Updated July 25, 2023
Difference Between Interest vs Dividend
A dividend means Pro-rata payment done by the company to equity shareholders. Dividends are payments made like compensation on the amount invested by the Shareholders. Dividends are considered as a safer option to invest and known as a passive source of income. Generally, it is assumed that dividend-paying companies are safer than the growing company. Dividends are part of the profit which is distributed amongst all the shareholders and preference shareholders.
What is Interest and Dividend?
Dividends can be of two types: Qualified and not qualified dividends. In the case of preference shareholders, they are given preference and a fixed amount of dividends. In the case of common shareholders, the choice is with the company whether to pass on the profits to the shareholders or not. Dividend yield is generally considered around 2-3 percent. Dividends could be through different types of investments made. Dividends do not act as an expense to the company or reduce any Net Income e.g. When a dividend is declared as Rs 1000, cash from the assets is reduced by Rs 1000 and retained earnings in the balance sheet decrease by Rs 1000. Interest is the cost that is taken by the company on the amount borrowed in the period.
You keep money in the bank and receive interest on it because you give the bank the money to use it. Interest is like a charge which is based on the amount of money used. Interest can be from any banks or lenders or any other corporations. Interest simply means money received on behalf of taking loans. Interest expense reduces the net income of any company. Cash reduces in the interest expense side whereas cash will be saved by saving it in income tax.
Head To Head Comparison Between Interest vs Dividend (Infographics)
Below are the top 8 differences between Interest and Dividend.
Key Differences Between Interest vs Dividend
Both Interests vs Dividend are popular choices in the market, let us discuss some of the major Differences Between Interest vs Dividend:
- The company has to earn a profit before deciding whether to distribute it amongst the common shareholders. The company can do anything with earnings. It can be retained for further growth or further passed. Dividends can be generally given in an annual format. Quarterly dividends are rare in the company. Special dividends are to be given by companies in the interim between the year if suppose the company made more profit. In the case of preferred shareholders, the company pays dividends only when on profit however in common shareholders it’s an option ( can/cannot pay the dividend in profit or loss) can happen that the company doesn’t earn a profit so won’t pay dividends. Irrespective of any net profit the person or the organization has to pay interest to the debenture or the lenders.
- Interest paying is mandatory even if you earn the profit or not. In the case of dividends, the payment of the dividend is optional on the company. Sometimes the company decides to reinvest the money in the future expansion and growth else the company can even give the profit shares and distribute it to all the shareholders. Few companies follow a fixed pattern of dividends distribution and do not change it drastically. Companies don’t initiate and end the dividend distribution pattern on a regular basis.
- Interest and Dividends are paid to lenders and creditors who take loans for business or any personal use. Dividends are paid to the shareholders (common and preferred) which are considered as the owners of the companies.
- The percentage of interest on the principal amount is fixed at the initiation time of the contract. e.g While taking a home loan a person gets a plan say 7% which is fixed and cannot be changed. The percentage of dividends is variable based on the strategy of the company.
- Interest paid is compulsory: If you are taking the loan for your business. Regardless of whether your business is making a profit or loss, you have to pay interest. If interest income is not paid on the given time frame the company has to face some legal issues. In dividends company’s BOD and members depending upon the future goals of the company. There is no legal compliance for the distribution of dividends. The company can decide to keep it in reserves for further company use. Corporations can any time decide and change the policies to start or stop it change the pattern.
- Tax benefits are not at all helpful in dividends. Interest can be in any category. In the case of interest, the company has tax benefits because the amount of interest paid is deducted from the revenue, and then on the balancing amount further tax is calculated. However, the interest could be deductible for treasury bonds. After deducting the tax the net income is calculated. So the company gets tax benefits on the amount of the interest paid and taxes are paid less and saved by the company. Financial leverage increases in case of interest.
- By looking at the dividend distribution pattern one can determine how much of the amount the company is reinvesting in itself. Paying dividends regularly means the company’s ability to perform is great. For doing fundamental analysis if any company pays a dividend and continues to do so. This gives a positive response to all investors. It can be determined to know how much profit/loss a company has made. The company not having an interest in the financial statements means the company is debt-free.
Head To Head Comparison Between Interest and Dividend
Below is the topmost comparison between Interest and Dividend.
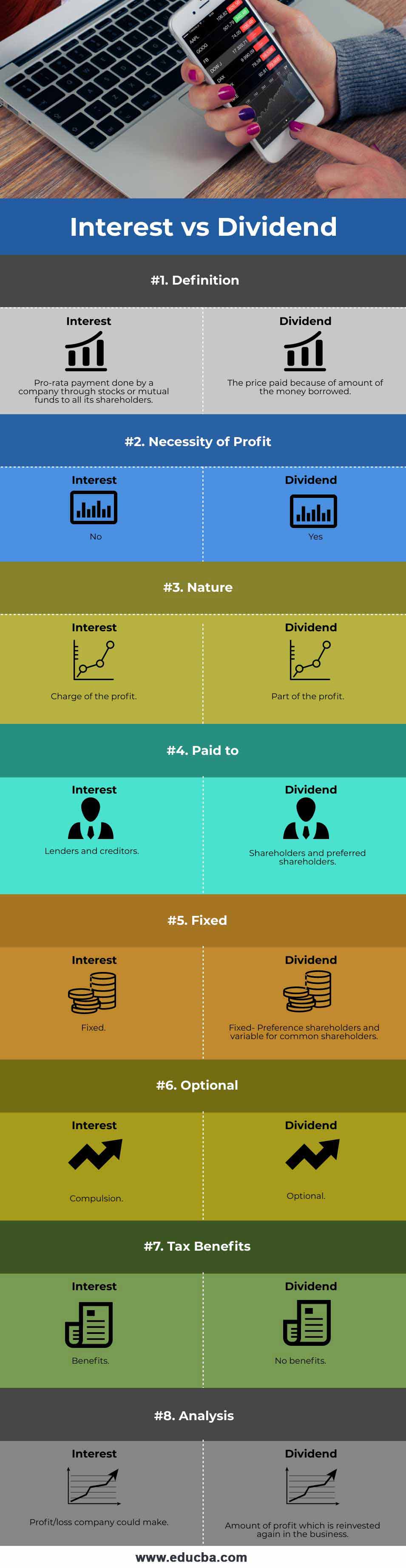
| Basis of Comparison | Interest | Dividend |
| Definition | Pro-rate payment done by a company through stocks or mutual funds to all its shareholders. | The price paid because of the amount of the money borrowed. |
| Necessity of Profit | No | Yes |
| Nature | Charge of the profit. | Part of the profit. |
| Paid to | Lenders and creditors. | Shareholders and preferred shareholders. |
| Fixed | Fixed | Fixed- Preference shareholders and variables for common shareholders. |
| Optional | Compulsion | Optional |
| Tax benefits | Benefits | No benefits |
| Analysis | Profit/loss company could make. | Amount of profit which is reinvested again in the business. |
Conclusion
Even if the company is not paying dividend doesn’t mean you cannot invest in it. Investor’s aim is to maximize its wealth which can be in two ways either by dividends or by the change in the market value of the stocks. So just investment analysis only based on dividend payment is wrong. Dividends and interest are two different types but a major component of the business. Before deciding any type of investments one needs to check the tax effects and the potential income gain. One needs to check the past performance of the distribution and needs to analyze the annual statements before coming to any conclusion.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to the top differences between Interest vs Dividend. Here we also discuss the Interest and Dividend key differences with Infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –