What do You Mean By Insurance?
Insurance is a promise of financial protection that reimburses an individual/organization for any loss arising from an uncertain event. For example, hurricane Ian struck Florida on September 28, 2022. Most residents had a viable policy, so they initiated a claim with their insurers. The amount is said to be around $60 to $70 billion.
While the person claiming protection is the insured, the insurer provides it. The policyholder pays a periodic premium amount to the insurer. This amount is according to the value guaranteed in the policy. Since several companies sell these contracts, they are available with affordable premiums.
Key Highlights
- Insurance provides financial support by protecting the insured from the loss incurred through injury, damage, etc
- The one getting the protection is the insured, and the one who provides it is the insurer
- Various policies are available based on unforeseen dangers affecting human life. The most common are life, vehicle, health, home, property insurance, and more
- Premium, policy limit, and deductible are the main components of a coverage policy. Therefore, the policy buyer should read them thoroughly.
How Does Insurance Work?
- It works on the risk-sharing principle among people exposed to similar risks. Its fundamental function is to provide damage control to the insured by pooling clients
- A group of people contributes towards forming a pool of funds. Hence, any loss to the insured due to uncertain events goes from this pool. The consolidated collection helps an individual to recover from the loss
- For example, 50 people buy a life insurance plan and pool their premium payments. Suppose one of them passes away. The insured amount for that person goes out of the payment pool
- The companies act as a trustee to this pool and charge a premium to guarantee the insured on losses. The premiums usually depend upon the type of plan
- In simple terms, it is a risk management tool as the quantified risk of various volumes can be insured.
Insurance Examples
Example 1
One real-life example is Cristiano Ronaldo has insurance of $90-$100 million (90-100 million euros) for his legs. As he is an asset for the team he plays for, Real Madrid F.C. bought the policy for him.
Example 2
Steve purchased a new car two years ago and got it insured for 15 years through a service. The premium calculation is $15,000 annually, and the insured value is $1 million.
While traveling with family, they meet with an accident, which causes damage to the car. The repair costs are around $500,000. As per the contract, the insurer pays compensation for the damage.
Suppose Steve did not need to claim the policy throughout its validity, and Steve received $1 million at maturity. The taxable amount will be $775,000 after subtracting the total premium ($15,000 * 15) from $1 million.
Example 3
Mary has a healthcare policy for a yearly premium of $500. It gives coverage of $1 million. After a few years, she is diagnosed with cancer. However, she claims the policy, and the company pays for her complete medical treatment.
Types of Insurance
Life
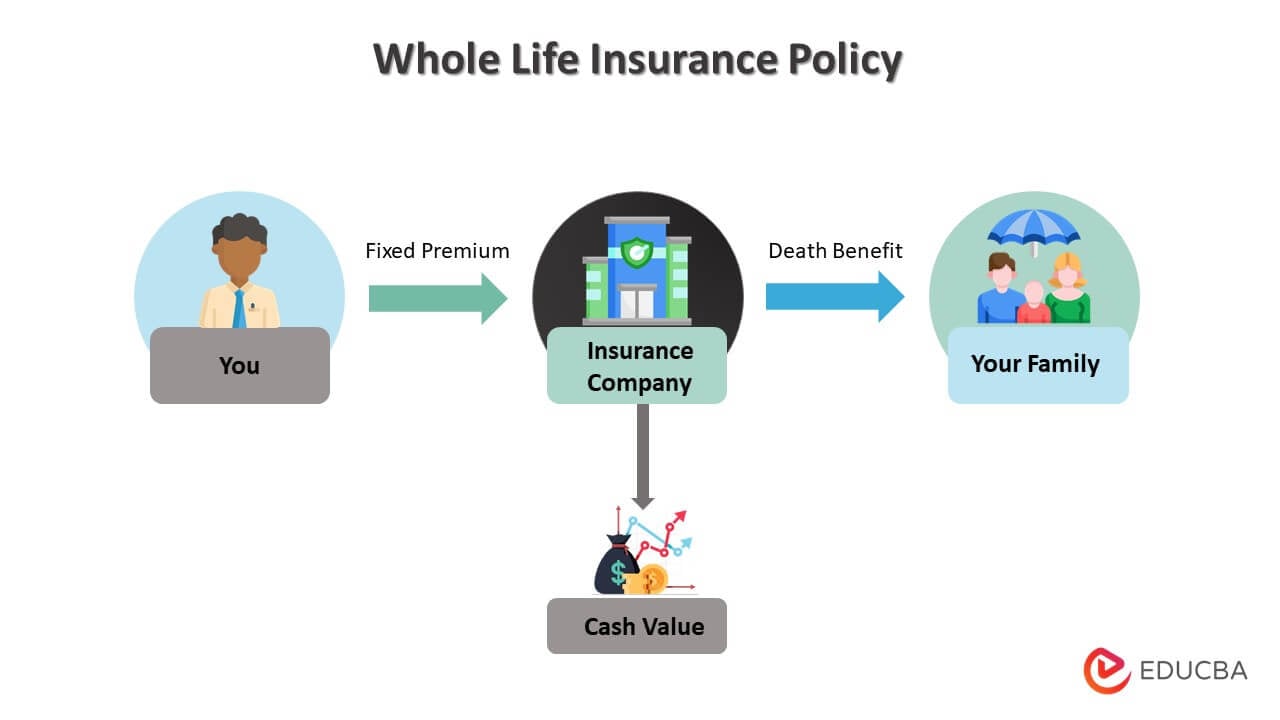
- Life insurance guarantees financial security and benefits to the descendants in case of the sudden death of the family member
- The insurer makes the guaranteed payment in case of the insured person’s demise or when the policy matures.
Vehicle
- It covers losses that occur to cars, motors, or any other vehicle because of accidents, theft, and others
- It also covers the financial expenditure of medical care for anyone injured during the incident.
Health
- This policy covers the expenses for medical treatments for critical and minor illnesses
- Additionally, it ensures against any harm from accidents and workplace injuries. The coverage differs from policy to policy.
Property/Home
- It usually safeguards a person’s real estate properties, like home, factory, office, etc
- As mentioned in the policy, it protects against theft, fire, and natural calamities such as earthquakes, floods, and others.
Credit
- It is when a person fails to repay debts, loans, and mortgages due to unavoidable situations of death, job loss, or accident
- It is a basic plan where the insurer pays for those things.
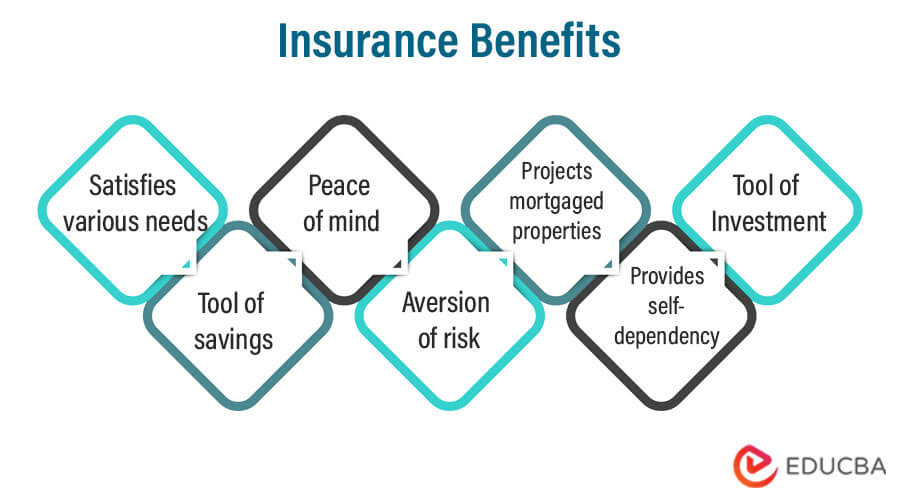
Benefits of Insurance
- It provides financial support during crises and also supports the individual with psychological loss by providing counseling services
- It provides certainty and, in turn, peace of mind during vulnerable times
- Pooling is a widely renowned technique that mitigates financial regularities among clients. It enables risk-sharing as the clients pay a nominal fee in the pool to take care of the damage caused to another client.
Principles of Insurance
Uberrimae Fidei (Utmost Good Faith)
- It means that the insured and the insurer must have absolute belief and trust between them
- Both parties in the contract should disclose all relevant facts for the subject matter of the coverage plan.
Insurable Interest
- It states that the policyholder must have a close connection or interest in the insured object (person, property, etc.)
- The policyholder must suffer a loss due to the non-existence or damage of the thing.
Indemnity
- The purpose of insurance should not be to make profits out of the claims but to protect against potential damage
- This principle does not apply to life insurance since the value of human life cannot be measured in money.
Contribution
- The insured can claim the total loss from either only one insurer or claim contribution from multiple insurers
- It does not apply to life insurance as we cannot measure the value of human life.
Subrogation
- This principle states that when an insurer compensates for property damage, the policyholder cannot claim the property anymore
- The ownership then shifts to the insurer.
Loss Minimization
- According to this principle, the insured should be responsible regarding their insured properties
- They should try to minimize their losses in any accident or damage.
Causa Proxima (Nearest Cause)
- In case of more than one cause of damage, the amount of compensation is according to the nearest cause.
Components of Insurance
Policy Limit
- It is the maximum amount an insurer will compensate the nominee under the plan
- The total amount that policyholders can claim depends upon the premiums, the extent of damage, and the period.
Deductible
- The percentage that the insured pays out of pocket before the insurer steps in to settle the claim is deductible
- The companies release the claim only after it surpasses the deductible limit.
Premiums
- The policy buyer has to pay an amount to the insurance provider in exchange for the security of the insured item
- These premium payments can be periodical, i.e., monthly, quarterly, or even annually.
Tax Benefits
- The tax applies to the amount one gets after the expiration; less the total amount one paid in premiums. For instance, James buys a policy that pays $100,000 at maturity. The premium payments totals $45,000. Thus, the tax will apply to the $55,000 ($100,000 – $45,000)
- Taxation rules differ for every policy. For example, US employer-provided life insurance that pays above $50,000 is taxable
- Section 80C of the Indian Income Tax Act, 1961 allows deduction of premiums for life insurance plans from taxable income. These deductions have a cap of 1.5 lakh INR per annum.
- Additionally, Section 80D of the Indian Income Tax Act allows you to deduct health insurance costs as per conditions.
Conclusion
Daily life carries the risk of financial losses, like theft, natural disaster, or sudden death. As they can affect the lives of people and their dear ones, insurance helps protect people against these dangers. It assures financial assistance in damage, harm, or injury. Moreover, it provides tax benefits, depending on the coverage plan.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
Q1. What is Insurance? What are its types?
Answer: It is a mechanism to protect the insured from financial losses arising from damage, harm, or injury. The most common five types are life, home, credit, health, and vehicle insurance.
Q2. What is Insurance for Non-profit?
Answer: Nonprofit insurance protects the individual/organization from any scenario that advances liability lawsuits. Nonprofits face lawsuits from volunteers, donors, employees, and government regulators due to accidents, oversights, or misunderstandings. They receive proper coverage for legal costs or damage awards.
Q3. Define Insurance For small businesses
Answer: Insurance for small businesses is a risk-financing mechanism that protects them from lawsuits, potential claims, business damages, and more.
Q4. Name some insurance companies.
Answer: Various companies provide a wide variety of insurance options. Thus, a purchaser can buy one as per his need and preference. There are accident, health, casualty insurers, and financial guarantors. Some famous insurance companies are Berkshire Hathaway Insurance, Progressive Insurance Groups, State Farm Group, and Care Insurance Private Limited.
Recommended Articles
This article guides you through Insurance. We discuss its definition, types, benefits, tax laws, and more. To know more, read the following articles,