What is Homeowners Insurance?
Homeowners insurance safeguards the insured property and compensates for any damage/loss to the home and its belongings. For example, Mr. Dawson inherits his family home and decides to buy insurance for the house. He, therefore, purchases $3,000,000 in home insurance. A sudden fire due to an electrical short circuit causes significant damage to the house and its possessions. Mr. Dawson claims the insurance and gets $2,000,000 (the home’s current market value).
Homeowner’s insurance covers damages from lightning, fire, and natural disasters. It generally reimburses for the home and its contents, such as furniture and appliances, and provides liability coverage if someone gets injured on the property.
Key Highlights
- Homeowners insurance protects the home against damages or loss and provides coverage in case somebody gets injured during the incident.
- Although not legally required, most mortgage lenders make it a precondition before disbursing a loan.
- Personal property coverage protects the belongings inside the home, such as furniture and electronics. Whereas liability coverage protects the homeowner when another person suffers an injury on the property
- The average policy covers fire damage, wind damage, hail damage, theft, and vandalism.
How Does Homeowners Insurance Work?
- The homeowner purchases insurance as protection against losses that may occur as a result of owning and maintaining a home
- They pay an insurance premium to the insurer, and in return, the insurer agrees to pay for specifically covered losses in case of unfortunate events
- Some policies also cover temporary living expenses if the residence is uninhabitable. Suppose a home gets damaged in a fire, then the policy may cover the cost of staying in a hotel during repairs on the house
- The insurance costs can vary on factors, including the value and location of the home, the required coverage, and more.
Homeowners Insurance Coverage Levels
Actual Cash Value:
- Actual cash value accounts for property costs as well as the value of the possessions after depreciation
- It determines the price of the property as per current market worth after considering the age and condition of the place.
Replacement Expense:
- The replacement value plans pay the actual cash value of your home and valuables without accounting for depreciation
- It computes the total costs of goods according to their present value.
Guaranteed Replacement Cost or Value:
- It pays the entire cost of repairing or rebuilding the house up to the policy’s maximum coverage
- It gives more coverage than the total premiums, but there is a limit; typically, it is 20% to 25%.
Types of Homeowners Insurance
| Type | Perils | Coverage |
| HO-1: Basic | The most basic policy covers limited perils, like fire, theft, vandalism, etc. | It pays in actual cash value |
| HO-2: Broad | It is an advanced HO-1 policy that covers extra perils such as water overflow, freezing, sudden accidental cracking, and more. | It compensates for dwelling in replacement costs and property in actual costs. |
| HO-3: Special | It is the most commonly available insurance that covers most perils, excluding earthquakes, sinkholes, etc. | It pays replacement costs for both dwelling and property but still can differ on the policy. |
| HO-4: Contents Broad | It is for renters to secure their belongings under most perils, similar to HO-3. | It covers the renters’ damaged possessions in replacement costs. In addition, it can provide living expenses. |
| HO-5: Comprehensive | It covers single-family homes under all possible perils, from fire to snow blockage. | It covers the damages in replacement costs for all possessions and the house. |
| HO-6: Unit-owners | It is for people living in condos, and the perils included vary on the plan. It can be limited or all perils. | The coverage is mainly for renovations, liability, asset losses, etc |
| HO-7: Mobile Home | It is generally for mobile houses like trailers and modular homes. The perils depend on the plan. | It covers the policyholder only for losses when the home is not in transit |
| HO-8: Modified Coverage | It is an HO-1 policy for houses that do not fall under any other category, such as high-risk location-based homes. | The coverage is for actual cost value, similar to HO-1. |
Homeowners Insurance Examples
Example #1
In August 2022, Mark Orminski experienced a fire at his house due to a faulty LED bulb. He claimed the homeowner’s insurance from State Farm Insurance, and the company had to pay $246,000. However, the company sued Amazon, where Mark bought the bulb from, as they had warranted it.
Example #2
Harper owns a guest house in Florida which she rarely uses. While the place was empty, some burglars broke in and stole most of the valuables from the property.
Harper had homeowners insurance and raised an insurance claim with her agent. After the necessary investigation by the company, they approved the request, and Harper got reimbursed for her losses.
What Does Homeowners Insurance Cover?
- A typical policy covers losses of fire, lightning, wind, hail, and water damage from burst pipes.
- It also covers the theft of personal belongings, such as electronics, furniture, etc. Nonetheless, most policies limit the amount to specific items, such as jewelry, art, and other valuables.
- It covers dwellings, like farmhouses, guest houses, etc., for events like fire, explosion, water damage, etc. For example, homeowners insurance may be used to cover the services provided by restoration pros for water damage to the structure of the property.
- Personal property coverage for residencies additionally covers events such as theft or vandalism.
- However, it does not cover damage by floods, earthquakes, termites, or insect damage control. As a result, homeowners living in areas prone to these events may require additional coverage.
- You may also need a separate, specialized policy if you run a business from home, particularly if customers or clients visit you in person. The same goes for if your work involves visiting clients’ homes. Additionally, in such scenarios, seeking assistance from a home services marketing agency can help ensure the success of your business and justify the insurance expenses.
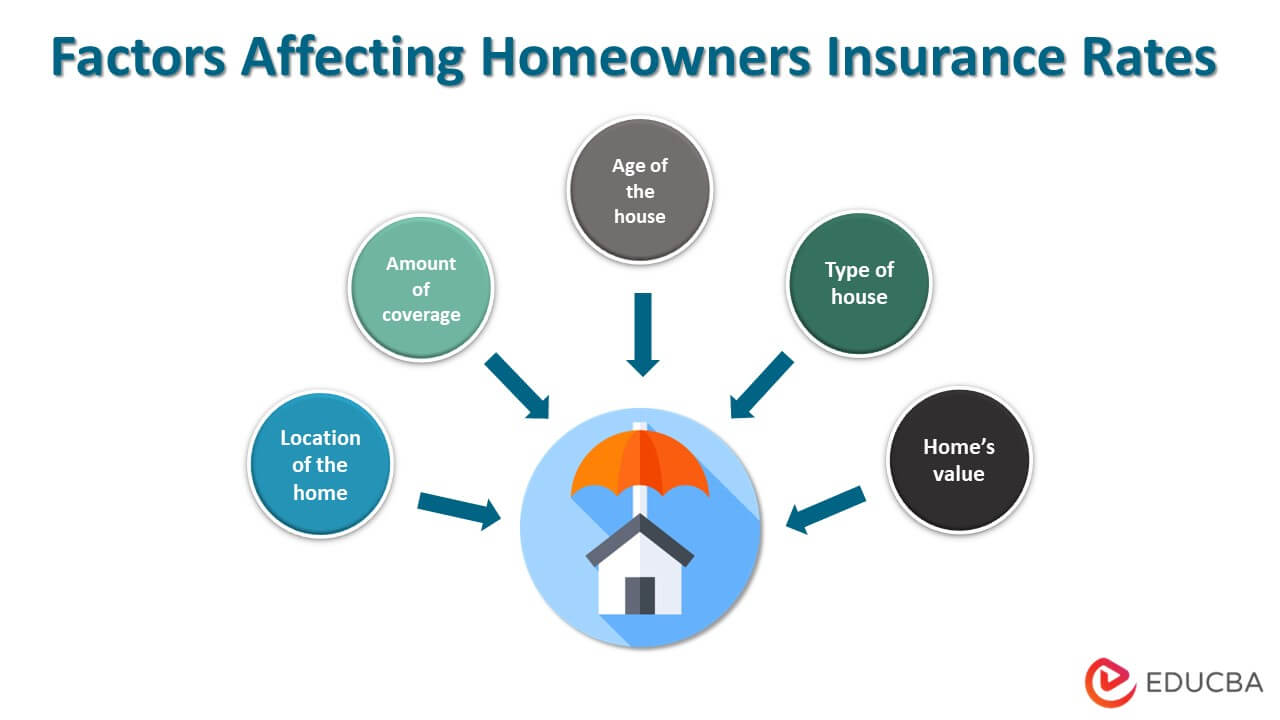
Factors Affecting Homeowners Insurance Rates
- Home’s value: If the home is worth more, the policy will cost more
- Age of the house: As older homes are less valuable, they are less expensive to insure
- Location of the home: If the property is in a natural disaster-prone area, insurance will be expensive
- Type of house: Insurance for a brick house costs more than a wooden frame house
- Amount of coverage: The greater the required coverage, the higher the insurance costs.
Homeowners Insurance vs. Home Warranty vs. Mortgage Insurance
| Homeowners Insurance | Home Warranty | Mortgage Insurance |
| Purpose | ||
| It protects homeowner’s property from fires, burglaries, other natural disasters, etc. | It is a service contract to protect major systems and appliances in a home from wear and tear. | Protects the lender from borrower default |
| Costs | ||
| The costs fall in the $1,250 and $1,900 annual range. The monthly premiums are $140 to $160 | The prices are between $200 and $600 per annum, depending on the covered appliances. | It costs between 0.5% to 5% of the total coverage value |
| Coverage | ||
| Reimburses for losses or damages to homes, belongings, and any injured person due to the event. | It only covers damage to systems and appliances such as a furnace, air conditioners, water heaters, ovens, etc. | It pays the lender if the borrower can’t make payments on their mortgage. |
Homeowners Insurance Benefits
- It offers financial protection for homes and their belongings during disasters and helps with finances to rebuild your home or replace damaged belongings.
- Protecting you and your family can also provide peace of mind in an emergency and vulnerable situation.
- As these insurance premiums are tax-deductible, one can save money on taxes.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. How much does homeowners insurance cost?
Answer: The homeowners’ insurance policy cost can vary by many factors, including where you live and the coverage you require. However, the premium can typically cost around $1,800 per year.
Q2. When do you need homeowners insurance, and when is a home warranty more appropriate?
Answer: Homeowners insurance protects your home and belongings during natural disasters or other unforeseen events. In contrast, a home warranty is a contractual service that covers significant home systems and appliances for repair or replacement.
Q3. What are some homeowners insurance companies?
Answer: Some well-established and professional insurance companies are Erie Insurance, State Farm Insurance, USAA, and Chubb. However, the premiums for these companies might be expensive as well.
Q4. Is homeowners insurance tax deductible?
Answer: Yes, the premiums the policyholder pays for the homeowners’ insurance are tax deductible. Furthermore, compensation from insurance claims is also tax-exempt. However, when the policy expires without any claims, and the holder receives the coverage amount, they are not tax exempted.
Recommended Articles
This article guides you through Homeowners Insurance. We discuss its meaning, types, coverage, and more. Read the following articles to learn more,