Updated November 25, 2023
Introduction to NLP (Natural Language Processing)
The following article provides an outline for Introduction to NLP. NLP (Natural Language Processing) will be the biggest leap of humankind shortly and in the field of AI so far. Readers, do not confuse yourself with any resemblance to the Hollywood movie of Will Smith – iRobot. No resemblance to it in any way.
Let’s see what exactly NLP is and why so much hype is associated with it.
You must have heard these names somewhere Google Assistant, Siri, Alexa, and Cortana. Now it’s time to add one more addition to this list; we are discussing GOOGLE DUPLEX. This blog is focused entirely on the introduction to NLP and not on Google Duplex. For our readers, we have provided a kind of latest and most relatable practical example of NLP. GOOGLE DUPLEX is the future of GOOGLE ASSISTANT.
What is NLP?
The definition is straightforward if you understand the 3 words, i.e., Natural Language Processing. NLP involves machines or robots to understand human language and the way we humans talk so that they can effectively communicate with us. It means the processing of human language automatically.
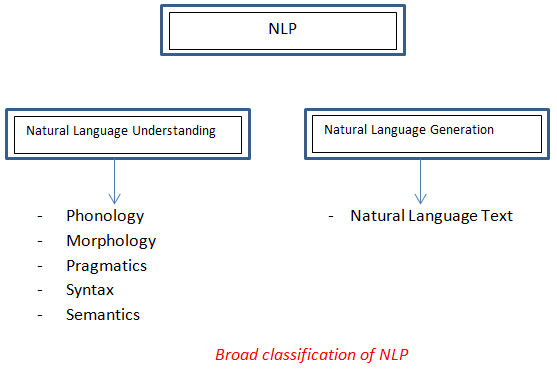
Classification of NLP
Given below are the classifications of NLP:
NLP is classified into two areas:
- Natural language understanding
- Natural language generation
Phonology refers to the science of understanding sound, Morphology refers to word formation, and syntax refers to the structure, whereas Pragmatics relates to understanding.
Components of NLP (Natural Language Processing)
Here there are two things that we have discussed in the classification section. For any communication to take place, these two things are necessary. The first understands, and the other generates (known as a response in a more common language).
When humans talk to each other, the first thing that other humans do is understand the context. Later formulate the response accordingly that makes sense. The two terms try to say this with Natural language understanding, which means understanding the context, and Natural language generation relates to sensible response to the context.
1. Natural Language Understanding
If you know what ambiguity (different meaning of any particular thing) is, this term directly relates to this word.
- Lexical (Word Level): Lexical work at the word level; imagine any word used as a verb and used as a noun. These are crucial to deciding on NLP.
- Syntactical (Parsing): As per NLP, parsing is a synonym for syntactical. E.g. “Call me a cab” This sentence has two implications if you think. One is a request to get a cab, while the other implementation says; my name is the cab, so call me a cab. This is syntactical, which lays its role at a sentence level.
- Referential: Let’s see a new scenario to understand this better. “Alex went to Dave; he said that he was hungry”. This is just an explanation statement demonstrating how complex the interpretations can be for the computers to understand in their initial NLP phase. So, in the above information, the confusion for a computer to understand two he’s is meant for which person (means Alex or Dave).
2. Natural Language Generation
So the machine has understood that we asked them to do something; now comes their turn to provide a proper response or feedback. NLG does the same thing.
- Text Planning: This means plain text from the knowledge base, just like humans have a vocabulary that helps us frame sentences.
- Sentence Making: To arrange all the words and make an arrangement in a meaningful pattern.
- Text Realization: To process all the sentences in a proper sequence or order and give the output is called text realization.
History
Until 1940 this term had no existence, but the first term that came was ‘Machine Translation (MT)’. Russian and English were major languages working after this technology. Late in the 1960s, some influential work regarding AI began, and LUNAR and WINOGRAD SHRDLU were carried in their names.
Applications of NLP (Natural Language Processing)
NLP has a wide spectrum of applicability. Only the tip of the iceberg features has been explored; the rest is still in progress. So far, areas like Machine Translation, Email Spam Detection, Information Extraction, Summarization, and question answering are some of the explored and worked areas.
- Machine Translation is crucial as the entire world is online, and making data accessible to each individual is a huge challenge. Language barrier contributes most to the challenge, with every language associated is a multitude of structures and grammar.
- Spam filtering works using text categorization. Various machine learning techniques have recently been applied to text categorization or anti-spam filtering, like Rule learning and Naïve Bayes models.
- Information extraction is concerned with identifying more relevant and correct textual data. Many applications for whom extracting entities such as names, places, dates, and times are a powerful way of summarizing the relevant information as the user’s need is concerned.
- Summarization, we are currently surrounded by data, which means our ability to understand it. Since data is on an ever-increasing trend and the ability to summarize it with exact meaning is in high demand. This gives us a better chance to manipulate data and make necessary decisions (which is what NLP is trying to do).
Advantages
Though the introduction to the NLP article revolves around other ways NLP can make our life easier.
- Automatic summarization with a click-readable summary.
- Co-reference resolution.
- Discourse analysis.
- Better result.
- Search processing translation.
- More data extraction and more data growth.
- Complex search results.
Technologies using NLP
- Mental illness analysis.
- Electronic health monitoring.
- NLP algorithms.
- NLP site search.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Introduction to NLP. Here we discussed the classification, components, history, and advantages of NLP. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –