Updated June 8, 2023
Definition of Held to maturity securities
Held to maturity securities are debt securities for which a firm can and intends to hold until maturity. These have fixed payments, and these securities are reported at cost, not the fair value in the balance sheet. The reason for not adjusting this to fair value is that the security owner will keep these till maturities, and at that point, the face value of investments will get redeemed. Hence temporary price change is not recognized for these securities.
Components of Securities
Investment Securities are classified into 3 types:
1. Held to maturity Securities
As mentioned before, these are to be held until maturity, which is recorded at cost in books. Coupon or interest payment from these securities is recorded in the income statement as interest income. The value of these securities is not adjusted each year as per the market.
2. Trading Securities
These are debt and equity security, which can be resold. They are held at market value. The income statement records any unrealized gain or loss. Each year, they adjust the value of these securities based on market value.
3. Available-For-Sale Securities
These are the same as Trading Securities, but unrealized gain or loss is credited into the balance sheet in an equity account. Investors do not expect to hold these securities until maturity and will sell them as soon as the bond prices increase.
One of the perfect examples of Held to maturity securities is bonds. They have a specific maturity date, and companies tend to keep it till maturity. Stocks cannot be classified in Held to maturity securities because they do not have any maturity date. If these securities mature in less than a year, accountants show them as a current asset; otherwise, they record them as fixed asset in the accounting books.
Accounting Treatment for Held to Maturity Securities
Let’s say in 2016, a company bought $10,000 worth of bonds with a maturity of 10 years, and the company intends to keep it till maturity. So, in the balance sheet below, accounting entries will be recorded:
Held to Maturity Securities (debit)…………………. $10,000
Cash (Credit)…………………………………………………. $10,000
In 2017, the company received a coupon or interest payment from these securities of $50. So, this $50 will go into interest income in the income statement.
Interest Income (Credit)………………. $50
Cash (Debit)…………………………………$50
Example of Held to Maturity Security
Suppose a company decides to buy bonds with a have a maturity of 10 years. The company can either sell bonds before maturity when it sees profit in selling the bonds, or it can hold the bonds for 10 years until maturity. If a company has bonds until maturity, it records this security as an asset in its balance sheet as held-to-maturity securities.
SouthWest Georgia Held to Maturity Securities
Southwest Georgia is a Georgia bank mainly in banking services to individuals and companies. It also provides various kinds of mortgage services.
Below is the snippet of the balance sheet for SouthWest Georgia. As we can see, in 2017, its “held to maturity securities” value was around $44.6 million, while the fair value of securities in the same year was $45.2 million.
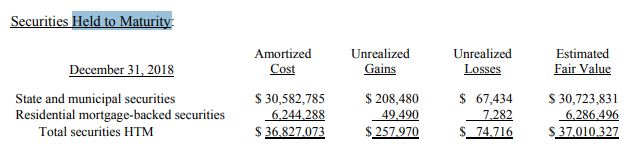
Some securities matured in 2018; that’s why securities value has reduced from $44.6 million to $36.8 in 2018; the fair value of securities in 2018 was around $37 million.
Source: https://www.sgb.bank/assets/files/kauMfNkl/10K18%20-%20Final.pdf
The classification of these securities is as follows: Out of $36.8 million, they held $30.5 million as ‘State and municipal securities,’ while they held around $6 million as ‘Residential mortgage-backed securities.’
Source: https://www.sgb.bank/assets/files/kauMfNkl/10K18%20-%20Final.pdf
Advantages
Below are the advantages of held to maturity securities:
- These securities are usually safer in nature. Security holders have assured return guaranteed if an issuer has no default.
- Since they pre-specify the bond return and won’t sell it between maturities, any bad news won’t affect the bond prices much.
- Investors or companies buying these securities can quickly identify their investment portfolio based on these bonds because they know the expected returns from these bonds in the coming years, and their portfolios also can be diversifiable since these bonds are less riskier and have a lesser beta.
- These securities can be used to hedge against market fluctuations.
Disadvantages
Below are the disadvantages of held-to-maturity securities:
- These securities are not good for the liquidity of the company. Since companies have decided to hold these until maturity, they cannot sell them for cash before maturity.
- If investors predetermine the return, these securities won’t present any upside potential, and investors will have to settle for the return mentioned at issuance.
- The purpose of these investments is for them to be long-term investments.
Conclusion
Held to maturity securities’ positive or negative side depends on what the investor wants to achieve. If an investor wants to hedge its portfolio and is ok with locking in its securities long-term, it is positive. Still, if that same investor needs some cash soon, these securities can be a pain because they won’t be able to sell before maturity.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Held to Maturity Security. Here we have discussed the concept of Held to Maturity Security with the help of an example. You may also look at the following articles: