Updated March 21, 2023

Introduction to IP Address
In this article How do IP Addresses Work? An IP Address stands for Internet Protocol Address. It is defined as the address which uniquely identifies a device in the network using TCP/Internet Protocol to establish communication. An IP address comprises four hexadecimal numbers of 8 bits field separated by symbol dot “.” Each number varies from one to three digits and these four number ranges from 0 to 255 bits.
For Example, 198.134.45.6
If we want to send a letter to anyone we need their mailing address similarly computer uses the IP address of the device to communicate to another computer within the network. Internet addresses are allocated by the InterNIC an organization that administers the Internet.
Types and Commands in IP Address
Below are the types of IP Address Version:
- IPV4
- IPV6
1. IPV4: Internet Protocol Version 4 having a storage capacity of a 32-bit number. Due to security concerns and the growth of technology IPV4 got depleted so IPV6 came into the picture.
2. IPV6: Internet Protocol Version 6 uses the 128-bit number to store the address.
Below is the command to know the IP address of any device/network:
- ifconfig -a: Used to view every configuration and setting.
- hostname -i: It displays the IP address of your machine.
- ip addr show: It shows IPv4 or IPv6 address on a device.
Parts in IP Address
It is comprised of two parts:
- Host: It uniquely identifies a device/machine in the network that we can assign to each host. It takes 8 bits of the address. The host part will remain the same but the network part of the IP address will change.
- Network: It uniquely identifies the network and its class. It also takes 8 bits of the address.
Classification of IP Address
It can be of types which are listed below:
1. Static
The static IP addresses usually never change but they may vary as a result of network administration. They are a permanent Internet address that provides a simple and reliable way for communication. From the static IP address, we can get any important details such as geographical information in which a computer resides. The Internet Service Provider (ISP) usages these details to communicate through the devices. The best example of a Static IP Address is DNS Server(Domain Name Service). However, Statistic IP Address is less secure in comparison to a Dynamic IP Address due to its assignment.
2. Dynamic
When we connect any devices like mobile, computers, etc to the internet then Internet Service Provider (ISP) provides an IP address from the range of available IP addresses to the device through which we can connect, send and receive information. Next time when we again connect the same device to the internet ISP will provide different IP addresses but from the same available range of IP addresses. Since the IP address keeps on changing every time we connect to the internet so such an IP address is termed a Dynamic IP address. An example of a Dynamic IP Address is DHCP server(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
Uses and Classes of IP Addresses
Below are the different class in it:
- Class A address
- Class B address
- Class C address
- Class D address
- Class E address
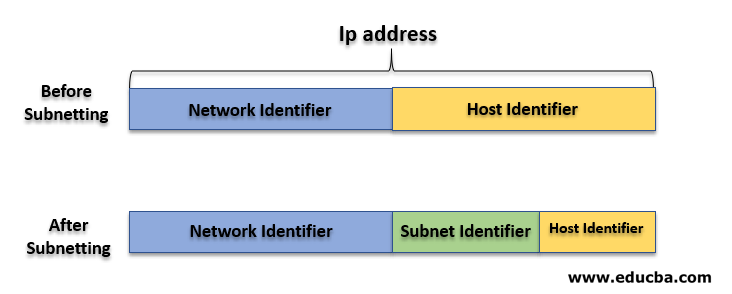
Before getting into the Classes we must have an idea of subnetting. Subnetting is a process of diving a bigger network (host part ) into smaller ones for better administration and usage.
For Example, In a corporate firm, there are four departments; sales, production, development, and management. In each department, there are 30 users. The firm used a private class C IP network. Without any concept of subletting, all computers will work in a single large network.
Now let us understand the classes:
** 1 byte = 8 bits
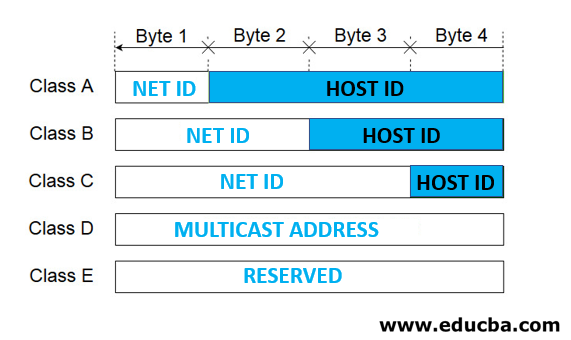
- Class A: The IP Address in this class ranges from 0 – 126 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0. It supports approx.16 million hosts on each of 127 networks. Mostly used by Internet Service Providers (ISP)
- Class B: The IP Address in Class B ranges from 128 – 191 with a subnet mask of 255.255.0.0.It supports approx. 65,000 hosts over each of 16,000 networks. Used by medium and large-sized networks in enterprises and organizations.
- Class C: IP Address ranges from 192 – 223 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. It has 254 hosts on each of the 2 million networks. This class address is most common and used in small business and home networks
- Class D: IP Address ranges from 224 -239 with no subnet mask. It is reserved for multicast groups.
- Class E: IP Address ranges from 240 -255 with no subnet mask. It is reserved for future use, or research and development purposes.
Uses of IP Address
- To assign Static/Dynamic IP addresses to new devices in a network in order to have communication.
- Different protocols like DNS, DHCP, etc work on the concept of IP Address.
- Proper tracking, security and monitoring of millions of devices in the network.
- Source routing features which allow the sender of a packet to specify which route the packet should take on the way to its destination.
IP Addresses Based Network
Let’s see how do IP Addresses Work, based on two types of network:
- Public: A public IP address is an address assigned to a computing device to allow direct access over the Internet. An email server, email server and any server device directly accessible from the Internet are public IP address which is globally unique and can only be assigned to a unique device.
- Private: Private IP address is assigned to computers within your private space without letting them directly exposed to the Internet. For example, if we have multiple computers, mobile devices within your home you may want to use private IP addresses to address each computer within your home. Private IP address starts with :
Class A:10.0.0.0
Class B: 172.16.0.0
Class C: 198.168.0
Conclusion
IP Address is used for communication between two or more different devices within/outside the network using TCP/IP protocol to locate and administrate devices using Internet Service Provider(ISP).
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to How do IP Addresses Work?. Here we discuss types, class, classification, command, IP Address-based network,s and uses. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –