Introduction to Blockchain
The following article provides an outline for Introduction to Blockchain. Blockchain refers to a technology that brings in the solution to the age-old human trust problem. It emerged in the market with the renowned cryptocurrency Bitcoin. It provides an architecture that allows us to trust a decentralized system (Internet or Web) rather than trusting any actor within it.
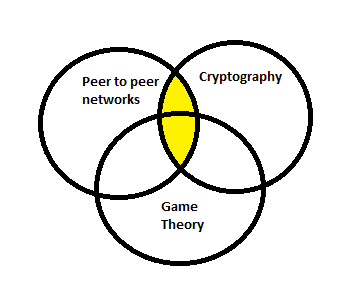
It runs on top of a peer-to-peer network and holds identical copies of the ledger of transactions. This helps to avoid any middleman, and the entire process of transaction takes place through machine consensus. It is a ledger that is shared between multiple entities that everyone can inspect, but not any single user can control it. It is a distributed cryptographically secured database that keeps the record of every transaction from the very initial one.
Major Components of Blockchain
The information in a Blockchain is stored in cryptographically encrypted chunks called blocks. The next successive block contains information about the previous block and hence forms a chain. Thus, the name comes as Blockchain. The privacy of the Blockchain is maintained by high-end cryptographic hash functions and public-key cryptography. It also helps to achieve transparency.
The new transactions are added to the existing information on a consensus of the miners participating in the network. The rules of validating the transactions are coded in the form of algorithms and get implemented by the miners who also get rewarded a native token as per existing economic mechanisms like Proof of Work, Proof of Stake, etc. Here Game Theory comes into play.
The ledger runs on a peer-to-peer network, and thus all the nodes participating in the network get a copy of the original information. Here every node in the network is a client as well as a server, depending on scenarios.
Introduction to Major Characteristics and Application of Blockchain
- It runs on peer to peer network; thus, if any of the nodes tamper with any information, that will not match the existing copy on the other nodes. As a result, the tampered copy will get discarded as any decision is made on a majority basis in the network, and here majority will not agree on the tampered copy to be true. Hence, any middleman or broker can be removed by building a secured, trusted peer-to-peer network and implementing rules based on a consensus basis.
- In the case of Bitcoin, when sending money from A to B – in place of a bank validating the transaction, the same is done by a peer-to-peer network running the validity protocol on a consensus of the majority. Smart contracts are one of the most used applications where transactions are automatically triggered when certain preconditions are met. Essentially, smart contracts are sets of codes running within a blockchain network, executing predefined agreements without human intervention. These contracts also enhance decentralized applications, which can significantly transform digital interactions. For example, in the emerging platform for metaverse interoperability called Somnia, smart contracts enable seamless digital experiences by automating various tasks and transactions within virtual environments. This is achieved by decoupling the contract layer from the blockchain layer – here; a smart contract uses a ledger only to trigger transactions. It has been introduced by the Ethereum blockchain.
- Essentially smart contracts are a set of codes that run in a blockchain network and implements a predefined set of rules or contractual agreements, which in turn controls the transactions. When all the actors in the contract meet the set of predefined rules, the transactions are auto-executed. Thus it provided superior transaction security than the prevalent traditional system reducing the cost of law enforcement. These can be used for various purposes, starting from registries of intellectual properties to administering groups with similar interests and many more. In the coming days, it can be imagined that all the transactions are put into a digital code that is shared in a database in transparent form. These are also protected from deletion, tampering, etc. Various intermediaries like lawyers, brokers, etc., would lose importance as machines and algorithms will do most of the business. For organizations looking to leverage this technology, blockchain development services can help design and implement tailored solutions.
Types of Blockchain
There are basically two types of blockchain networks related to access control.
- Public Blockchain
- Private Blockchain
1. Public Blockchain
Public Blockchain is accessible to everyone – anyone who wants to read, write can join the blockchain and can perform respective operations. The information, once validated in the network, cannot be changed, and no single entity can have control over the network. Bitcoin is one of the first private blockchain networks to prove the value can be moved anywhere around the world without banks or other third parties.
2. Private Blockchain
These blockchains work in the same way as public blockchain but with restricted access. The restriction is applied to the users who are authorized to join the network and operate. They may have one or more entities that control the network. Hyperledger is one of the renowned private blockchain networks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain
Given below are the advantages and disadvantages of Blockchain:
Advantages:
The main advantage of blockchain is the achievement of automation of control over transaction security. Apart from this, blockchain can prevent fraud and abuse.
- Since blockchain is an open-source system, every transaction is in the public domain, so the chance of fraud is very less. The transactions are continuously monitored by the miners around the clock. Thus, under such supervision, it’s very unlikely that someone might fraud into the system.
- There is no control of the government or any financial institutions on cryptocurrencies, and they have no chance at all to get affected by inflation or hyperinflation of the currencies.
- The transactions are almost instant as compared to traditional banks.
- It lets the users make transactions directly to the end-user removing third parties hence decreasing the cost involved. This increases the efficiency of the system and lets the users be not at all dependent on banks or any financial institutions for making any transaction.
Disadvantages:
Just like every system has its own merits and demerits, blockchain also has below demerits.
- The cryptocurrencies might be highly volatile at some time as they are pretty new in the market, and all the organizations need to adopt the same.
- Blockchain might be illicitly used for crime because of the anonymity that exists in the decentralized blockchains and virtual currencies relying on them.
- Adapting blockchain might not be so comfortable for people having less knowledge of technologies.
The blockchain is a revolutionary technology in a present-day business model, and it’s now up to the industry how it takes it up, but nevertheless, it has the potential to transform our economy and society.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Introduction to Blockchain. Here we have discussed the components, application, advantages, and disadvantages of the blockchain. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –