Updated November 10, 2023
Difference Between Inflation vs Deflation
In Inflation vs. Deflation, inflation is when prices of products and services go up, making them expensive. On the other hand, deflation is when prices of products and services go down, letting you buy more things with the same amount of money.
What is Inflation?
There have been instances in the world economy where certain countries witnessed an extremely fast increase in their inflation rates. This phenomenon is known as “Hyperinflation”. Under Hyperinflation, inflation grows at unusual rates of 500% – 1000%. Currently, Venezuela is experiencing a high inflation rate.
The two main causes of Inflation are:
- Demand-pull Inflation: Demand-pull inflation occurs when the aggregate demand for goods exceeds the aggregate supply. When too much money chases a few goods, suppliers raise the prices to benefit from the rising demand.
- Cost-push Inflation: Cost-push inflation is a scenario where the increase in the prices of factors of production leads to a significant increase in the cost of the goods, thus prompting suppliers to raise the prices.
People do not always consider a decrease in the inflation rate as deflation. A decline in the inflation rate, such as from around 10% – 15% to 4% – 5%, is termed Disinflation. Disinflation is different from Deflation because the inflation rate during disinflation is still positive even after falling dramatically.
What is Deflation?
- During Deflation, as the price levels fall, companies typically experience a fall in their revenues, leading to increased debt levels. The companies, short of enough cash, cut their spending, investments, and labor; lower investments, spending, and increased unemployment further deteriorate the economy leading to recession.
- Deflation is considered bad for the economy because it causes immense damage. Companies experience less profitability due to lower prices, leading them to spend and invest less. As prices continue to fall, consumers delay their purchases in anticipation of even cheaper prices, reducing demand. This prompts companies to slash prices even more.
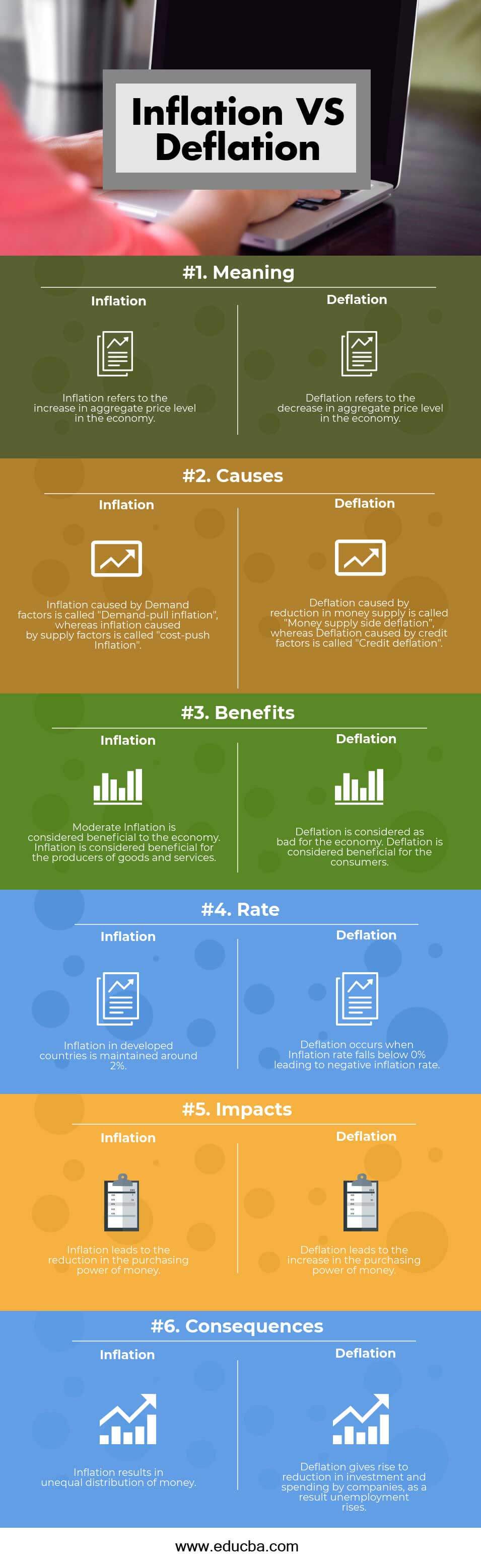
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Inflation vs Deflation (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 difference between Inflation vs Deflation
Key Differences Between Inflation vs Deflation
Both Inflations vs Deflation are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences:
- Inflation leads to a decrease in the value of money, whereas Deflation leads to an increase in the value of money.
- A moderate inflation rate is healthy for the economy; however, Deflation causes the economy to deteriorate.
- Producers consider inflation to be beneficial, while consumers consider deflation to be beneficial.
- Economists consider a 2% inflation rate healthy, while deflation is characterized by a negative inflation rate (below 0%).
- Demand and supply factors primarily cause inflation, while money supply and credit factors cause deflation.
- Inflation leads to uneven distribution of money, whereas Deflation leads to reduced spending and increased unemployment.
Inflation vs Deflation Comparison Table
As you can see, there are many Comparisons between Inflation vs Deflation. Let’s look at the top Comparison between Inflation vs Deflation –
| The basis of comparison | Inflation | Deflation |
| Meaning | Inflation refers to the increase in the aggregate price level in the economy. | Deflation refers to the decrease in the aggregate price level in the economy. |
| Causes | Inflation caused by Demand factors is called “Demand-pull inflation”, whereas inflation caused by supply factors is called “cost-push Inflation”. | Deflation caused by a reduction in money supply is called “Money supply-side deflation”, whereas Deflation caused by credit factors is called “Credit deflation”. |
| Benefits | Moderate Inflation is considered beneficial to the economy. Inflation is considered beneficial for the producers of goods and services. | Deflation is bad for the economy. Deflation is considered beneficial for consumers. |
| Rate | The inflation rate is around 2% in developed countries. | Deflation occurs when the Inflation rate falls below 0% leading to a negative inflation rate. |
| Impacts | Inflation leads to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. | Deflation leads to an increase in the purchasing power of money. |
| Consequences | Inflation results in unequal distribution of money. | Deflation gives rise to a reduction in investment and spending by companies; as a result, unemployment rises. |
Conclusion
The economy always follows a cyclical process that the central banks constantly monitor to adjust the interest rates according to the cycle. We cannot control the economy’s cycles, but central bank intervention can marginally control the impact of these cycles. When the Inflation rate rises above a certain level where central banks feel the economy is overheating, they raise the interest rate to reduce demand, thereby cooling down the economy.
Central banks lower interest rates when they feel the economy is slowing down and the inflation rate falls below a certain level to increase demand and revive economic growth.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top differences between Inflation vs Deflation. Here we also discuss the Inflation vs Deflation key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles