Overview of IoT Features
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a connected smart device technology with incremental use cases across industries. With the increasing use across various sectors, defining a common standard of IoT ecosystems is becoming necessary. As a design standard, any IoT device has common features like connectivity, analytics, endpoint management, etc. Let’s discuss the high-level feature maps of IoT devices.
Features of Internet of Things (IoT)
Any IoT device comes up with the following features:
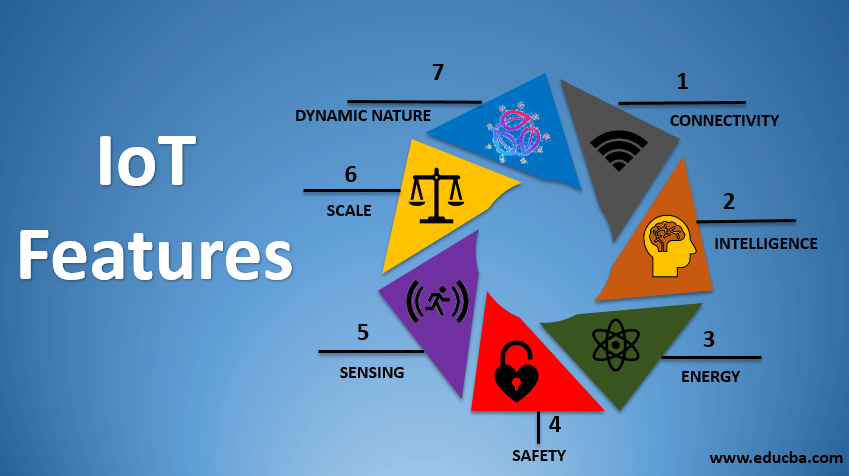
1. Connectivity
In the case of IoT, the most important feature one can consider is connectivity. Without seamless communication among the interrelated components of the IoT ecosystems (i.e., sensors, compute engines, data hubs, etc.), it is impossible to execute any proper business use case. IoT devices can be connected over Radio waves, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Li-Fi, etc. We can leverage various protocols of internet connectivity layers to maximize efficiency and establish generic connectivity across IoT ecosystems and Industries. Special cases may involve building the IoT ecosystem on-premises or within an intranet.
2. Sensing
Humans can naturally understand and analyze our circumstances easily based on past experiences with various things or situations. In the case of IoT, we need to read the analog signal and convert it to derive meaningful insights from it to get the best of it. We use Electrochemical, gyroscope, pressure, light sensors, GPS, Electrochemical, pressure, RFID, etc., to gather data based on a particular problem. For example, we use Light detection and pressure, velocity, and imagery sensors for automotive use cases. We must choose the proper sensing paradigm to make a use case successful.
3. Active Engagements
IoT device connects various products, cross-platform technologies, and services that work together by establishing an active engagement. In general, we use cloud computing in blockchain to establish active engagements among IoT components. Regarding Industry grade IoT solutions, raw analog data need to be acquired, preprocessed, and rescaled as per business capacity. As per Google, only 50% of structured and 1% of unstructured data is used to make important business decisions. So while designing the IoT ecosystems, carriers need to consider the future needs of manipulating such a huge scale of data to satisfy incremental business needs. One can confuse the need for active engagements with scale; practically, it means your systems should be able to handle huge amounts of data across various technologies, platforms, products, and industries.
4. Scale
Designing IoT devices with easy scalability, both up and down, on-demand is essential. IoT is utilized across a wide range of applications, ranging from smart home automation to the automation of large factories and workstations. As a result, the scale of use cases varies significantly. A carrier should design its IoT infrastructure depending on its current and future engagement scale.
5. Dynamic Nature
For any IoT use case, the first and foremost step is to collect and convert data so that business decisions can be made out of it. In this whole process, various components of IoT need to change their state dynamically. For example, the input of a temperature sensor will vary continuously based on weather conditions, locations, etc. IoT devices should be designed with this keeping in mind.
6. Intelligence
In almost every IoT use case in today’s world, the data is used to make important business insights and drive important business decisions. We develop machine learning/ deep learning models on top of this massive data to obtain valuable insights. The analog signals are preprocessed and converted to a format on which machine-learning models are trained. We need to remember the proper data infrastructure based on business needs.
7. Energy
Ecosystems demand a lot of energy from end components to connectivity and analytics layers. While designing an IoT ecosystem, we need to consider design methodology such that energy consumption is minimal.
8. Safety
One of the main features of the IoT ecosystem is security. Connectivity components pass sensitive information from endpoints to the analytics layer in the entire flow of an IoT ecosystem. While designing an IoT system, we must adhere to proper safety, security measures, and firewalls to keep the data from misuse and manipulation. Compromising any component of an IoT ecosystem can eventually lead to the failure of the whole pipeline.
9. Integration
IoT integrates various cross-domain models to enrich user experience. It also ensures proper trade-off between infrastructure and operational costs.
Conclusion
The expansion and design of optimal IoT systems are still an active area of research, so in practice, not all IoT products come up with this set of features of the standard. It mainly depends on the use cases and industry where the ecosystem needs to be incorporated. The Internet of Things (IoT) is a connected smart device technology with incremental use cases across industries. With the increasing use across various industries, defining a common standard of IoT ecosystems is becoming necessary. As a design standard, any IoT device has common features like connectivity, analytics, endpoint management, etc. Let’s discuss the high-level feature maps of IoT devices.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the IoT Features. Here we discuss the overview and various important features of an IoT, such as sensing, connectivity, endpoint management, scalability, etc. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –
