Updated March 6, 2023
Difference Between Hibernate and JDBC
Hibernate is mainly popular for handing object-relational mapping in a specific environment of the Java ecosystem. Developers are normally preferred to use Hibernate due to its data caching ability and supporting multiple databases very easily by changing that specific database’s dialect. Whereas in the case of JDBC, object relation mapping has not been done automatically, the developer needs to concentrate on proper developing architecture for maintaining the same, which is manual, so that the mistake can be possible. And also, initial architecture design is a too costly or extra effort for any developer, which can be easily avoidable in the case of using hibernate.
JDBC is using a simple database query or simple query language for communicating with a specific database as per the requirement of that specific project. So it will be never independent for multiple relational databases. In this case, a developer can also develop one specific design for using the same codebase for multiple databases in the case of JDBC as well by maintaining varieties queries for individual databases in multiple properties files and mapping them at the time of loading that specific application. That multiple properties files will hold specific relational databases SQL query’s requirement. But again, it will be a big cost for the developer and not easy to do. Also, every time properties files need to be updated before moving to another relational database.
Head To Head Comparison Between Hibernate and JDBC (Infographics)
Below is the top 3 difference between Hibernate vs JDBC
Key Differences
Both are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major difference:
- Hibernate is maintaining a general Object Oriented mapping concept which designed in Java Platform. Hibernate has to define a session factory as well as own transactional management with any relational database, which makes this ORM tool most popular to a maximum developer. Whereas JDBC maintains normal JDBC connectivity between the application and relational database, it does not maintain any automatic object mapping mechanism or database transaction handling. A developer needs to be involved in preparing proper object-oriented mapping and transactional boundary, which is always a costly effort anytime for any developer.
- Hibernate can able to easily configurable for any popular relational databases without any changes or design in the data access object codebases. As it is maintaining proper object-oriented mapping, so changing in the dialect is enough for switching the relational database at any time. It also has one big utility: creating all the related tables based on that database definition by enabling one specific property in the hibernate configuration file. So the migration of an existing project in a different database will always be very much easy on anytime approach by using hibernate. In the case of JDBC, changing of the database is not only configuration changes, but there also have big efforts on architectural changes of an entire application, as it is a totally manual effort for changing the same. As JDBC fully depends on the database-specific SQL query, we need to consider all the defined query dynamic based on database changes. A different approach can define that dynamic approach; one of the popular approaches is the properties file defined for each and every database. And before application loading developer needs to identify those properties files of an individual database based on their names. Even design can be done for using a different database for the same application. Whereas hibernate actually do it automatically, nothing need to design manually.
- One of the strong characteristics of Hibernate is a caching mechanism. As per considering any application performance ability, the developer always provided the main concentration on less database connectivity, which means communicating with a database as much less as possible. This caching mechanism helps on the same lot to a developer for any time on improving the performance of the application. Different kind of caching mechanism available in hibernate which can be used by the developer anytime based on project requirement. This feature’s actual utility is caching that specific relation object data in application memory and use the same without reconnecting with a database. Whereas JDBC doesn’t have any define caching mechanism available.
Hibernate vs JDBC Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Hibernate vs JDBC
| The basis of comparison |
Hibernate |
JDBC |
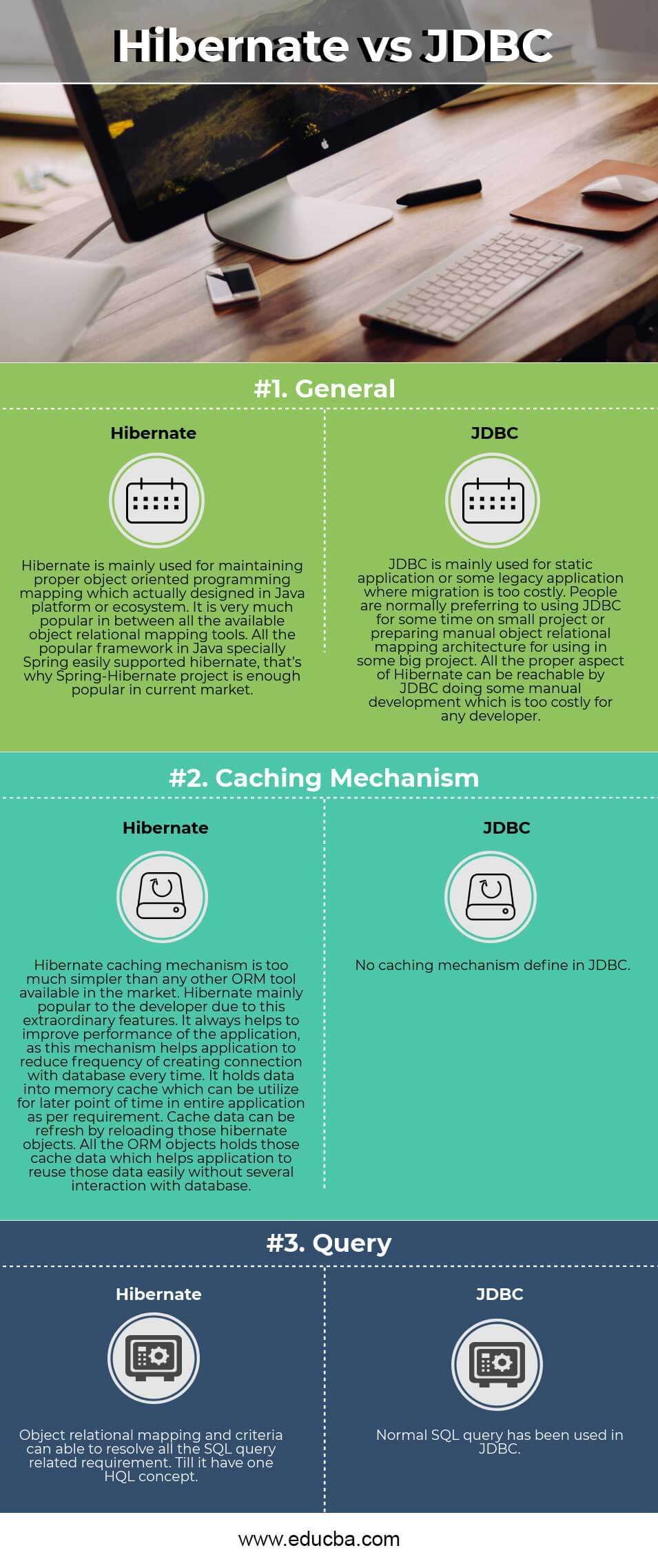
| General | Hibernate is mainly used for maintaining proper object-oriented programming mapping, which actually designed in Java platform or ecosystem. It is very much popular in between all the available object-relational mapping tools. All the popular framework in Java, especially Spring, easily supported hibernate; that’s why the Spring-Hibernate project is popular enough in the current market. | JDBC is mainly used for static application or some legacy application where migration is too costly. People are normally preferring to using JDBC for some time on a small project or preparing manual object-relational mapping architecture for using in some big project. All the proper aspect of Hibernate can be reachable by JDBC doing some manual development which is too costly for any developer. |
| Caching Mechanism | Hibernate caching mechanism is too much simpler than any other ORM tool available in the market. Hibernate mainly popular with the developer due to this extraordinary features. It always helps to improve the performance of the application, as this mechanism helps the application to reduce the frequency of creating a connection with the database every time. It holds data into a memory cache, which can be utilized for a later point of time in the entire application as per requirement. Cache data can be refresh by reloading those hibernate objects. All the ORM objects hold those cache data, which helps the application to reuse those data easily without several interactions with the database. | No caching mechanism define in JDBC. |
| Query | Object-relational mapping and criteria can able to resolve all the SQL query related requirement until it has one HQL concept. | The normal SQL query has been used in JDBC. |
Conclusion
Hibernate vs JDBC both can be used for connecting with the database and fetching data from there in case of any business purpose of the application. Developer normally preferred JDBC if there don’t have any chance of changing the database or continuation of a complex legacy application. Hibernate is always preferable if people are really looking for proper object-relational mapping and define a transactional boundary without any manual effort.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Hibernate vs JDBC. Here we also discuss the key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.