Introduction to IoT in Agriculture
In the era of the internet and connected devices Internet of Things (IoT) is the next big thing for the industry. On the other hand, it is anticipated that by the next 30 years, the population of the world will exceed 6 billion, and the incremental throughput needed to produce food for this population is 70%. Incorporating IoT based smart agriculture systems is essential to cope up with this need. Let’s take a look at the challenges facing the agriculture industry and how IoT is an answer to the problems.
Challenges in the Modern Agriculture Industry and How IoT is an Answer?
The main challenges faced by the agriculture and farming industry can be classified briefly in the following ways.
- Global warming and environmental changes.
- Lack of workforce, a huge supply-demand gap in manpower.
- Lack of proper monitoring and need for large manual intervention.
- Challenges to analyze large scale unstructured data.
IoT Applications in Smart Farming and Agriculture
The ease of internet connectivity and cheap computing has made it possible to incorporate IoT solutions in farming.
Following are some of the important use cases of the IoT in the agriculture industry.
1. Real-time crop monitoring
Smart sensors, motion detectors, smart motion-sensing cameras, and light detectors provide farmers with real-time data about their farms, enabling them to monitor product quality, optimize resource management, and improve crop yields.
2. IoT analytics in agriculture
Data from smart sensors can be analyzed for predictive analysis and automated decision-making. It helps farmers with smart, automated decision-making instead of classic rule-based systems or manual procedures. Predictive analysis and machine learning can help farmers to cope up with extreme weather conditions like floods, drought, etc. The main advantage of IoT analytics is the inclusion of soil quality, temperature, humidity as a parameter.
3. Livestock management
As industry agriculture strongly depends on the manual workforce. Given the changes in the global economic landscape, the supply-demand gap is increasing day by day. Livestock is one such area that needs regular monitoring. IoT based smart tracking can help farmers to get the stock information directly to their smart devices. It enables farmers with stock management to detect flue breakouts much earlier and separate infected breeds with non-infected ones.
4. Drone-based use cases
Industry grade drones also have multiple use cases in smart farming. On the one hand, drones are used to monitor air, soil, moisture quality; on the other hand; they can help with physical activities like automated spraying of fertilizers, preventing physical breakouts in farms, etc. Obviously, there are some challenges incorporating drones in farms, but successful deployment and use cases can help to reduce the manual workforce in agriculture significantly.
5. Smart greenhouse solutions
Greenhouses are conventionally used to maintain the necessary atmosphere for plants, and this process demands continuous monitoring and manual intervention. Industrial IoT solutions can be incorporated to automate this process. Data collected by smart sensors can be automatically analysed, and deep learning-based systems can be deployed to make decisions and create a certain climate automatically. With these smart sensors, climate variables and water consumption can be monitored via SMS or Wi-Fi-based systems.
6. Smart waste management
One of the main differences between agriculture and other industry is the value of industrial waste. Biological waste produced from farming can be reused for making fertilizers; IoT solutions can help manage the process remotely in a smart way. Smart sensors can be used to measure the presence of toxic chemicals in wastes and manage the proper agricultural lifecycle.
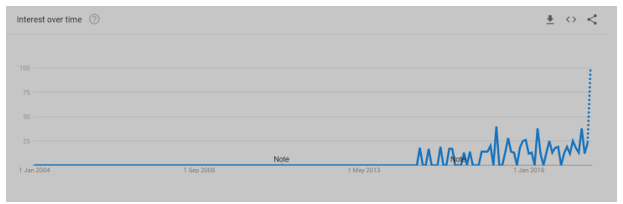
Global Trends on IoT applications in Agriculture
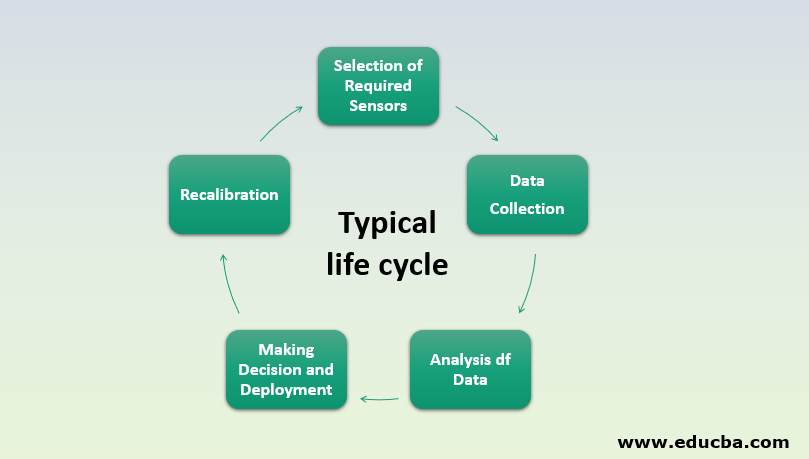
Typical Life Cycle of an IoT Analytics based Agricultural Use Case
The life cycle of a typical IoT based use case, If we breakdown a sample use case of IoT analytics, it consists of the following stages:
1. Selection of sensors: The selection of sensors differs from use case to use case; for example, the sensors required for livestock management is very different from the sensor requirements for a smart greenhouse use case.
2. Data collection: Collection of data from deployed sensors and converting them to the required format.
3. Making decisions and deployment: Data collected from the sensors can be used to draw insights and make automated business decisions. After getting through proper data science, life cycle models are deployed to the cloud or local servers as required.
4. Recalibration of models: The results obtained from the previous processes are monitored and recalibrated based on the business KPI and deviation from the result.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the various problems the agricultural sector faces and how industrial IoT can help mitigate the problems. IoT with machine learning and computer vision can change the industrial landscape of smart farming. We have also discussed the various phases of a typical IoT use case and the global trends on IoT in the agriculture sector. Though It is a fact that the scalability of IoT use cases is still very limited compared to other sectors, incorporating the same is becoming essential for global food management.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the IoT in Agriculture. Here we discuss a brief overview, challenges in modern agriculture, the global trend in Iot application with a typical lifecycle based on Iot Analytics. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –