AWS uses Glacier, Azure uses Archive Storage, and Google Cloud uses Coldline.
- For search services, AWS uses Amazon CloudSearch, Azure uses Azure Search, and Google Cloud does not have a similar service.
- As for analytics, AWS uses Amazon Kinesis, Azure uses Azure Stream Analytics, and Google Cloud uses Cloud Dataflow and Cloud Data Preparation.
- For automation, AWS uses AWS OpsWorks and AWS Config, Azure uses Azure Automation, and Google Cloud uses Compute Engine management with Puppet, Chef, etc.
- In AWS, AWS cloud HSM is being used for Compliance. Azure trust center is being used for Azure and googles cloud platform security for compliance. For compliance, AWS uses AWS CloudHSM, Azure uses Azure Trust Center, and Google Cloud Platform uses its own security measures.
- In AWS, the AWS Key Management Service is used for managing security credentials. For Azure, the Azure Key Vault is used, and for Google Cloud Platform, the Google Cloud Security is used for managing security credentials.
Comparison Table-
| The basis of comparison |
AWS |
Microsoft Azure |
Google Cloud |
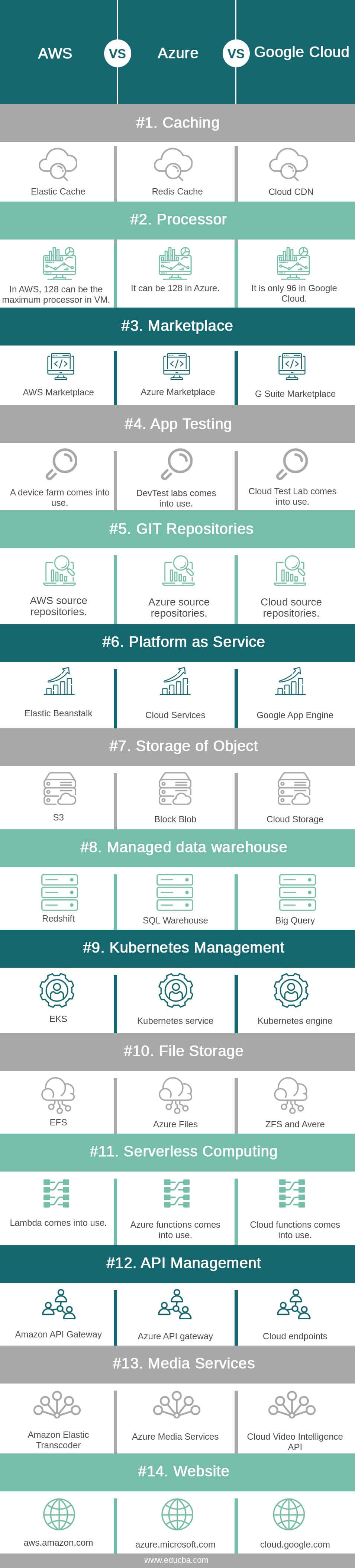
| Caching | Elastic Cache | Redis Cache | Cloud CDN |
| Processor | In AWS, 128 can be the maximum processor in a VM. | It can be 128 in Azure | It is only 96 in Google Cloud |
| Marketplace | AWS Marketplace | Azure Marketplace | G Suite Marketplace |
| App Testing | A device farm comes into use. | DevTest labs come into use. | Cloud Test Lab comes into use. |
| GIT Repositories | AWS source repositories | Azure source repositories | Cloud source repositories |
| Platform as service | Elastic Beanstalk | Cloud Services | Google App Engine |
| Storage of Object | S3 | Block Blob | Cloud Storage |
| Managed data warehouse | Redshift | SQL Warehouse | Big Query |
| Kubernetes Management | EKS | Kubernetes service | Kubernetes engine |
| File Storage | EFS | Azure Files | ZFS and Avere |
| Serverless computing | Lambda comes into use. | Azure functions come into use. | Cloud functions come into use. |
| API management | Amazon API Gateway | Azure API gateway | Cloud endpoints |
| Media services | Amazon Elastic Transcoder | Azure Media Services | Cloud Video Intelligence API |
| Website | aws.amazon.com | azure.microsoft.com | cloud.google.com |
Conclusion
AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud are all used for the same purpose, providing similar services that support all platforms, operating systems, and structures. While there are differences between them, some features only differ in name but have similar functionality. To select the best cloud platform, opt for the free trial version of each and determine which suits your requirements most effectively. This means using and choosing the most suitable one.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further articles for expanding understanding: