
Introduction to Cloud Computing
The following article provides an outline for Introduction to Cloud Computing. It is a way of accessing computing and storage systems without actively owning and managing the resources. In today’s world, add and storage demands are very dynamic; purchasing, maintaining, and upgrading systems could be a considerable investment of time and money. Companies like AWS (Amazon Web Services), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provide and Ace Cloud compute and storage servers on-demand and charge for what you use. These cloud services can be used to host a static website, e-commerce store, company’s internal data, etc. It has proven extremely useful for startups where compute resources vary mainly over time. Let’s see more in this article, Introduction to Cloud Computing.
Cloud Computing can be classified in terms of the following models:
- Service Models
- Deployment Models
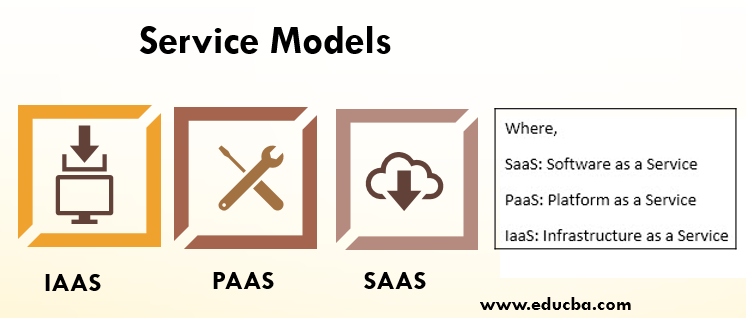
Service Models
Service models are classified in terms of abstraction provided to the end-user.
1. SaaS (Software as a Service)
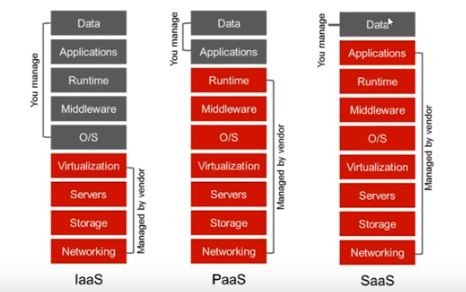
In the SaaS-based model, the cloud service provider, the user, only needs to upload and download data. The service provider handles maintenance, downtime, upgradation, and security.
2. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
In PaaS, the user manages applications along with data. The users often want to launch and maintain their applications over the cloud, where PaaS comes into the picture. The service provider meets all the Hardware, Networking, and O/S needs. The user can use any programming language of choice. PaaS services are cheaper compared to SaaS.
3. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
In IaaS-based service hardware, the vendor provides virtualization and networking services while the user takes care of OS, applications, and data.
To give a brief analogy between different service models, we can take the example of a Pizza order. SaaS is similar to ordering Pizza at home; in PaaS, you visit the restaurant and eat there, while in IaaS, you make Pizza yourself using bread and sauces.
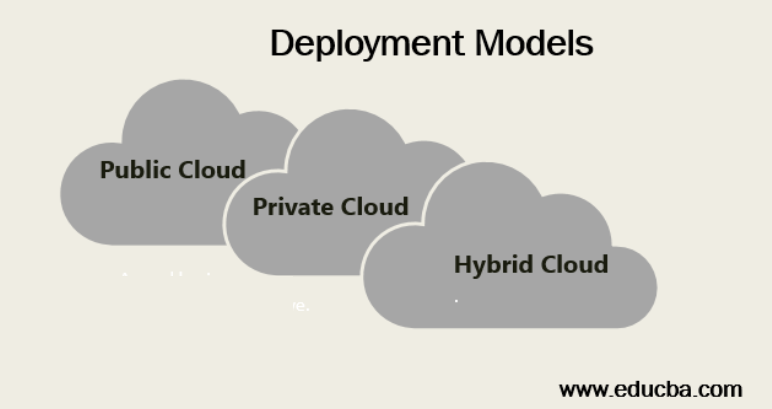
Cloud Computing Deployment Models
Below are the three kinds of Deployment models: Public Cloud, Private Cloud, and Hybrid Cloud.
1. Public Cloud
- Service Provider makes resources such as computing, storage, and applications available to the general public over the Internet.
- Any user can log in and use these services.
- You pay for the number of resources you use.
- Users have lesser control over their data.
2. Private Cloud
- The vendor offers hosted services to fewer users with firewall security.
- The private cloud minimizes security issues.
- It provides greater control over the data.
- Organizations typically use them with a focus on data security.
3. Hybrid Cloud
- Hybrid cloud computing, as the name implies, combines private and public cloud services. Certain services are hosted with a private cloud while others with a public cloud.
- With a hybrid cloud service, enterprises can keep crucial data in private space and other data in public space, thus leveraging the best of both worlds.
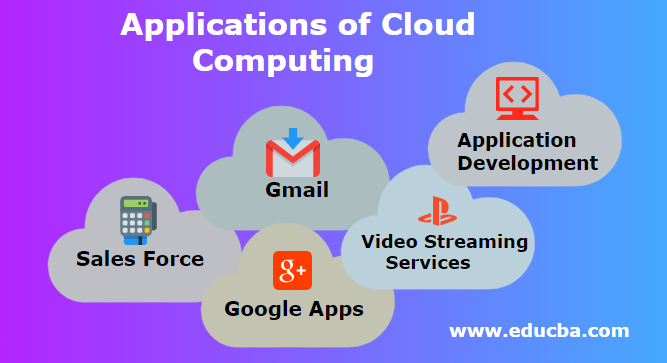
Applications of Cloud Computing
Given below are the applications of cloud computing:
- SalesForce: Sales Force provides CRM (Customer Relationship Management) services and EPR (Enterprise Resource Planning) on cloud infrastructure and charges on a use basis. Salesforce develops and maintains the software, providing add-on services for premium users.
- Gmail: We know Gmail use for personal emails. But Gmail also provides its infrastructure to businesses with their business email-id with additional features.
- Google Apps: Applications like Google Sheets and Google Drive allow cloud storage and computing for the general public.
- Video Streaming Services: Several streaming services, such as NetFlix, Amazon Prime, and Hotstar, rely on cloud computing storage to stream personalized data to billions of users simultaneously.
- Application Development: With more and more companies providing their services via Mobile Apps, companies like Zoho Apps allow users to create apps over the cloud and make modifications. Wix and WordPress offer the same service for website creation and hosting.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Given below are the advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing:
Advantages
- No need to buy a stack of servers, thus avoiding high Capital expenditure.
- Easy to scale: As demand varies with time number of servers can be easily changed.
- As more data gets generated, provisioning can be made to flush old data or add additional space dynamically.
- Monitoring and maintenance of servers are taken care of by the vendor.
- The environment benefits as resources are shared among different users.
Disadvantages
- Cloud computing can be costly for a few large enterprises, with huge amounts of data generated daily; owning and maintaining computing and storage resources makes sense.
- For some applications, internet bandwidth can be a bottleneck where users’ requests and transmits can big time to come online.
- Customization of applications is limited; the cloud-based app may not precisely meet your needs.
- When a vendor stops service and has to look for alternate options, it affects several users.
Cloud Service Providers
Following are the major cloud service providers Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM Cloud, Digital Ocean
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS leads the market with the most significant computing capacity among cloud providers. It allows users to try the basic version of cloud services for a year. The user can either set up Windows or Linux OS systems. AWS services are used for various tasks, from website hosting, E-commerce store to Machine learning models. Big companies like Netflix, Quora, etc., rely on AWS for their services. AWS charges on an hourly basis. Additionally, AWS credits provide startups and developers with free access to various cloud resources, helping them experiment and scale without upfront costs.
2. Microsoft Azure
Azure is a close competitor of AWS for designing and managing cloud services. It allows using various programming languages, Operating systems, databases, etc. and offers new users a 30-day free trial.
 3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP uses Google data centers to provide services such as virtual machines, storage, and numerous applications. It can also be integrated with live data, giving dashboarding features. New users get a certain amount of accessible credit available using GCP services. Unlike AWS, it charges on a second basis. So if you use the service for 5 minutes, you don’t need to pay for the entire hour.
 4. Ace Cloud
4. Ace Cloud
Ace Cloud empowers businesses to thrive in the digital age with a robust suite of public cloud, GPU, and storage solutions. When evaluating cloud-based services, Cloud GPU Pricing is an important factor to consider, as it ensures scalable GPU options that can be tailored to specific operational needs, optimizing efficiency while controlling costs. We go beyond just providing technology; our experienced professionals become an extension of your team, crafting customized strategies that optimize your operations, maximize efficiency, and propel your growth.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Introduction to Cloud Computing. Here we have discussed service & deployment models, applications, and various other cloud computing service providers, along with the advantages and disadvantages. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


 3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
