Updated April 13, 2023

Definition of Golang Interfaces
The interface gives the developer flexibility where they can write a code in such a way that whoever will use the interface they will define the methods of the interface inside them according to their uses. In golang interface generally considered the custom type where we have to define a signature for the methods (Here signature of the method means we do not have to define the purpose of the method only we need to mention the name and type of the method), one important thing about the interface is whoever is using the interface they need to use all the method of the interface else it will through an error and will not allow for further execution.
Syntax
We can explain the concept of the below syntax in the following steps.
- First, we have to define the type of the interface, here type is a keyword which we need to write before the name of the interface.
- Second, we have mentioned the name of the interface.
- Finally, inside the interface, we need to write the signature of the method with the data type.
- We need to note the point that whoever is using this interface needs to define all the method signatures mentioned inside the interface.
type name_of_interface interface{
Method1 data type
Method 2 data type
}How do Interfaces Work in Go?
The interface is useful because once we write any interface, anyone can use the methods of the interface and define the purpose of the method according to their requirement. Let us understand the working of the interface in the go language, we can explain the working of the interface in go language in the following steps.
- First, we need to write the keyword type, once we write the keyword type go compiler will expect an interface name.
- After writing the type we need to mention the name of the interface.
- The name of the interface should be always relevant to the purpose of the interface.
- The interface always contains the signature or simply the abstract method.
- This means the interface only contains the name of the method along with the data type for the methods.
- If anyone is trying to use these methods of the interface then they need to mention all the methods of the interface inside them.
Examples of Golang Interfaces
Let us understand the concept of the interface in go language with some real-world examples.
Example #1
Create a file with a name interface.go and paste the below command and run the command go run the interface. In the below example we are creating an interface X, and this interface contains a method signature method1. Here method1 does not contain the definition of the method. Whoever will use this interface need to define the interface method definition.
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
type X interface {
method1()
}
type Test struct {
String string
}
func (tr Test) method1() {
fmt.Println(tr.String)
}
// Defining the main method
func main() {
var j X = Test{"How are you friend"}
j.method1()
}Output:
Example #2
Create a file with name interface.go and paste the below command and run the command go run the interface. In the below example we have defined an interface with the name tank dimension. This interface contains a few methods with only the signature of the methods. This means the interface contains two methods GetArea and GetVolume.These two methods are for calculating area and volume.
Code:
package main
import "fmt"
// Here we are creating an interface
type tankDimension interface {
// Methods signature with data types of the methods .
GetArea() float64
GetVolume() float64
}
//Defining the data section which will contain the radius and height variables .
type data struct {
r float64
h float64
}
// Using the methods here
// tankDimension interface
func (d data) GetArea() float64 {
return 2*d.r*d.h +
2*3.14*d.r*d.r
}
func (d data) GetVolume() float64 {
return 3.14 * d.r * d.r * d.h
}
// Defining the main method
func main() {
// Here we are trying to access the elements or attributes
// Creating a tankDimension interface
var tank tankDimension
tank = data{10, 14}
fmt.Println("The area for given tank is :", tank.GetArea())
fmt.Println("THe Volume for given tank is :", tank.GetVolume())
}Output:
Example #3
Create a file with name interface.go and paste the below command and run the command go run the interface. Below is an example where we are focusing on the types.
Code:
// Below example is displaying about the type assertions
package main
import "fmt"
func funcExample(interf interface{}) {
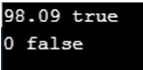
val, ok1 := interf.(float64)
fmt.Println(val, ok1)
}
// Defining the main method
func main() {
var inter interface {
} = 98.09
funcExample(inter)
var intrf interface {
} = "TesteInterface"
funcExample(intrf)
}Output:
Example #4
Create a file with name interface.go and paste the below command and run the command go run the interface. Here we are mixing the switch cases with the interface. Switch case contains where we are checking the types of the called interface method and if the type matched it enters into that particular switch case.
Code:
// Here we are using example of interface with switch cases
package main
import "fmt"
func funcExample(intr interface{}) {
// Using type switch
switch intr.(type) {
case string:
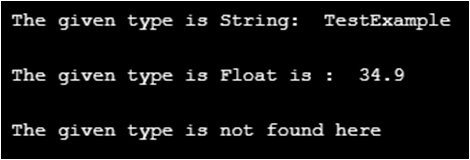
fmt.Println("\n The given type is String: ", intr.(string))
case int:
fmt.Println("\n The given type is Integer: int, Value:", intr.(int))
case float64:
fmt.Println("\n The given type is Float is : ", intr.(float64))
default:
fmt.Println("\n The given type is not found here")
}
}
// Defining the main method
func main() {
funcExample("TestExample")
funcExample(34.9)
funcExample(false)
}Output:
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Golang Interfaces. Here we discuss the introduction, syntax, and working of interfaces in the go language along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –