Updated March 27, 2023

Introduction to Generalization in DBMS
Generalization can be described as a method used to create a general entity by picking all the common attributes from other entities in the Database Management System. Hence this resulting entity is called a Generalized Entity for that particular Database. This is achieved by following the bottom-up approach in the hierarchy of the entities.
If any two entities in the bottom-most layer have common attributes, that attribute can be picked out to form a Generalized Entity. If an already generalized entity has any common attribute with any other entity, that attribute can further be processed to derive another new generalized entity. This flow can continue until all the common attributes are processed into separate generalized entities in the database management system.
Reasons for Choosing Generalization
For any given scenario, in turn, to create a database management system, a conceptual data model needs to be created. This Model is known as the Entity-Relationship model or an ER Model. This Model gives a high-level conceptual figure that has the real-world entities as its foundation. This ER Model helps in understanding the relationship between the entities, as the name implies.
Basically, this helps the Database Architect to define, analyze and differentiate the data and the related requirements thoroughly, so as to construct a smart and systematic database management system. Generalization is applied on to the ER Model in an attempt to identify the common attributes in the Entities in each level of the hierarchy of the ER diagram.
As this is a bottom-up approach, the flow gets started from the lowest hierarchy of the diagram, heading towards the higher levels until the topmost level of the hierarchy. Generalizing the attributes to form a single generalized entity facilitates in identifying the columns most required for each table in the database management system. Generalization is a significant step to establish a relationship between the tables, by analyzing and making use of all the attributes related to the entities in the hierarchical system.
Implementation of Generalization
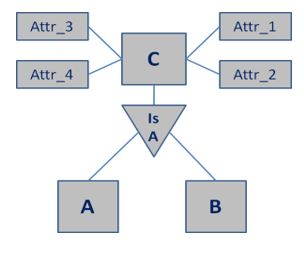
Here are the basic steps to be covered for implementing generalization in a DBMS, explained using the below ER Model (Fig. 01),
Fig. 01
- Analyze the existing real-time Entities A and B for all the possible attributes it can possess.
- Identify the common attributes that describe the characteristics of A and B Entities, which can have the same values in the table.
- Derive a separate Entity C, which is termed as the generalized entity here in Fig. 01, to hold the common attributes of A and B.
- This Entity C can be further branched out to mark all the common attributes, that are, Attr_1, Attr_2, Attr_3 & Attr_4 in Fig. 01.
- If any other Entity in the ER Model has another common attribute with the Entity C, that can be further broken down to form another Generalized Entity in the System.
Deeper Explanation with Example
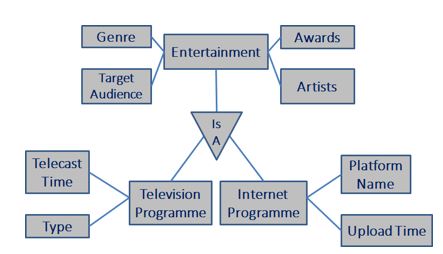
Let us consider the below Example (Fig. 02) to get a deeper understanding of the Generalization process in a Database Management System.
Fig. 02
In this example, we are picking the entertainment media as the subject, which has two main Entities, such as Television Programmes and Internet Programmes. The Entity Television Programme can have multiple attributes, like Genre on which a particular programme falls in, the Target Audience for each programme, the Awards that it has received or getting nominated to, the list of Artists or the main Artist who acts as a face of that particular programme, telecast time on the television, the type of the programme can be comedy or news or a television series, public ratings, critics approval ratings, etc.
While on the other hand, the Entity Internet programme can also have multiple attributes, like the Platform that they are using in the Internet, again the Genre on which the programme falls in, the target audience for each programme differs in Internet programmes as well, the type of Awards presented to Internet Programmes, the Artist name who runs the programme or who acts as the face of the programme, the time of upload on the Internet, number of views, likes and share the programmes gets from the Audiences, watcher’s ratings, ratings in feedback forums, etc. Both these entities have a few common attributes. Hence it can be created as new generalized entities for covering only those common attributes.
In this case, the generalized entity is named as Entertainment. The common Attributes that fall under Entertainment are the Genre under which the programmes can be categorized into, the type of Audience or the target audience for all the programmes can be attributed under generalized entity as well, the awards type can be generalized as both the Entities are subjected to Awards, Artists can be generalized as the same artist can be working a television programme and the internet programme as well. If in future any new attributes or entities added to the DBMS, that can be further generalized by evaluating it with all the three entities.
Significance of Generalization in DBMS
Below are the significant features of applying the Generalization method in a Database Management System:
- Generalization of Entities helps in establishing relationships between the tables, as they have common attributes to be identified.
- It makes the structuring of the database management simpler and easy to identify all the relevant attributes.
- By segregating the common attributes and creating a generalized entity, the repetition of data is avoided, as there is no need to mention the same attribute and data in two different tables. Instead, it can be pulled from the generalized entity table.
- Bottom-up approach aids in concentrating more on the details like the attributes, instead of the high-level entities in the Database.
Conclusion – Generalization in DBMS
In this generalization method, the entities in the higher level of the Entity-Relationship Model can also be merged with other entities in the lower level of the hierarchy, in order to make adding more entities in the higher level. This provides scalability, as the newly formed generalized entity can be generalized again in the future if and when the requirement occurs.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Generalization in DBMS. Here we discuss the introduction, implementation, significance and reasons for choosing generalization. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –