Updated April 27, 2023

How to Install Fedora?
Fedora is a Linux-based operating system. To install Fedora, follow these steps:
Go to https://getfedora.org/ to access the Home page of Fedora.
Choose one of the three options provided:
- Fedora Workstation: This option provides a user-friendly and powerful operating system for desktops and laptops. GNOME comes as default, and SPINS allows you to install other desktops directly.
- Fedora Server: This option is suitable for servers and data center technologies, but not for desktop installations.
- Fedora Atomic: This option provides the bare essentials and serves deployment of images on the Cloud using Docker containers.
T
Steps to Install Fedora
One may choose the Workstation option to install Fedora”
The following are the installation steps:
The ‘Download Now” option copies the Fedora media writer for Windows onto the local machine. After running the file, the entire installation package, which is approximately 1.8GB in size, is downloaded.
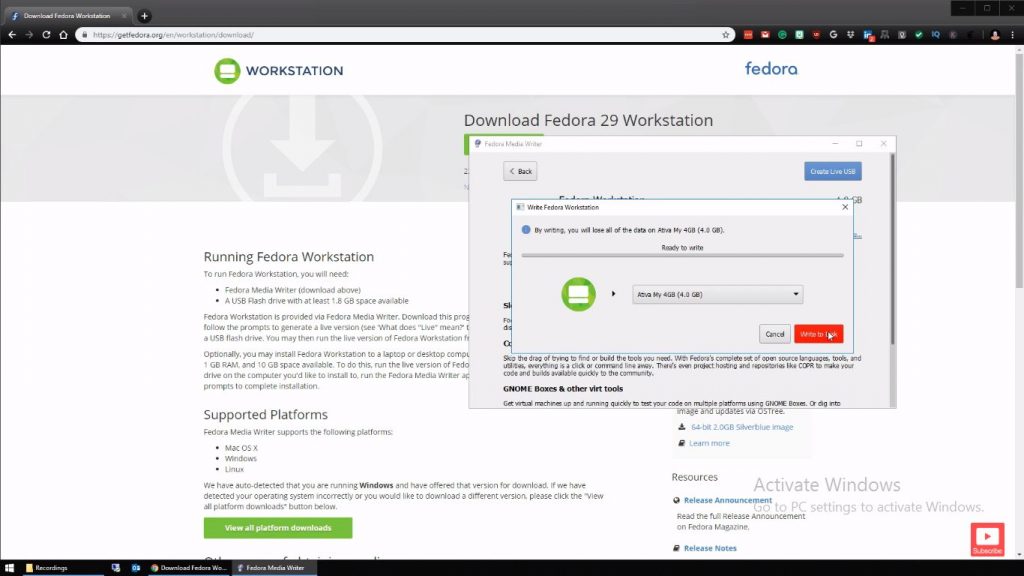
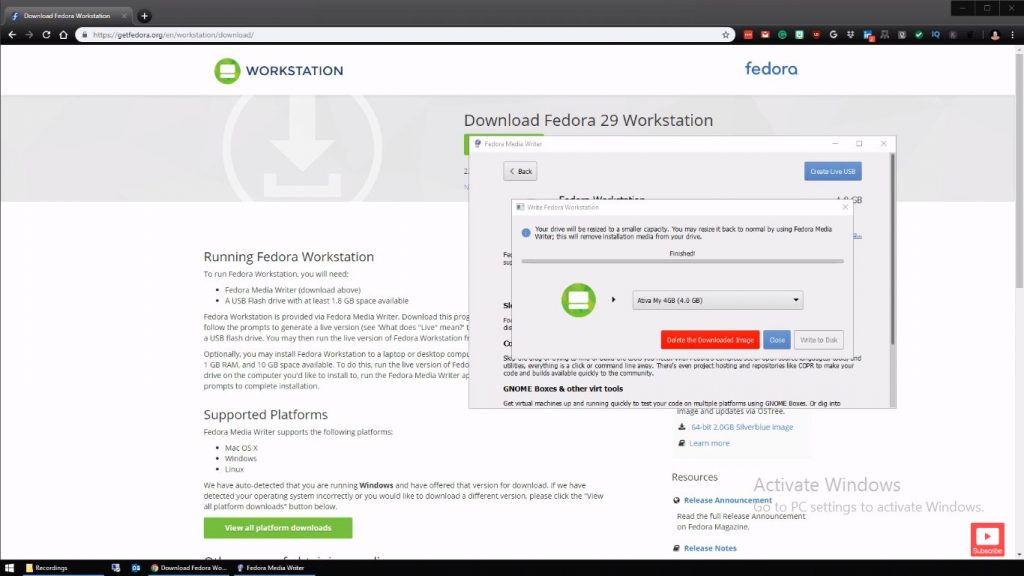
Plug in the USB into which the installation is to be copied and select ‘write to disk’ from the pop-up window.
One can install Fedora on a different computer or the same one, but one should know that it will delete the Windows OS if there is not sufficient space to partition the drive. Thus, it is a risky installation process.
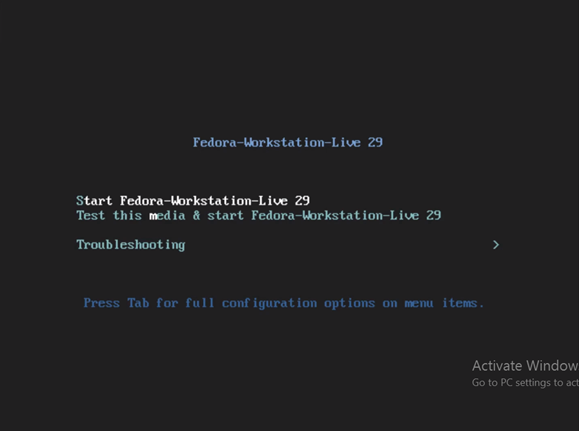
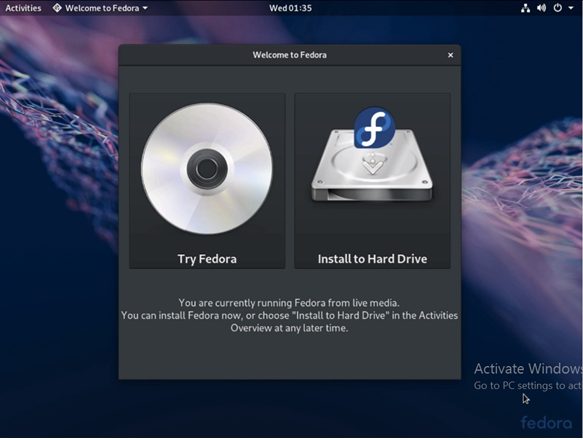
One selects the second option if one wishes to test the media and navigate the live environment options. However, to install Fedora, select the first option.
Click on the ‘Install to Hard Drive’ option to load the installation and create the necessary partitions.
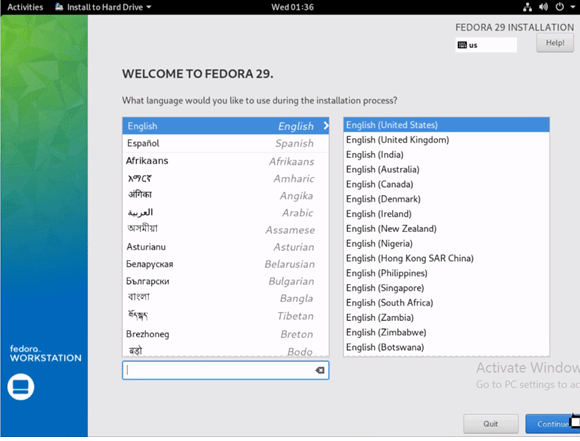
Choose the preferred language from this window. Once selected, proceed to click on the ‘Continue’ button.
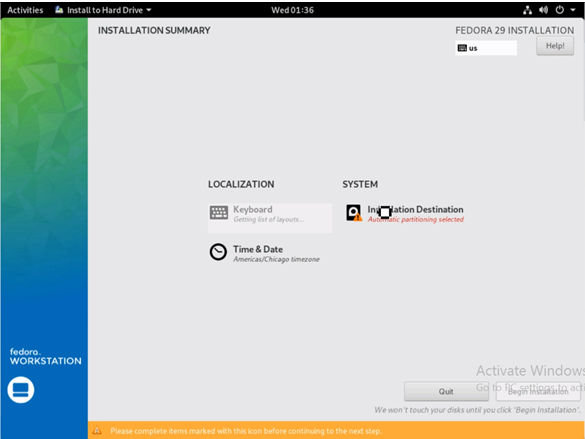
Now, click on the ‘Installation Destination’ option.
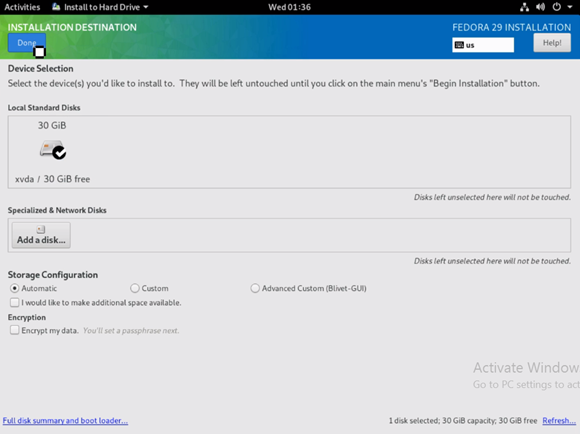
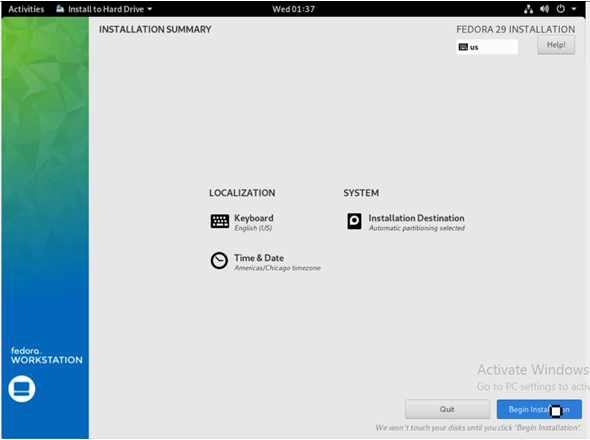
Here, under ‘Local Standard Disks’, one can select the targetted hard drive for installation. If this is occurring on a machine using an existing OS (Windows or Linux), a prompt comes up to reclaim the space. Click on ‘Done’ once all the checks are complete.
The configurations are now saved. Now choose the option ‘Begin Installation’.
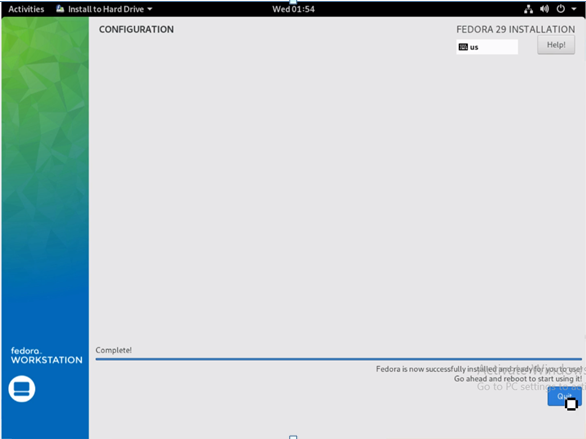
Click on ‘Quit’ once Fedora installation is complete.
Since Fedora does not provide an auto-prompt to reboot, a manual restart is necessary to install Fedora completely.
While the system is restarting, the USB can be removed, as it is not needed anymore.
The Welcome Screen appears on the first boot, as shown below:
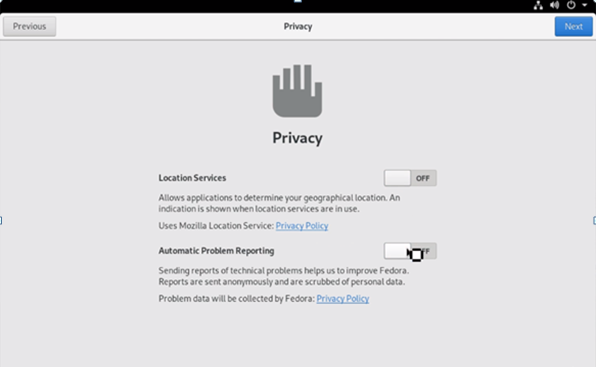
First, the ‘Privacy’ page opens up. Here, the ‘Location services’ and the ‘Automatic problem reporting’ can be ‘Enabled/Disabled’. One can change these options from the system settings even at a later stage. Click on ‘Next’ to view the subsequent windows and the options provided.
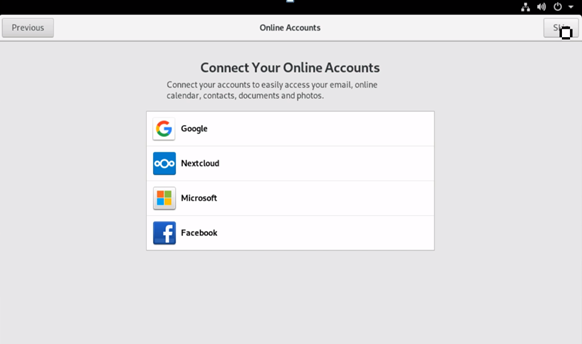
One can connect other accounts from Google, Facebook, or Microsoft using the Online Accounts page.
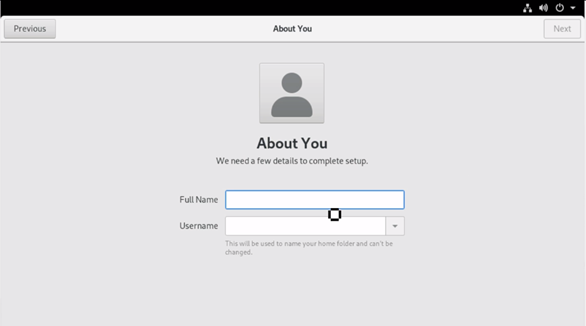
Provide the ‘Username’ which will be used for the ‘Home’ folder, and it cannot be changed. One can also set up Enterprise-level logins using this window.
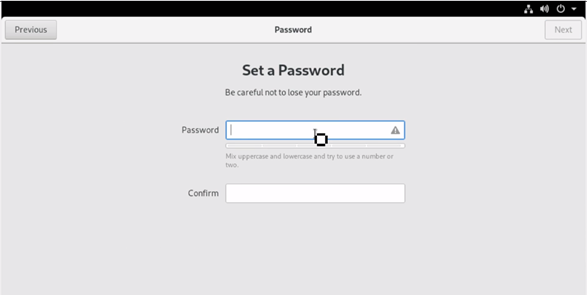
Setup a ‘Password’ for the login credentials provided on the previous page.
The installation is now complete with the below confirmation window.
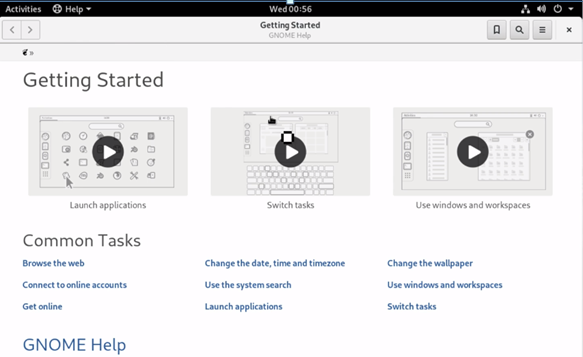
One can make use of the ‘Activities’ option to open the ‘Help’ window. The ‘Getting Started’ guide and ‘Gnome Help’ option is available as well. There are various tutorials provided on using Fedora’.
One can open the Gnome software and find the applications and updates available for download. Click on the ‘Let’s go shopping’ option and give a minute to refresh in order to check for pending updates. ‘Updates Tab’ helps check any spinning updates in progress. One can do the updates directly from the terminal window as well.
Open the terminal and type:
sudo yum updateAfter completing the update, click on “Yes,” and then manually reboot the system to complete the process. It is always a bad idea to install updates via the terminal without using a utility such as a screen or terminal, unless it is a disposable installation. The newly updated Fedora is now available, with actual application listings provided.
Fedora also supports enabling third-party software repositories, and we can find the Google Chrome repository in the Open Software repositories. This is a significant change for Fedora, which traditionally does not facilitate proprietary applications. The kernel version can be checked, and the latest version is available. Firefox and Libre Office come installed by default.
The latest version of Fedora has a very basic look and feel, with the Adwaita theme being the default for Gnome. By default, Fedora creates a separate partition for the home and root directories. This separates the home partition from the distribution, providing a decent default setup that desktop distributions should follow.
New Features of Fedora
The new features of Fedora include:
- Fedora modularity: Provides a new option that allows applications to have dependencies of different versions and use them simultaneously.
- GNOME: The system settings now include Thunderbolt device.
- Screen sharing: It is now possible in the newest release.
- Memory efficiency: Improved in version 29, resulting in faster system booting and an overall better user experience.
- Power PC: Support for Power PC has been discontinued in this release.
- New packages: Various packages such as Python, MySQL, and Node.JS have newer updated versions.
Other default applications that are available include:
- Gnome boxes, which are set up and can help in installing virtual machines right away.
- Cheese serves webcam support.
- Rhythmbox serves music collection.
Using the Ubuntu theme may provide a better experience for users as Fedora makes use of the Vanilla Architecture. In Fedora, the package installers should be more responsive, and the developer-centric distribution provides only limited libraries by default. Thus, additional libraries require installation. The distribution and the number of packages available make Ubuntu a better choice.
Wayland and XORG are display servers that form integral parts of the display in the monitor. They help communicate between graphic instances and remote terminals. Wayland, which comes with Gnome, can cause hiccups during seizure time, resulting in displaying only a black screen. One can overcome the issue by disabling Wayland, allowing XORG to take over and provide an easy fix for display issues.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Install Fedora” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.