Updated July 21, 2023
What is General Ledger Accounting?
The general ledger is a set of accounts that records the day-to-day transactions of a business entity by using the double-entry accounting method.
The accounting for the general ledger is a summary of all the subsidiary ledger in which all the transaction has been recorded. Each transaction has two parts one is debit and one is credit, and a total debit balance of the general ledger will always match with a total credit balance.
General Ledger Accounting Types
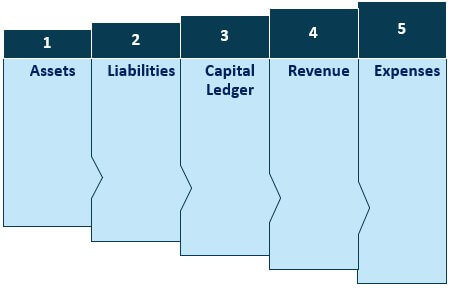
1. Assets
All types of assets owned and used by the entity for business operations are recorded under assets. It may be current or non-current, tangible or intangible. This ledger includes cash, bank, land & building, debtors, Plant & Machinery, Copyright, Trademark, Furniture & fixture.
2. Liabilities
This ledger pertains to the entity’s financial obligation to the outside. This also includes current liabilities & non-current liabilities. This sub-ledger includes creditors, long-term borrowings, and short-term borrowing.
3. Capital Ledger
This ledger pertains to the money invested in the entity. This includes equity, general reserve, and retained earnings out of the profit. Drawing will also fall under this ledger.
4. Revenue
This ledger pertains to the income earned by the company either from the entity’s main business or other sources. This includes income from sales, interest, discount received, dividends, and investment (Capital Gains).
5. Expenses
This ledger pertains to all expenses incurred by the entity for the business operation. It may be direct expenses or indirect expenses. Direct expenses include a purchase account where the cost of raw materials has been posted and indirect expenses include day-to-day operational expenses like rent, electricity, maintenance & other utility expenses.
Benefits of General Ledger Accounting
- It helps prepare trial balances, an essential requirement for preparing financial statements.
- This will provide the financial position of the business entity at any point in time because, in the general ledger, all items are recorded separately according to nature.
- This is prepared by using the double-entry method of accounting. Therefore, the chances of mistakes are very minimum.
- It also facilitates bank reconciliation because all the bank-related transactions are posted in one place.
- In General ledger accounting, all the transactions are recorded in separate heads. This helps in analysis and comparison with last year; accordingly, measures can be taken for the future.
- This also helps in preparing accounting ratios and ratio analysis.
- With the help of a general ledger amount receivable from debtors, the amount payable to creditors can be ascertained at any time.
How Does it Work?
Step 1: Since General Ledger works on a double-entry accounting system, it must first post journal entries for every transaction.
Step 2: In double-entry accounting, below are the rules for posting the entry:
- If assets increase, then assets will be debited similarly; if assets decrease, then they will be credited
- If liability increases, it will be credited; if it decreases, it will be debited.
- The capital account always has a credit balance
- Expenses will be debited, and income will be credited.
Step 3: For every transaction, two accounts will be affected for sales one revenue account and another cash/bank account.
Step 4: Similarly, all the transactions will be posted in the above manner over the period.
Step 5: At the end of the year, the ledger balance will be transferred to the trial balance, and all the ledgers will be closed.
Step 6: After transferring all the ledger balance into the trial balance, the total debit balance of the trial balance will be equal to the total credit balance
Step 7: If there is a difference between the debit balance and credit balance, there must be mistakes during the balance transfer from the ledger to the trial balance, or there is an error in a posting journal entry in the general ledger.
Step 8: After preparation of the trial balance, the Balance sheet and profit & loss account will be prepared.
Example
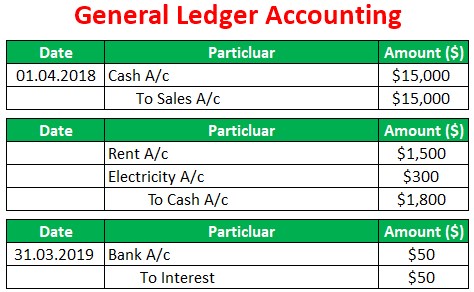
Apple Inc has a business of laptops & computers, and as of 01.04.2018, Apple Inc has sold 100 laptops @150 each for $ 15000; Apple Inc has received interest of $50 on 31.03.2019 and Incurred expenses of rent of $ 1500, the electricity of $300.then below journal entry will be passed and posted in the general ledger:
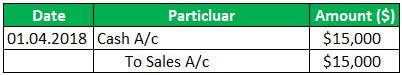
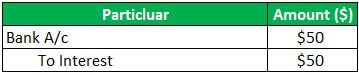
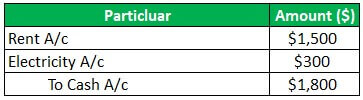
Now the above Entry will Reflect in General Ledger in below Manner:
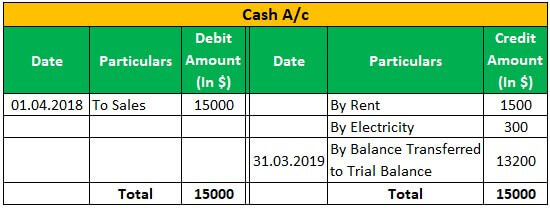
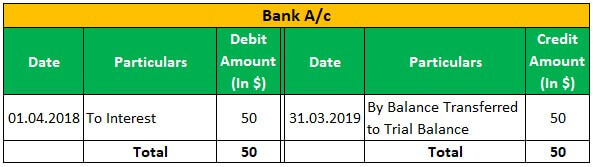
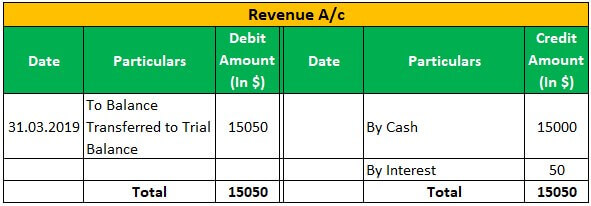
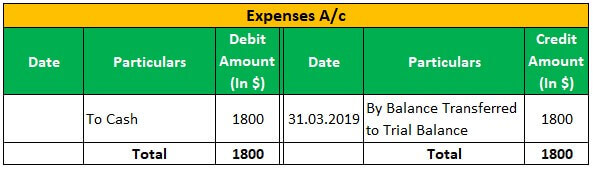
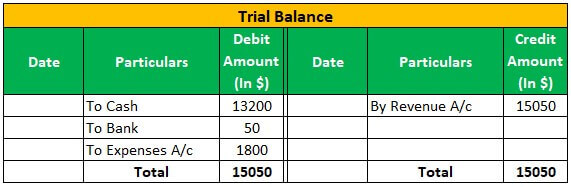
Conclusion
- In modern business settings, the general ledger functions as a book where defined rules are used to record financial transactions, enabling it to provide the entity’s financial position at any given time. Due to the large scale and division of responsibilities in today’s businesses, this accounting method is employed to manage the recording of transactions.
- It also helps prepare the trial balance, profit & loss account, and balance sheet. At the same time, this requires skilled manpower to maintain these transactions; therefore, this is a costly affair also.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What general ledger accounting is. Here we discuss the types of general ledger accounting and how it works, along with examples and benefits. You can learn more about it from the following articles –


