Updated June 9, 2023

Definition of Haskell let Function
In Haskell let, binding is used to bind the variables, which are very local. In Haskell, we can define any type of variable using let keyword before the variable name in Haskell. But their scope is local, we also have let in Haskell which is another form of defining the variable and use them after it. There is no such let function but let is rather used to binding of the variable values and used to perform desired operations on them. Also in Haskell let is supposed or called as the alterative of ‘where’, so we can say let in is an expression which is used to define and use variable at very local scope in Haskell. In the coming section of the tutorial, we will discuss more the internal working of the let in expression in detail, which will give us clear understating of the let function in Haskell and help us to implement it while programming.
Syntax:
As we discussed that let is used to bind variable and we have two types for this, let’s take a look at its syntax for a better understanding of the let in Haskell for beginners see below:
1) let variable name = variable value
2) let … in …
As you can see in the above lines of syntax we have two ways to define it and use it in Haskell, it is very simple and easy to use and we have just use the let keyword before it. Let’s take a look at one practice syntax for beginners to understand it better see below;
e.g. :
let demo = "some value"As you can see in the above lines of practice syntax it is easy to understand, in the coming section f the tutorial we will see the internal working of the let in function in detail.
How let function works in Haskell?
As now we already know that let is not a function but rather it is an expression in Haskell, or simple it is used to bind the variable in Haskell, it is very easy to use and implement. Also, it is termed as the alternative for the wherein Haskell. We can define or bind variable using let in Haskell, one at a time or multiple at the same time. For this, we can use let in expression provided by Haskell. One thing, let is the ins built feature of the Haskell, so to use it we do not require to include any dependency or install any plugin, it is already available in the Haskell. Let take a look at the signature and understand how it actually works internally let’s get started to see below:
1) let variable name = variable value: In this, we are only defining the variable which means we are also binding the value to the variable, but it can be used locally. We will see one example to use this while programming in Haskell see below;
e.g. :
let demo = 100;
As you can see in the above lines of code we are defining one variable and trying to bind some values to it, using let keyword here. It is easy to use and implement, but here we are only able to define a single value at a time, so to define multiple at once we have to use let in expression provided by Haskell library.
2) let … in … : By using this we can define several variables or we can say we can bind multiple variables. This expression allows us to define the variable anywhere but that will be very local, and we cannot scope them using guard in Haskell programing. As you can see in the above syntax for this we have two things include in the let expression one is let itself and another one is in. Now we will discuss more the expression in detail to start using it while programming see below;
Two part of let in expression which are defined below ;
1) let: The first one is let itself which is used to declare the variable inside it, it can be any number of variable.
2) in: The second part of let in expression is ‘in’ here, which uses the variable defined in the let part, we can easily access the variable which are defined in the ‘in ‘ part of the expression.
3) pattern matching: By using let we can also perform pattern matching in Haskell, also inside the let part we can define the
list comparison and inside in part we can have value to perform more operation.
Now we will see one sample piece of code for beginners to understand it better way, see below;
e.g :
(let x = 10 in x + 100) + 200
As you can see in the above lines of sample piece of code, we are using let in function to define and calculate it. first, we have defined the x with a value of 10, after this, we are using in part to continue the calculation, where we are trying to add 100 again to the existing variable defined in the let part of the expression. After the complete le in expression, we are trying to add 200 at the end which is not mandatory but depend on the requirement.
Examples
In this example we are trying to use let in in Haskell, we are creating single and multiple variable to show the working of let in Haskell. This is a sample example for beginners, to show the basic usage of let in Haskell.
Code:
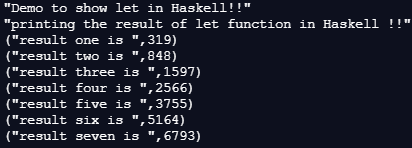
main = do
print("Demo to show let in Haskell!!")
let exp1 = 1 * (let x1 = 10 in x1 + 300) + 9
let exp2 = 2 * (let x2 = 20 in x2 + 400) + 8
let exp3 = 3 * (let x3 = 30 in x3 + 500) + 7
let exp4 = 4 * (let x4 = 40 in x4 + 600) + 6
let exp5 = 5 * (let x5 = 50 in x5 + 700) + 5
let exp6 = 6 * (let x6 = 60 in x6 + 800) + 4
let exp7 = 7 * (let x7 = 70 in x7 + 900) + 3
print("printing the result of let function in Haskell !!")
print("result one is " , exp1)
print("result two is " , exp2)
print("result three is " , exp3)
print("result four is " , exp4)
print("result five is " , exp5)
print("result six is " , exp6)
print("result seven is " , exp7)Output:
Conclusion
By using the let binding in Haskell we can easily binding the variable we can do this n two ways possible. let if not an function but rather is used to bind the variables, we can have multiple variables at the same time and used them in the in part of the expression.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Haskell let” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.