Introduction to Project Management
In this Topic, we will learn about the Introduction to Project Management. As everyone widely knows, Henry Gantt, one of the pioneers of project management, developed the popular Gantt Chart, which serves as a diagram for project management. ‘Projects’ could be part of our routine lives or any business. Projects could include preparing a meal at home or organizing a vacation tour. And, if it’s business or work-related, developing a website or software, product or a tool, construction of a building can be termed a ‘Project.’
Thus, the project has temporary tasks implemented to attain targeted objectives within a defined time, scope, resources, and cost. The distinguishing factor between ‘project management and ‘management’ is that the latter is an ongoing process while the former has a definite period and deliverable. In simpler terms, ‘Project Management is a process which requires applying knowledge, skills, expertise, tools, techniques, and deliverables to make the project successful and attain the desired objectives/goals.
Elements of Project Management
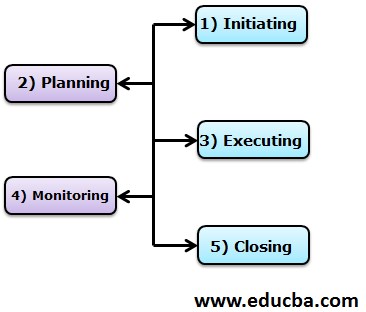
As we learned about the Introduction to Project Management in the above section, so let’s understand the five elements:
- Initiating: The first stage of PM, where formalizing of the project plan, charter, and scope are defined to determine the cost, resources, timeline, and budgeting for the project.
- Planning: The most crucial stage of all, this stage includes strategist the scope of a project, identifying risks, if any, and developing mitigation plans by creating a set of tasks to administer the project.
- Executing: This stage is where the project team is ready to launch or administer the project. The tasks are delegated and resumed to keep track of the project and efficiently manage the same.
- Monitoring/Controlling: At this stage, project performance is evaluated by comparing the real-time results to the defined actuals to ensure all the goals and deliverables are met.
- Closing: The last stage of a project where deliverables are surrendered to the customers, forwarding of documents to the business, releasing resources, and notifying the closure of the project to the stakeholders are carried out.
Apart from the phases mentioned above, project management includes many discrete functions, such as defining project scope, schedule, resources, and budgeting. Procurement, managing risks, communication, and negotiation with the stakeholders also form an integral part of the management of the projects.
Types of Project Management
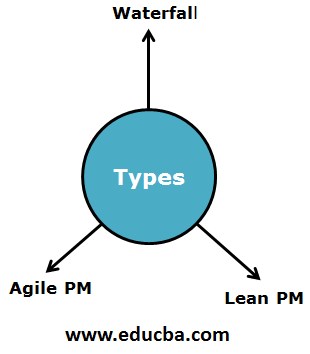
After going through the wide Introduction to Project Management and the five elements, we will explore the different types of project management developed to align with the requirements of particular industries or projects. Let’s explore them.
- Waterfall PM: As the name suggests, this is the conventional type of PM that follows the traditional pattern wherein the next task is resumed only after the completion of the previous task. Therefore, project timeline and attention to the sequence of tasks are paramount in this type of PM. In this type of project management, the team size expands as the smaller tasks are finished, and the larger ones begin.
- Agile PM: The IT sector was the pioneer who used this type of PM. Unlike the conventional one, Agile follows the continual improvement process through monitoring, continuous follow-up, and interactions with the team members per the business conditions. Thus, it helps identify and rectify errors without repeatedly resuming the entire process, which is a plus!
- Lean PM: Lean PM is based on the principle of avoiding waste of time and resources. It practices creating more value from less, primarily based on the Japanese functioning. So, the lean way of PM focuses on adding value by eliminating everything that fails to add value!
Role of Project Manager
The Project Manager is the ‘captain of the ship’ who leads the project team and plans and executes a project. The project manager must ensure whether or not the project aligns with the customer’s vision and quality standards. The Project Manager shoulders the success or failure of the project.
Here are the roles and responsibilities of a Project Manager:
- Identifying and defining the project scope, timeline, resources, and budget development.
- Formalizing the identified factors, putting forth the documents, and preparing schedules and charts.
- Monitoring, evaluating, and reporting the progress to the stakeholders
- Conducting risk analysis, managing risks, and developing mitigation plans.
- Communicating and negotiating with the stakeholders
- Maintaining the quality standards of a project.
- Monitoring and managing the results as per the defined actuals.
- Closing the project by analyzing the results and communicating the same to the stakeholders.
Want to Start a Career in Project Management? Here is What you Need to Know
As organizations continually strive to improve the success rates for their projects, there is a substantial and emerging market for skills in project management. Globalization has resulted in a demand for project management roles. Whichever the industry, project management professionals are in constant demand. Every organization in every sector needs project managers. Be it the public or private sector or an NGO, the demand for project managers is increasing. Therefore, keeping it as a career option will land you many job opportunities in different sectors worldwide. The compensation offered for project managers is quite good because project management is a job with great responsibilities and requires specific skill sets.
A professional course/degree in project management would enable me to acquire skills in any professional tasks and develops expertise in handling stakeholders and managing risks and resources. Many different types of certifications are available for those willing to kickstart their career in project management. Having said so much about project management and its applicability in today’s world, don’t miss an opportunity to make your dream career in project management!
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Introduction to Project Management. Here we have discussed the basic concept, role, five elements, and the types of Project Management. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –