What is Green Economy?
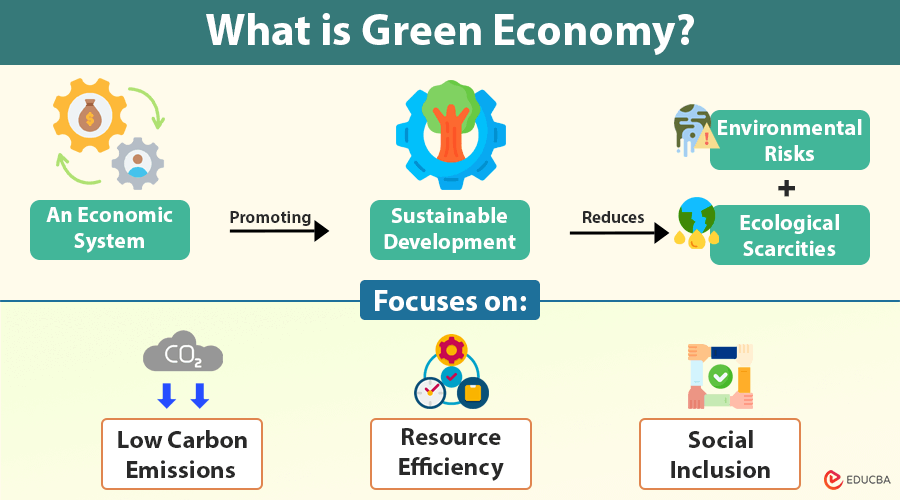
An economic system that promotes sustainable development while reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities is known as a green economy. It focuses on creating low-carbon, resource-efficient, and socially inclusive economy benefiting both people and the planet.
The idea of a green economy has gained considerable momentum due to growing concerns about climate change and environmental degradation. This model aims to foster economic growth while simultaneously promoting environmental sustainability. This article will examine the principles of this model, its effects on different sectors, and its crucial role in fostering a sustainable future.
Why is a Green Economy Important?
The shift towards a greener Economy is essential for several reasons:
- Climate Change Mitigation: Promotes efforts to combat climate change by reducing carbon footprints, adopting renewable energy, and supporting sustainable practices in agriculture and forestry.
- Economic Growth with Sustainability: This Economy creates job opportunities in renewable energy, green technologies, sustainable agriculture, and waste management sectors.
- Environmental Protection: Emphasizes resource conservation and pollution reduction, helping to protect natural ecosystems, biodiversity, and public health.
- Social Benefits: A focus on inclusive growth ensures that economic opportunities are accessible to marginalized communities, leading to better health, education, and quality of life.
5 Principles of a Green Economy
While interpretations may vary, the following five principles are widely recognized:
- Well-being: A green economy prioritizes the well-being of all individuals, focusing on human development, health, happiness, education, and community cohesion. It seeks to create genuine, sustained, and shared prosperity beyond mere monetary wealth.
- Justice and Good Governance: This principle emphasizes equity, equality, and community cohesion. It promotes good governance through accountable, transparent, and resilient institutions, encourages inclusive decision-making processes, and ensures that the benefits of this economy are accessible to all.
- Poverty Eradication: This Economy aims to reduce poverty by creating new economic sectors that offer investment and job opportunities. It is inclusive and non-discriminatory, promoting equal income distribution and opportunities while reducing disparities among people.
- Energy Efficiency: This principle focuses on using resources efficiently and sustainably, reducing waste to a minimum. It aims to shift from a consumer-driven model to a more sustainable one regarding natural resource consumption.
- Low-Carbon Development: A green economy uses renewable energy sources—such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and hydrogen—that generate little or no greenhouse gas emissions. It encourages extensive electrification with energy produced sustainably from renewable sources in various sectors, including industry and transportation.
Effects of the Green Economy on Different Sectors
Here is an overview of how this economy affects key sectors:
#1. Energy Sector
The transition to a green economy significantly impacts the energy sector, where renewable energy sources replace traditional fossil fuels. Solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal energy have replaced fossil fuels in many regions, reducing carbon emissions and reliance on non-renewable resources. This shift leads to:
- Lower Carbon Emissions: Using clean energy sources reduces greenhouse gas emissions, addressing climate change concerns.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in solar panels, wind turbines, and energy storage solutions rapidly evolve, creating new industries and job opportunities.
#2. Transportation Sector
The green economy encourages the shift toward cleaner, more sustainable transportation systems, including electric vehicles (EVs), public transit, and cycling infrastructure. The effects on this sector include:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Adopting electric cars, buses, and trucks reduces air pollution, contributing to healthier cities and less dependence on fossil fuels.
- Green Logistics: Supply chains are being reimagined with an emphasis on electric delivery trucks and optimized logistics to minimize fuel consumption.
#3. Agriculture Sector
Agriculture plays a crucial role in the green economy by promoting sustainable farming practices that safeguard the environment while addressing global food needs. Key effects on this sector include:
- Organic and Sustainable Farming: Practices like crop rotation, organic farming, and reduced pesticide use support soil health, biodiversity, and water conservation.
- Climate-Resilient Agriculture: Climate-smart farming practices are being adopted to deal with drought, soil degradation, and changing weather patterns.
#4. Construction and Building Sector
The construction industry has undergone a major transformation, promoting energy-efficient buildings, sustainable materials, and environmentally friendly construction methods. The effects include:
- Energy-Efficient Buildings: Green building standards such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) result in energy-efficient designs that lower utility costs and reduce environmental impact.
- Eco-Friendly Design: Green architecture incorporates renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, green roofs, and energy-efficient insulation, to create eco-friendly buildings.
#5. Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector is evolving to incorporate more sustainable production practices in response to the green economy. This transformation results in:
- Circular Economy Practices: Many manufacturers are designing products for longevity, repairability, and recyclability, ensuring that materials are reused and waste is minimized.
- Green Supply Chains: Companies adopt sustainable practices across their supply chains, choosing suppliers who follow environmentally friendly practices and reduce carbon footprints.
#6. Financial Sector
The financial sector supports this economy by investing in sustainable projects and green bonds. The effects on the financial sector include:
- Green Finance: Investment in renewable energy, sustainable infrastructure, and environmentally responsible businesses is rising. Green bonds, which fund environmentally friendly projects, are gaining popularity.
- Sustainable Investments: Investors prioritize companies and projects with strong environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria, aligning economic growth with sustainable practices.
Real-world Examples
Several countries and industries have already embraced the green economy model. Here are a few examples:
- Denmark’s Renewable Energy Success: Denmark is a worldwide leader in renewable energy. Over 40% of the country’s energy comes from wind power, and the government has set ambitious goals for becoming a carbon-neutral nation by 2050.
- Tesla’s Contribution to Clean Transportation: Tesla’s electric cars (EVs) have revolutionized the automobile business. By emphasizing environmentally friendly mobility, Tesla contributes significantly to lowering dependency on fossil fuels and fostering a greener future.
- Circular Economy in the Fashion Industry: Brands like Patagonia embrace the circular economy by promoting clothing recycling programs and using sustainably sourced materials. The fashion industry’s shift toward sustainability is vital to the green economy.
Challenges in Implementing
While transitioning to a greener economy offers immense benefits, several challenges must be addressed:
- High Initial Costs: Many green technologies and infrastructure projects require substantial upfront investment, which can be a barrier for some nations and businesses.
- Political Will and Policy: Governments must create supportive policies and regulations promoting green initiatives and incentivizing businesses to adopt sustainable practices.
- Technological Innovation: Continued research and development are needed to create more cost-effective green technologies.
- Education and Awareness: It is essential to the widespread adoption of a green economy to educate businesses, communities, and individuals about its importance and practicalities.
How Can You Contribute to the Green Economy?
Here are some actions individuals, businesses, and governments can take:
- Individuals: Reduce energy consumption, support eco-friendly businesses, recycle, and adopt sustainable transportation options.
- Businesses: Invest in green technologies, reduce waste, and develop sustainable products and services.
- Governments: Create supportive policies, invest in renewable energy, and incentivize green businesses and technologies.
Final Thoughts
A green economy is an environmental necessity and a pathway to long-term economic prosperity. By embracing sustainability, reducing environmental impact, and promoting social inclusion, we can build a better future for the planet and all its inhabitants. The transition may be challenging, but the rewards for environmental protection, economic growth, and improved quality of life are well worth the effort.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on the green economy helps you understand its importance for sustainable growth and environmental responsibility. Check out these recommended articles for insights into green business practices and how they shape industries’ future worldwide.

