Updated March 18, 2023
Difference Between H.323 and SIP
The multimedia communication system widely uses H.323 in Internet Protocol networks and Packet switch internet protocol. But it is the oldest standard protocol described by International Telecommunication Union. The H.323 is composed of a bunch of protocols used for decoding, encoding, and packetization of audio and video signals to enable signal and control of voice calls. Session Initiation Protocol is similar to H.323 designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force and uses Real-time transport protocol to facilitate media flow. SIP is an application layer which is enabled to control to setup or modulate multimedia call or session. H.323 vs SIP also handles the communication flow between people, including endpoint addressing and user location.
Head to Head Comparison Between H.323 and SIP (Infographics)
Below are the top 13 differences between H.323 vs SIP:
Key Differences
Some of the major key differences are mentioned below:
- The H.323 protocol pack has some important functional components.
- The terminal enables an endpoint with an internet protocol network, and it can offer signalling and its control in dual-way communication in real-time scenarios and codecs. Gateway is a communication path established between the circuit-switched network and packet-switched network and can be disconnected when there is no other established connection. It used to run the local area network endpoint to a switched circuit endpoint or vice versa. It also enables the installation set up, control and translation flow done by gateways. Gatekeepers implement bandwidth control, translation of address, zone, call, and bandwidth management, admission and call control, but its main function is to manage the endpoints. There are multiple paths in H.323 which manage the exchange information between communication entity like H.245 logic and control channel and RAS.
- RAS stands for Register, Admission and status channel, which develops the intercommunication in between endpoints and gatekeepers and asks for allowance to call the other endpoints. After the call, the gatekeeper transmits the call signalling path’s transport code to bring up the endpoint. The call signalling channel manages the call data, and associated service control data is transmitted. The transport address is mention on this communication channel to set up the call. H.245 transmit media control and have the exchange support capability of H.245 protocol messages. This H.245 manages the logical channel needed for media after exchange data with call participants. The logical channel carries media transformations and is made by uni-directional channels with real-time transport protocol and Real-time transport control protocol. H.323 explains unreliable transport protocol is employed to transfer RAS and logic channels. The control channel defines the transport data over a reliable transport protocol such as TCP.
- In the SIP protocol, the functioning elements are the Network server and User-Agent. The SIP endpoint’s user agent constitutes of user agent client and user agent server where service requests and replies are processed. The redirect server, proxy server, and registrar constitute a network server. Additional servers are not essential for basic SIP call.
- The network server and user agents are dependent on the gatekeeper and H.323 terminal. The two operations SIP UAC request and SIP proxy server operates as the location identification of end-user and SIP UAS asses the call. The invitation of SIP composed of INVITE request and ACK request. The message which hosts the event requirement and notification is sent about media type, and the caller can access the media request.
- The SIP uniform resource locator is known to SIP addresses. The SIP message template is built on HTTP Hypertext Transport Protocol which is available as text, and the readable encoder method is used. Redirect servers manage the INVITE notifications through the transmission and reception of SIP-URL. In SIP-URL, the details and information of the caller are available.
- Proxy servers deploy application layer in directing of SIP responses and request. The server could be stable or unstable. Session description protocol is coupled with SIP protocol to achieve high performance in call signalling functions in Internet protocol telephone communication. IP telephony emerged to implement cost reduction, which makes regulative tax and usual voice calls long distant.
- The established data is cost-effective for some range of voice calls. In the olden days, telephonic services with circuit-switched networks, also called Public switched telephone networks or Paid old telephone service, is some applicable in some areas.
- H.323 is a lightweight protocol and coined by telephone industry standards. It explains the protocol stack and defines what type of data should be permitted and not permitted. The systematically determines the easy handling of interoperability protocols and inflexible. But H.323 is hard to adapt to trending generations. This is a complex process. SIP is a general internet protocol which is functioned by interchanging little lines of ASCII messages. But they are advanced in nature, modular, simple and easily adaptable. This IP easily integrates with other internet protocols but doesn’t mingle with telephone signalling protocols.
H.323 vs SIP Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the top comparison:
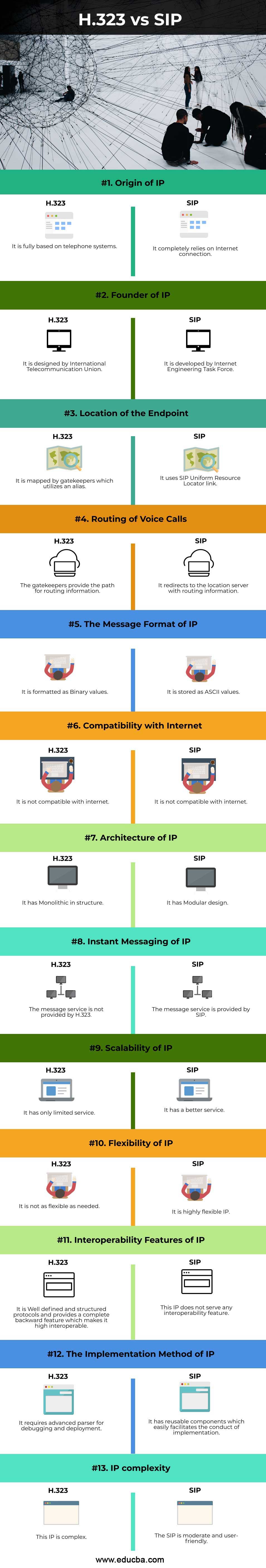
| Basis of Comparison |
H.323 |
SIP |
| Origin of IP | It is fully based on telephone systems | It completely relies on Internet connection |
| Founder of IP | It is designed by International Telecommunication Union. | It is developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force. |
| Location of the Endpoint | It is mapped by gatekeepers who utilize an alias. | It uses the SIP Uniform Resource Locator link. |
| Routing of voice calls | The gatekeepers provide the path for routing information. | It redirects to the location server with routing information. |
| The message format of IP | It is formatted as Binary values. | It is stored as ASCII values. |
| Compatibility with Internet | It is not compatible with the internet. | It is not compatible with the internet. |
| Architecture of IP | It has a Monolithic in structure. | It has a Modular design. |
| Instant messaging of IP | The message service is not provided by H.323 | The message service is provided by SIP. |
| Scalability of IP | It has only limited service. | It has better service. |
| Flexibility of IP | It is not as flexible as needed. | It is a highly flexible IP |
| Interoperability features of IP | It is Well defined and structured protocols and provides a complete backward feature which makes it high interoperable. | This IP does not serve any interoperability feature. |
| The Implementation method of IP | It requires an advanced parser for debugging and deployment. | It has reusable components which easily facilitates the conduct of implementation. |
| IP complexity | This IP is complex | The SIP is moderate and user-friendly. |
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to H.323 vs SIP. Here we discuss the difference between H.323 vs SIP, key differences with infographics, and a comparison table. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more–