Updated April 10, 2023
Difference between Ionic vs Covalent
Ionic and covalent are the major types of chemical bonds. Matters around us are held together with the help of chemical bonds. Chemical reactions break these bonds, but the broken parts like atoms, ions/ molecules rejoin together as another molecule. We need the energy to create bonds as well as to break it. In this topic, we are going to learn about Ionic vs Covalent.
What is Ionic Bond?
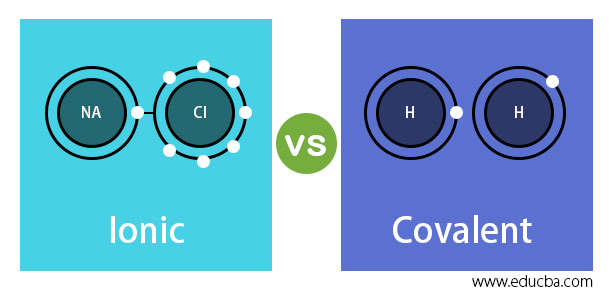
This bond is formed when two bonded atoms having opposite charges & varying electronegativity values, exchange electrons among them i.e. one atom transfers an electron to the other atom and the exchanged electron spends its time with the other atom. The atom that gave electron will have more protons and it will have a positive charge whereas the atom that gains an electron will have a negative charge. These types of bonding are called polar bond and in this compound, ions that lose electrons are called cations (metals) and the other ions that gain electrons are called anions (non-metals) and the compound neutralizes the positive charges of cations with negative gains of anions. An example of an ionic bond is chemical compounding between Sodium and Chloride that makes common salt NaCl. Sodium and Chloride having different electronegativity values when bonded will acquire a tendency to dissociate into ions in water. Sodium has 11 electrons and 11 protons and only one electron in outer shell whereas chloride has 17 protons and 17 electrons and 7 electrons in the outer shell. When they bond Sodium becomes Na+ and loses one electron to electronegative chloride which becomes Cl-. After the chemical reaction, in the bonded structure each sodium electron is surrounded by six chloride electrons.
What is Covalent Bond?
Electrons are shared between bonded atoms and their electronegative values remain the same or nearly close. The outer shells where the electrons are shared become fully occupied. This type of bonding where electrons are shared equally is known as a non-polar bond. Mostly the shared electron is attracted to one atom and in such cases, it is known as a polar covalent bond. An example of this type of bond is Water (H2O) formed by a polar covalent bond. These bonds usually happen using two nonmetallic bonds and the compound resulting from this bond will dissolve in water but does not separate into ions. The covalent bond is also known as molecular bonds and the bonding happens between nonmetallic atoms with the same or nearly closer values of electronegativity. Electronegativity is nothing but a chemical property that explains the ability of an atom to attract shared electrons to it. An example of a covalent bond is molecule Hydrogen formed from two hydrogen atoms with one electron each in its outer shell. One more example of this bond is Hydrogen Chloride (HCl) also known as hydrogen halide. 7 electrons in the outer shell of chlorine and 1 electron in the outer shell of hydrogen make a perfect combination for making a stable molecule.
Head to Head Comparison Between Ionic vs Covalent (Infographics)
Below are the top differences between Ionic vs Covalent
Key Differences of Ionic vs Covalent
- Covalent bonds are more prevalent than ionic bonds in Organic chemistry.
- Among living things, there are more molecules formed by covalent bonding and it is common.
- Electrons are shared in covalent bonds and electrons are exchanged in ionic bonds
- The chemical reaction between components in covalent bonds leaves electrically neutral conditions whereas in ionic bonds leaves a charged condition. Sodium chloride, when dissolved in water, leaves its components in a charged condition.
- It’s easier to break a compound formed using covalent bond than ionic bond
- Ionic bonds can be formed only between two different components whereas it is possible to have covalent bond between the same components.
- Ionic bonds are formed between one metal component with another non-metal component but covalent bonds are formed between two non-metal components only.
- Melting points and boiling points are low for covalent bonds and they are higher for ionic bonds.
- Ionic bonds take the solid-state at normal room temperature whereas molecules formed by covalent bonds take gas or liquid state.
Comparison Table of Ionic vs Covalent
Now let’s draft the comparison between Ionic and Covalent in a table below
| Attribute | Ionic Bond | Covalent Bond |
| Characteristics | Electrons are exchanged | Electrons are shared |
| Metals transfer the electrons to non-metals | Electrons are shared by two non-metals in their outer shells | |
| Stability | Leads to stable compounds | |
| Heat Transfer | Heat is released while bonding | |
| Valence Electrons | Involvement of valence electrons | |
| Net electrical Charge | Molecules formed irrespective of bonding has a neutral electrical charge | |
| Polarity | Highly Polar | Mostly non-polar |
| Boiling point and melting points | High | Low |
| The shape took at normal room temperature | Solid | Gas or Liquid |
| Bonding | Between metal and non-metal. Nonmetal (-ve) is stronger than metal (+ve) and it attracts electrons easily from metal. | Between two non-metals that have similar electro-negatives. Both are equally strong or weak to attract other electrons |
| Examples | Sodium Chloride (NaCl), Sulfuric acid (H2So4) | Water (H2O), Hydrochloric Acid (HCl) |
| Breaking the bond | Tough | Easier |
Conclusion
We have seen the differences between the ionic bond and covalent bond and also understood that Salt is ionic and it dissolves in water and it has good conductivity but sand is a covalent bond it does not dissolve in water.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Ionic vs Covalent. Here we discuss the Ionic and Covalent key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –