What is the Gig Economy?
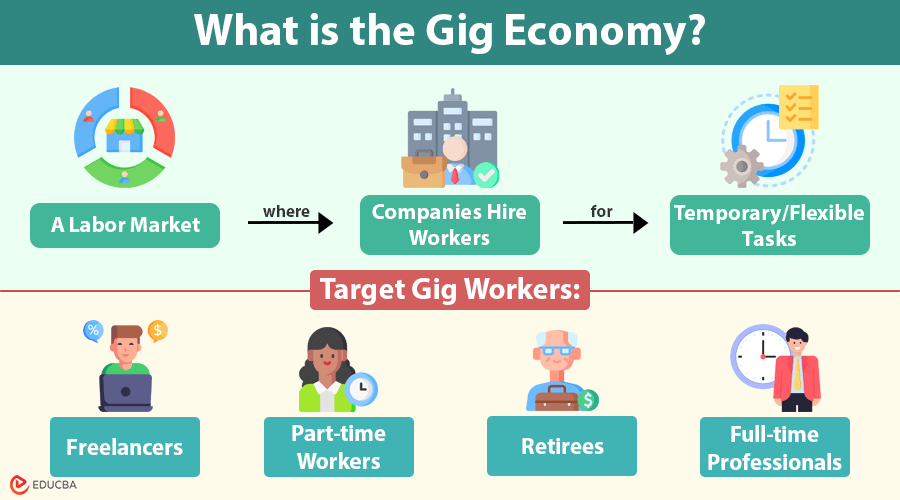
The gig economy is a labor market marked by temporary, flexible work, which is common, and companies hire people for specific tasks or projects instead of offering full-time employment. Gig workers are often self-employed, working as freelancers or contractors. They can choose when, where, and how much they want to work.
Table of Content
- Meaning
- How does it work?
- Benefits
- Challenges
- Who works in it?
- Popular Platforms
- Impacts
- How to succeed?
- Gig Economy vs. Traditional Employment
- Future
How Does the Gig Economy Work?
Online platforms often facilitate short-term, flexible jobs or freelance work in the gig economy. Here is how it works step by step:
- Job Creation: Companies or individuals post jobs or tasks (gigs) on platforms like Uber, Fiverr, or TaskRabbit.
- Worker Registration: Independent workers (gig workers) sign up on these platforms and create profiles showcasing their skills.
- Task Selection: Gig workers browse available tasks and select those that match their skills, location, or availability.
- Agreement: Once workers accept a gig, they agree on the payment and terms (often automatically set by the platform).
- Task Completion: The gig worker completes the job, which can range from ride-sharing to freelance writing or home repairs.
- Payment: After completing the task, the platform processes the payment, usually taking a commission, and sends the remaining amount to the worker.
- Rating/Review: Both the worker and the employer rate each other, influencing future opportunities.
Benefits of the Gig Economy
- Flexibility: Gig workers can decide when and where to work, making balancing work and personal life easier.
- Variety of Jobs: Gig workers can explore different jobs and earn money from multiple sources instead of being stuck in a single job.
- Independence: Gig workers often enjoy the freedom of being their boss and choosing the tasks they want to take on.
Challenges of the Gig Economy
- Lack of Job Security: Since gig workers do not have long-term contracts, they can face uncertainty regarding job availability. Work might be inconsistent, and there is no guarantee of regular income.
- No Employee Benefits: Gig workers do not receive traditional benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, or paid leave, which are common for full-time employees.
- Pressure to Keep Working: Some gig workers feel pressure to work long hours to make ends meet, as their earnings depend on how much they work.
Who Works in the Gig Economy?
The gig economy attracts a wide range of people from various backgrounds. While many associate gigs work with younger people or students looking for extra cash, they are not limited to one group.
- Freelancers: People with specialized skills, such as graphic designers, writers, or developers, often find freelancing a good way to earn a living.
- Part-time Workers: Those seeking flexible hours or a second income often do gig work.
- Retirees: Some retirees take gig jobs to stay active or earn extra money.
- Full-time Professionals: Some experienced professionals work in the gig economy full-time, taking on multiple projects from different clients.
The gig economy offers something for almost everyone, regardless of age or background.
Popular Platforms in the Gig Economy
There are numerous platforms where gig workers can find jobs, depending on their skills and interests. Some of the most popular ones include:
- Uber/Lyft – For ride-sharing drivers.
- Upwork/Freelancer – For freelance writing, design, and programming professionals.
- Fiverr – A platform for selling creative services like video editing, graphic design, and voiceovers.
- TaskRabbit – For people offering handyman services, cleaning, and other practical tasks.
- Airbnb – For people who rent out their homes or rooms to travelers.
These platforms act as middlemen, connecting workers with clients and managing payments, ratings, and reviews.
Impact of the Gig Economy on Businesses
For businesses, the gig economy provides flexibility and helps save costs. Companies can hire on-demand workers, reducing the need for full-time employees and lowering overhead costs. This is especially helpful for industries that experience seasonal or project-based fluctuations in demand.
Some key benefits for businesses include:
- Cost Savings: No need to provide employee benefits or pay salaries.
- Scalability: Businesses can easily adjust their size based on demand.
- Access to Global Talent: Companies can hire workers worldwide, giving them access to a diverse skill pool.
However, businesses must also manage the challenges of working with gig workers, such as maintaining quality and ensuring timely delivery.
How to Succeed in the Gig Economy?
If you are thinking about joining the gig economy, here are a few tips to succeed:
- Build Your Network: Whether through social media, freelance platforms, or word-of-mouth, building a network of clients can lead to more consistent work.
- Develop Specialized Skills: Gig workers with specialized skills, such as digital marketing, programming, or graphic design, often earn higher rates.
- Manage Your Finances: Since income can be unpredictable, managing your money carefully is important. Set aside savings for lean months and pay attention to taxes.
- Stay Organized: Juggling multiple gigs can be challenging. Use tools like calendars and project management apps to keep track of deadlines and tasks.
Success in the gig economy often comes down to the ability to market yourself, manage time effectively, and deliver quality work.
Gig Economy vs. Traditional Employment
It is helpful to compare gig work with traditional jobs to understand the differences better. Here is how they stack up:
| Feature | Gig Economy | Traditional Employment |
| Job Type | Temporary, freelance | Permanent, full-time |
| Work Schedule | Flexible, self-chosen | Fixed hours, set schedule |
| Income | Varies per job/task | Steady salary or hourly wage |
| Benefits | None (usually) | Health insurance, paid leave, retirement plans |
| Job Security | Low, task-based | High, long-term employment |
While traditional jobs offer more stability and benefits, gig economy work offers more flexibility and independence.
Is the Gig Economy Here to Stay?
Given its growth in recent years, the gig economy is a lasting trend. Many people enjoy the flexibility it offers, and businesses benefit from having access to a wide talent pool without the costs of full-time employees.
However, some challenges must be addressed, especially regarding workers’ rights and protections. As the gig economy grows, governments will likely step in to provide more regulation to ensure that workers have fair wages and access to benefits like healthcare and retirement savings.
Final Thoughts
The gig economy is transforming the way people work and businesses operate. It offers flexibility, independence, and a chance for workers to earn money on their terms. However, it also comes with challenges like lack of job security and benefits. As more people and businesses participate, finding the right balance between freedom and protection will be crucial in shaping the future of work. Whether you are considering joining the gig economy or just curious about its impact, it is clear that this trend is here to stay.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Do gig workers pay taxes?
Answer: Yes, gig workers are responsible for their taxes. Since they are independent contractors, they must report their earnings and may need to pay self-employment taxes, depending on their income.
Q2. How do platforms ensure quality work from gig workers?
Answer: Many platforms rely on ratings and reviews from clients to ensure quality. After completing each task, clients rate the worker, and vice versa. This helps maintain accountability, as workers with consistently high ratings are more likely to receive future opportunities.
Q3. Is the gig economy only for digital or online jobs?
Answer: No, the gig economy includes digital (e.g., freelance writing, coding, graphic design) and offline (e.g., dog walking, cleaning, moving services) work. It covers various industries, allowing people to find gigs that match their skills online or in person.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on the gig economy has been helpful. Check out these recommended articles for more insights on freelancing, remote work, and business trends.