Updated July 4, 2023
What are Imperfect Markets?
An imperfect market doesn’t meet one or more conditions of a perfectly competitive market. Perfect competition is a theoretical market structure that satisfies multiple conditions. These conditions include many buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, easy entry and exit, and perfect information.
However, in reality, most markets deviate from this ideal structure in some way and are therefore considered imperfect.
An example of an imperfect market is the market for cable TV services, in which consumers have limited options due to the presence of only one or two providers in many areas. Cable TV providers bundle channels together, which forces consumers to pay for unwanted channels. As a result, this lack of competition can result in higher prices and inferior service quality.
Key Highlights
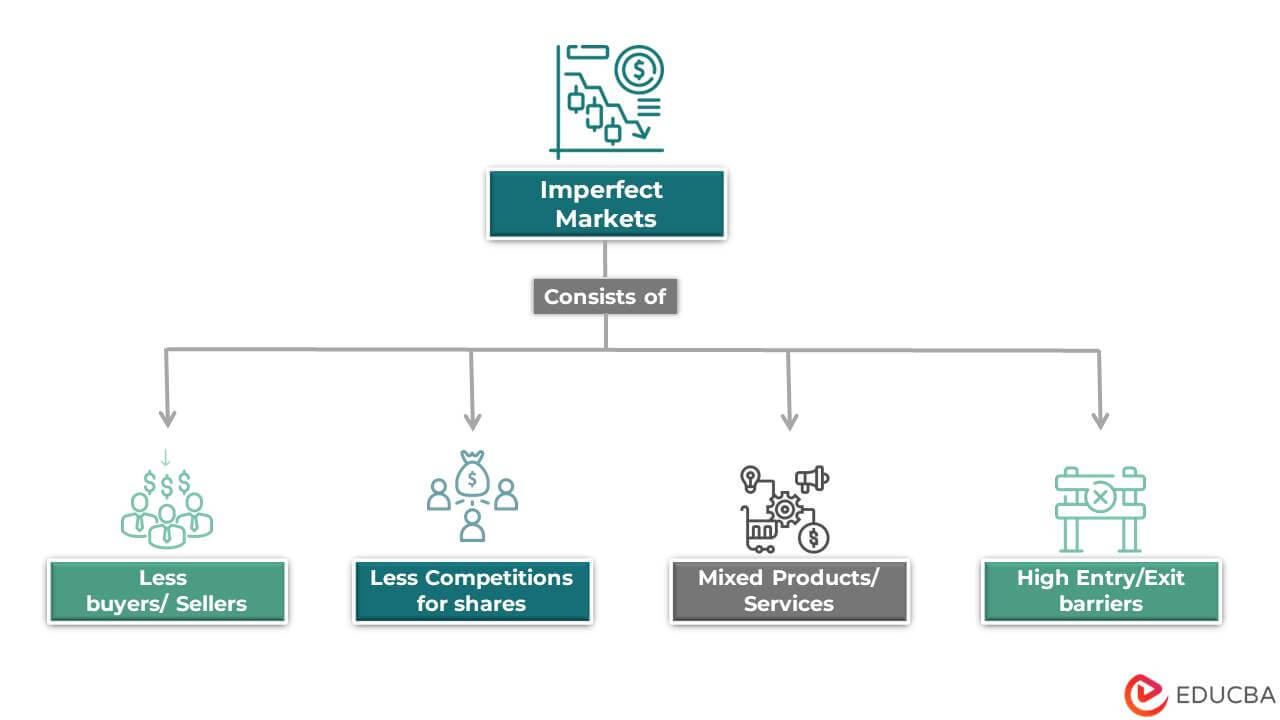
- Imperfect markets have fewer buyers and sellers, less competition for market shares, and a mixed set of products/services.
- One can recognize it by having many commodities, high entry/exit barriers, companies competing for the highest market share, and a small number of commodity buyers/sellers.
- Since perfect markets are theoretical, they cannot exist in reality. Therefore, all markets we see in the real world are imperfect.
- There are many such markets like monopolies, monopolistic competition, monopsonies, oligopolies, and oligopsonies.
How do Imperfect Markets Work?
In a perfectly competitive market, buyers and sellers have access to complete information about the goods and services that are up for trade. One or more of these conditions remain absent in imperfect markets, resulting in a less efficient market. The missing conditions might result from barriers to entry, a lack of perfect information, and the absence of enough large firms to control the market.
Understanding how these markets work is crucial for policymakers, business leaders, and consumers. It helps identify market failures and potential solutions for improving market efficiency. For example, the government, as a policy maker, needs to understand the working of such markets as they are responsible for regulating the market. They will protect consumers and promote competition by enforcing antitrust laws, setting price controls, and regulating the entry of new firms into the market.
Examples of Imperfect Markets
Some common examples of imperfections in markets include:
- Information asymmetry: One party has more information than another, which can lead to market power and inefficiencies.
- Market power: A single seller or buyer has the ability to significantly influence market prices.
- Barriers to entry: There are obstacles preventing new firms from entering the market, leading to reduced competition and potentially higher prices.
- Externalities: The actions of one party affect others in ways that don’t get reflected in market prices.
- Public goods: Here, the market fails because there are no restrictions on a product’s benefits to its consumers, raising the need for government intervention.
Real-World Examples
#1 Airline Industry
In the airline industry, there are barriers to entry, such as a single aircraft alone costs between $10 million and $100 million. This discourages many players from entering the market and creates a market with less competition, making it imperfect.
#2 Automobile Industry
In the automobile industry, there is significant asymmetric information. Sellers often know more about the history and condition of a car than buyers, who may need more information about the car’s past repairs, accidents, or other issues. It can lead to buyers paying more than the car is worth or sellers receiving less than the car’s actual value. The discrepancy of information makes the market imperfect.
Characteristics of an Imperfect Markets
- Products are identical and it’s possible to substitute them.
- Companies can’t set prices arbitrarily. They must adhere to the demand and supply law.
- There is a barrier to entering and exiting the market.
- There is an unlimited number of buyers and sellers.
- The price for all commodities gets determined by demand and supply.
- Buyers have identical and complete knowledge of all commodities and their prices.
Types of Imperfect Markets
|
Monopoly |
Oligopoly | Monopolistic Competition | Monopsony | Oligopsony | |
| Number of firms | One | Few | Many | Many | Few |
| Type of product | Unique | Differentiated or homogeneous | Differentiated | N/A | N/A |
| Control over price | High | Some control | Limited | High | Some control |
| Barriers to entry | High | High | Low | Low | High |
| Examples | De Beers, Microsoft | Airlines, Soft drinks industry | Clothing, fast food industry | Government monopolies | Grain market in the Midwest |
Importance of Imperfect Market
- In an imperfect market, firms may have a high degree of market power, which allows them to influence the price of their product. It can benefit firms, as they may earn higher profits by setting higher prices.
- This market can provide incentives for innovation, as firms can differentiate their products and charge a higher price for them. It can lead to the development of new and improved products, which can benefit both consumers and firms.
- Firms will focus more on customer satisfaction to differentiate themselves from their competitors and earn higher profits. It can lead to an emphasis on high-quality products and good customer service.
- With barriers to entry or exit, existing firms stay protected from competition, allowing them to earn higher profits.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Imperfect Market
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| There is more room for negotiation as there are more opportunities to negotiate a better price. | New players may need help to enter the market due to high entry barriers, economies of scale, market saturation, etc. |
| Buyers and sellers can specialize in specific goods or services, leading to better prices for buyers and sellers. | Since there are few sellers and alternatives, buyers must purchase what is on offer, regardless of the price. |
| It can lead to innovation, as all goods or services differ. | Large companies may use different means to gain an advantage over their competitors, hindering their growth and profitability. |
Final Thoughts
An imperfect market is one that does not offer perfect competition and has a variety of factors that influence the price such as monopoly power or asymmetric information. It has been shown that these types of markets can lead to higher prices and deadweight loss as well as other negative economic effects. Understanding how different types of markets work can help us better manage the economy in order to maximize efficiency and benefit all stakeholders involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an example of an imperfect market?
An example of an imperfect market is the market for education, which is often characterized by information asymmetry, as students may not have complete information about the quality of education provided by different schools. Additionally, there are barriers to entry, such as the high cost of establishing a new school, which limit the number of schools in the market.
What can be the harmful effects of an imperfect market?
Imperfect markets can have a number of harmful effects, including:
- Inefficiency: These markets can lead to market inefficiencies, such as overproduction or underproduction of goods and services, and a failure to allocate resources to their most productive uses.
- Market power: In these markets, some market participants may have more market power than others, which can lead to price manipulation, reduced competition, and reduced consumer welfare.
- Income distribution: They can result in unequal distribution of income, with some participants earning higher profits at the expense of others.
- Inadequate investment: They discourage investment in certain industries or areas, leading to a failure to develop the potential of these areas.
- Environmental degradation: They can lead to negative environmental effects, as market participants may not internalize the costs of environmental degradation.
- Consumer exploitation: In such markets, companies can exploit consumers with market power, who can charge higher prices and offer lower-quality products and services.
What are the four types of imperfect markets?
There are several ways to categorize imperfect markets, but one common framework identifies four types:
- Monopoly
- Monopolistic competition
- Oligopoly
- Oligopsony & Monopsony
What are perfect and imperfect markets?
Imperfect and Perfect markets are economic concepts used to describe the level of competition in a market. A perfect market has several ideal conditions:
- A large number of buyers and sellers
- Perfect information
- Homogeneous products
- Zero transaction costs
- No barriers to entry
In contrast, an imperfect market is any market that deviates from the ideal conditions of a perfect market. They can arise due to various reasons such as lack of information, barriers to entry, government intervention, and unequal bargaining power between buyers and sellers. Most real-world markets are imperfect, as they are affected by various factors that prevent them from being perfectly competitive.
Recommended Articles
We really hope that you find this EDUCBA information on Imperfect Markets to be useful. EDUCBA suggests the following articles for additional information on depreciation-related subjects.


