Updated August 10, 2023
Introduction to IoT Module
The Internet of Things is influencing our lifestyle from the way we react to the way we behave. From the air conditioners that we control on our own to the smart cars, which provide the shortest route that tracts our daily activities with connected devices. These devices gather into the environment in which they are supposed to be operated in any physical device by using sensors.
These sensors continuously emit data about the working state of the devices. They share a huge amount of data to provide a common platform for all the devices to communicate with each other. Information is transferred from various sensors and sent to the gateway. IoT platform integrates the collected data from the various sensors, and further analytics is performed on the data, and important information is extracted as per the requirement, and then the result is shared with other devices for better user experience in automation and improves the accuracy.
IoT Module Architecture
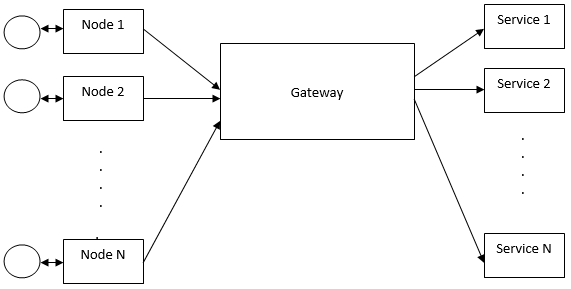
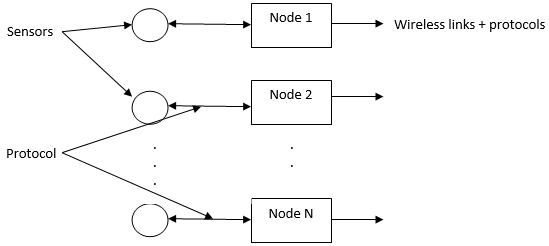
This module includes three main blocks Node, Gateway, and Services. In the following architecture, circles represent various sensors. location sensors, temperature sensors, humidity sensors, distance sensors, gas sensors, detection sensors, etc., are used in IoT as input to any system.
Then by receiving information and specific data from the sensors, some controllers and operators are used by protocols as per application; after that, this data sends to services. There is N number of services (for example, gas leakage detection, temperature monitoring, road path cracks detection, home automation, security, surveillance, and greenhouse monitoring. Agriculture water level measurement, soil moisture recording, garbage collection, bridge health detection, home or industry security, parking slot availability, water quality measurement, a map navigation system, machine learning application, etc.). In addition, there might be a wireless connection from one node to another.
Which Module is Best?
To choose the best model, there are certain criteria’s need to be understood;
- The size and scope of application.
- The expected power consumption of a specific application.
- The environment where the application will be deployed.
- Hardware and software requirements for application.
- The scalability of the specific application.
Examples of IoT Module
Following are the examples of IoT modules.
1. Smart Cities
There are various applications in the city based on IoT; these applications make the city a smart city. For example, now a day’s vehicle parking is one of the major issues in many cities, so sharing real-time information about parking area availability can be monitored. Similarly, the condition of bridges, historical places, and buildings can be monitored to avoid accidents. Roads can be monitored by sending warning messages for diversions and road conditions to the drivers. In society’s environment, it helps to maintain garbage collection, shopping mall convenience to avoid waiting time, navigation, etc.
2. Medical
Patient’s conditions inside the hospital and in old homes can be monitored by continuously sharing patients’ health data. Iot also helps in medical fridges to monitor and control the condition of medicines, vaccines, and organic elements.
3. Industry
In air quality applications, Iot helps to monitor oxygen levels and toxic gas levels inside the chemical plants to ensure working safety. In addition, it helps to maintain temperature for specific machinery to avoids overheating.
4. Domestic/Home Automation
The major role in home appliances is to save energy and water by keeping a record of power and water uses. Automatically it gives a warning after overuse and at the time of wastage. There are various remote control appliances that are more convenient for a good lifestyle. It also monitors conditions inside the art warehouse and museums.
5. Security
Iot applications detect the human interface in restricted and unauthorized areas to improve security in specific areas. For example, in nuclear power stations, it gives radiation level measurement to send a warning for safety. It also detects gas leakages in industries, environments and surrounding areas in society to avoid such accidents.
6. Agriculture
Iot measures and monitors soil water level as well as soil moisture .it helps the farmers to take according to action on plants. it improves quality in agriculture. Greenhouse monitoring is also one of the major applications of IoT.
Advantages
Below are the advantages of the IoT Module.
- The existing technologies improve their performance in terms of efficiency, energy, resource, etc., by using Iot.
- It reduces waste of resources in water management, automatic power uses (e.g. Electricity)
- In data collection, IOT arranges data so customers can see only data that is applicable and usable as per need.
- In IoT, devices become cheaper, smaller, powerful and cost-effective.
- IoT also provides a tease of living and comfort to society.
Conclusion
IoT is redefining our lifestyle and transforming the way we interact with technologies. the future of IoT is huge; as per one of the surveys, 24 billion IoT devices will be installed by 2025, and IoT revenue will reach around three hundred billion in the coming years.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to IoT Module. Here we discuss IoT Architecture, best model, along with examples and advantages, respectively. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –