Definition of an Incumbent
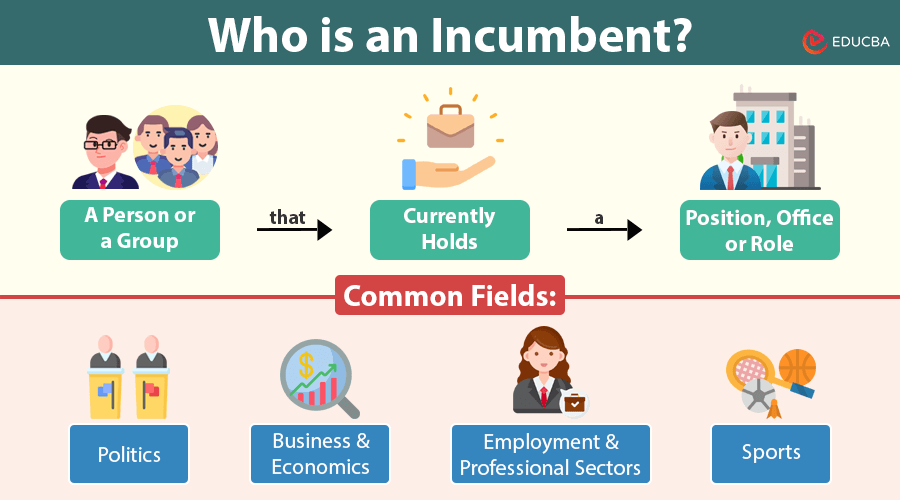
An incumbent is a person or group currently holding a position, office, or role. The term is commonly used in politics, business, and various professional fields to refer to an individual or entity already in power or operation.
For example, in an election, the current president or prime minister seeking re-election is called the incumbent. Similarly, in business, a company that dominates a particular market segment before new competitors emerge is considered an incumbent.
The role of incumbents is significant because they have existing authority, experience, and resources, giving them a competitive edge. However, they also face challenges from competitors, technological shifts, and changing public expectations.
Incumbent in Different Fields
The term is widely used across various fields, each with its own significance. Here is how the concept applies in different domains:
1. Politics
In political scenarios, it is an individual who currently holds an elected office. They often have an advantage due to their established public presence, access to government resources, and policy experience.
2. Business and Economics
In the corporate world, it refers to companies that already have a significant market share and customer base. These businesses have operational efficiency, brand loyalty, and financial stability, which give them a stronghold over new entrants.
3. Employment and Professional Sectors
In organizations, an incumbent is an employee who currently holds a particular job role. This term is often used in recruitment and HR discussions.
4. Sports
In sports, the reigning champion or titleholder is considered the incumbent. They often have the advantage of experience but must defend their title against challengers.
Examples of Successful and Struggling Incumbents
Here are some examples of incumbents who have successfully maintained their dominance and those who have struggled to keep up with industry changes:
- Successful: Apple has remained a dominant tech incumbent by consistently innovating and meeting customer demands.
- Struggling: Nokia, once a mobile phone giant, failed to adapt to smartphone trends and lost its incumbent status.
Advantages of Being an Incumbent
Here are several benefits:
- Experience and Knowledge: They have hands-on experience and institutional knowledge, making them more efficient in their roles.
- Established Reputation: A well-known name in politics, business, or sports can influence people’s trust and decision-making.
- Resource Availability: Companies and political figures often have better funding, infrastructure, and networks compared to new entrants.
- Customer and Voter Loyalty: Established brands and leaders often have loyal supporters who trust their work and continue to back them.
Challenges Faced by Incumbents
Despite their advantages, they also faces significant challenges:
- Competition from New Entrants: In politics, business, and sports, new players often bring fresh ideas and strategies that attract attention and support.
- Resistance to Change: It may be slow to adapt to new technologies, trends, or policies, making them vulnerable to disruption.
- Public or Consumer Dissatisfaction: Over time, people may become dissatisfied with an incumbent if they do not meet expectations or fail to innovate.
- Regulatory and Legal Challenges: Governments may introduce laws that affect business incumbents, while political incumbents may face stricter public scrutiny.
How an Incumbent Stays Competitive?
To maintain their position and relevance, an incumbent must:
- Innovate Continuously: Businesses should invest in research and development, while political incumbents must introduce progressive policies.
- Engage with the Audience: Whether voters or consumers, it must actively communicate with their audience to understand their needs and expectations.
- Adapt to Market Changes: Staying updated with trends and technological advancements can help incumbents compete effectively.
- Improve Efficiency: Enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and improving service quality can strengthen an incumbent’s position.
Final Thoughts
An incumbent holds a position of power, whether in politics, business, sports, or employment. While they benefit from experience, resources, and reputation, they also face competition and challenges that require them to adapt and innovate. Those who embrace change and engage with their audience can retain their status. At the same time, those who resist evolution risk losing their dominance. Understanding its strengths and weaknesses helps us appreciate the dynamics of leadership and competition in different fields.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can a company be an incumbent in multiple industries?
Answer: Yes, if it holds a leading position in multiple markets, such as Amazon in e-commerce and cloud computing.
Q2. Does “incumbent” always imply a long tenure?
Answer: Not necessarily. It only means the person or entity currently holds the position, regardless of how long they have been there.
Q3. What does “it is incumbent upon” mean?
Answer: It means someone has a duty or responsibility to do something. Example:
“It is incumbent upon teachers to educate their students well.”
Q4. Are incumbents always experienced?
Answer: Not necessarily—someone can be newly appointed and still be the incumbent.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on incumbents has been helpful. Check out these recommended articles for more insights on market competition, leadership strategies, and business innovation.
